
Featured image for this comprehensive guide about are doorbell wires live
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Picture this: You’re standing at your front door, doorbell button in hand, wondering if the wires poking out from the wall are carrying a harmless tingle or a potentially dangerous jolt. It’s a common question, especially for DIY enthusiasts or anyone looking to replace an old doorbell. The good news? For most traditional wired doorbell systems, the answer is reassuringly low-key.
Most homeowners breathe a sigh of relief when they learn that doorbell wires are typically low voltage. This design choice is intentional, prioritizing safety and ease of installation. However, “typically” isn’t “always,” and understanding the specifics of your system is crucial before you start tinkering. Misinformation can lead to unpleasant surprises, so let’s get to the bottom of whether your doorbell wires are live in a way that matters.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify doorbell wire voltage, explore how wired doorbells get their power, provide actionable tips for identifying your system’s voltage, and discuss critical safety measures. Whether you’re upgrading to a smart doorbell or just troubleshooting an existing one, knowing what you’re dealing with will empower you to tackle the task safely and effectively.
📋 Table of Contents
- Understanding Doorbell Wire Voltage: The Basics
- How Traditional Wired Doorbells Get Their Power
- Identifying Your Doorbell’s Voltage: What to Look For
- When Doorbell Wires *Could* Be “Live” (Higher Voltage)
- Safety First: Working with Doorbell Wires
- What About Smart Doorbells? Do They Use Low Voltage Too?
- Conclusion
Understanding Doorbell Wire Voltage: The Basics
When we talk about electrical wiring in a home, there are generally two categories of voltage: line voltage and low voltage. Understanding the difference is key to grasping whether your doorbell wires are live in a hazardous sense.
- Line Voltage (Standard Household Voltage): This is the power that runs your major appliances, lights, and wall outlets. In North America, it’s typically 120 volts (V) AC (alternating current). In many other parts of the world, it’s 230-240V AC. Contact with line voltage can cause severe electrical shock, burns, or even be fatal.
- Low Voltage: This refers to electrical circuits operating at 50V AC or less. For doorbells, this is commonly in the range of 8V to 24V AC. While you might feel a slight tingle if you touch low-voltage wires, it’s generally considered safe and doesn’t pose a significant shock hazard. Most low voltage doorbell wires fall into this category.
The vast majority of traditional wired doorbells operate on low voltage. This is why you often hear that doorbell wires are not live in the same dangerous way as the wires behind your light switch.
| Aspect | Traditional Wired Doorbell | Smart Wired Doorbell | Safety Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Voltage | 10-24 Volts AC (V AC) | 16-24 Volts AC (V AC) | Considered Low Voltage; not usually dangerous. |
| Live Status | Always live when transformer is powered. | Always live when transformer is powered for continuous operation. | Treat as live; disconnect power before work. |
| Shock Risk | Low; a tingle might be felt. | Low; a tingle might be felt, potentially stronger with higher voltage. | Direct contact can cause an unpleasant sensation; avoid bare wires. |
| Power Source | Dedicated doorbell transformer (reduces household 120/240V AC). | Dedicated doorbell transformer (often requires higher VA rating). | The transformer is the critical safety component. |
| Best Practice | Always test with a multimeter before touching wires. | Always shut off power at the breaker or transformer before installation/maintenance. | Prioritize safety: Verify power is off before any contact. |
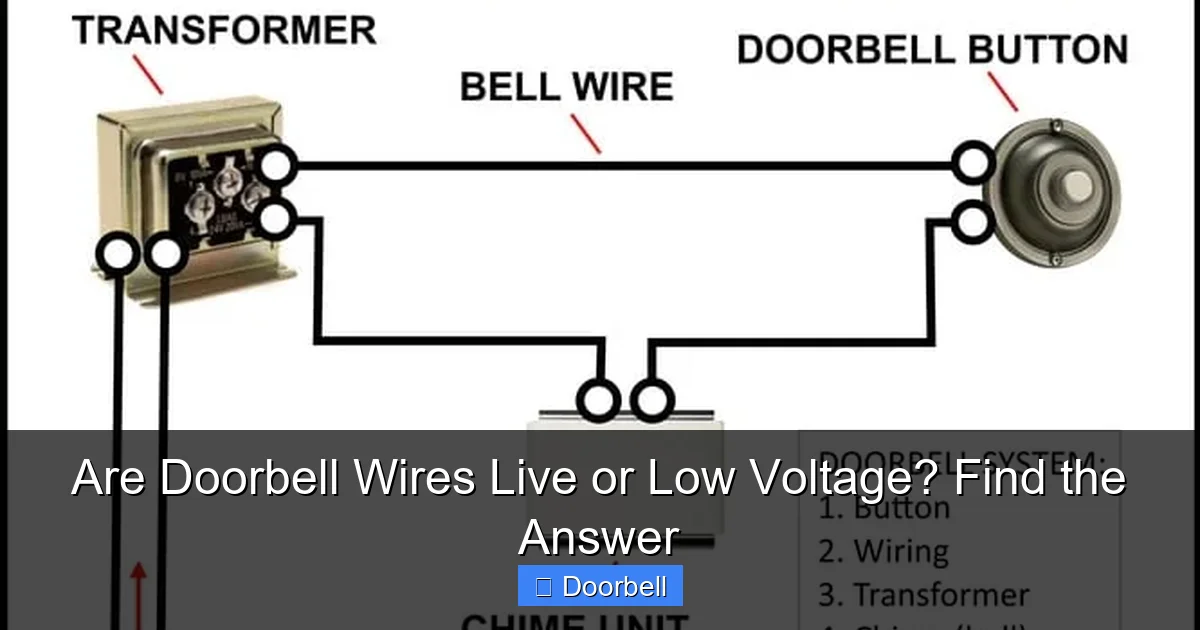
How Traditional Wired Doorbells Get Their Power
The secret to a doorbell’s low voltage lies in a small, often overlooked component: the doorbell transformer. This device is the unsung hero that converts your home’s high-voltage electricity into the safe, low-voltage power needed for your doorbell system.

Learn more about are doorbell wires live – Are Doorbell Wires Live or Low Voltage? Find the Answer
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Here’s a breakdown of the typical power flow:
- Main Household Power: Your home’s 120V (or 230V) AC electricity feeds into the primary side of the doorbell transformer.
- The Transformer’s Role: The transformer then “steps down” this high voltage to a much lower, safer voltage on its secondary side. Common output voltages for residential doorbells include 8V, 10V, 16V, 24V, or sometimes a combination.
- Low-Voltage Circuit: These low-voltage wires then run from the transformer to your doorbell chime unit and finally to the doorbell button itself. When you press the button, it completes the low-voltage circuit, activating the chime.
Because the transformer performs this crucial step-down, the wires leading from it to your chime and button are almost always low voltage doorbell wires. This makes installation and maintenance significantly safer.
Identifying Your Doorbell’s Voltage: What to Look For
While most doorbell wires are low voltage, it’s always best to verify. Knowledge is power, and in this case, it’s also safety. Here’s how you can determine your doorbell wire voltage:
Learn more about are doorbell wires live – Are Doorbell Wires Live or Low Voltage? Find the Answer
Image source: removeandreplace.com
Locate the Doorbell Transformer
This is your primary investigation target. Common locations include:
- Near the main electrical panel (breaker box).
- Attached to a junction box in the basement, attic, or crawl space.
- Mounted to a wall in a utility room or garage.
- Inside or near the doorbell chime unit itself.
Once found, look for a label on the transformer. It will typically specify input voltage (e.g., “120V AC”) and output voltage (e.g., “16V AC, 10VA”). The output voltage tells you the voltage running through your doorbell wiring.
Use a Multimeter for Direct Measurement
The most accurate way to check if your doorbell wires are live and at what voltage is with a multimeter:
- Safety First: Even though it’s likely low voltage, always exercise caution. Ensure your hands are dry, and avoid touching bare wires directly if possible.
- Set Your Multimeter: Turn the dial to measure AC voltage (often denoted by V~ or VAC). Start with a higher range (e.g., 200V AC) if your multimeter isn’t auto-ranging, then adjust down.
- Test the Wires: With the power to the doorbell circuit (usually not the whole house) still on, carefully touch one probe to each of the two bare doorbell wires. The reading on the multimeter will indicate the voltage.
A reading between 8V and 24V AC confirms you have a standard low voltage doorbell wiring system. If you get a reading of 0V, either the power is off, or there’s a break in the circuit. If you get a reading near 120V (or 230V), something is seriously wrong, and you should immediately turn off the power and call an electrician.
When Doorbell Wires *Could* Be “Live” (Higher Voltage)
While rare, there are specific scenarios where doorbell wires could be live with higher, more dangerous voltages:
- Faulty or Incorrect Wiring: If someone attempted to bypass the transformer or wired the doorbell directly to a line voltage circuit, the wires would carry dangerous current. This is a severe electrical hazard.
- Non-Standard Doorbells: Some very old, specialty, or commercial doorbell systems might operate on different voltages. However, for residential homes, this is highly uncommon.
- Short Circuits or Damage: A damaged wire or a short circuit can sometimes lead to unexpected voltage readings or hazards, though usually it would just cause a breaker to trip or the system to fail.
If you encounter unexpectedly high voltage readings (e.g., anything above 30V AC) when testing your doorbell wiring, treat it as a serious issue. Immediately cut power to the circuit at your breaker box and consult a qualified electrician.
Safety First: Working with Doorbell Wires
Even with low voltage doorbell wires, electrical safety should always be your top priority. Here are essential tips:
- Turn Off the Power: The most crucial step. Go to your electrical panel and switch off the breaker that controls your doorbell circuit. This usually isn’t labeled “doorbell” but might be labeled “lighting,” “general purpose,” or a specific room. If unsure, turn off the main breaker to the entire house, though this is often unnecessary.
- Verify Power is Off: Use your multimeter (set to AC voltage) to confirm there is no power at the doorbell wires before you begin working. This eliminates any doubt about whether doorbell wires are live.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for frayed insulation, exposed copper, or any signs of damage. Repair or replace damaged sections as needed.
- Wear Safety Gear: Electrical safety gloves and safety glasses are always a good idea when working with any electrical component.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: If you’re installing a new doorbell, always adhere to the manufacturer’s specific wiring diagrams and guidelines.
Taking these precautions ensures a safe and successful project, whether you’re dealing with a traditional wired doorbell system or upgrading to something smarter.
What About Smart Doorbells? Do They Use Low Voltage Too?
The rise of smart home technology has brought us video doorbells from brands like Ring, Nest, Arlo, and Eufy. The good news is that most wired smart doorbells are designed to work with existing low voltage doorbell wiring.
They typically draw power from your home’s existing doorbell transformer, utilizing the same 8-24V AC circuit. However, some smart doorbells have specific voltage requirements or might recommend upgrading your transformer if your existing one doesn’t provide enough power (measured in VA, volt-amperes).
Here’s a quick overview:
- Compatibility: Always check the smart doorbell’s specifications for voltage and VA requirements. Most are compatible with 16V-24V AC systems.
- Power Kits: Some smart doorbells include a “power kit” or “pro power kit” that installs within your chime unit. This helps regulate power and prevents issues like chime buzzing.
- Wireless Options: Many smart doorbells also offer battery-powered versions, completely bypassing the need for existing doorbell wiring if you prefer.
Even when installing a smart doorbell, the fundamental principles of doorbell wire voltage and electrical safety remain the same. Always confirm the power is off before disconnecting or connecting any wires.
Typical Doorbell System Voltage Ranges
To help you quickly reference common voltages, here’s a table summarizing typical expectations:
| Component | Voltage Range (AC) | Danger Level |
|---|---|---|
| Household Line Power (before transformer) | 120V (US) / 230V (EU) | High (Dangerous) |
| Doorbell Transformer Output | 8V – 24V | Low (Generally Safe) |
| Doorbell Chime Wiring | 8V – 24V | Low (Generally Safe) |
| Doorbell Button Wiring | 8V – 24V | Low (Generally Safe) |
Conclusion
So, are doorbell wires live? For the vast majority of traditional and even many smart wired doorbell systems, the answer is that they carry a safe low voltage, typically between 8V and 24V AC. This is thanks to the humble doorbell transformer, which steps down your home’s dangerous line voltage to a harmless level.
While generally safe, it’s never wise to assume. Always prioritize electrical safety by turning off the power at the breaker and using a multimeter to confirm the voltage before working with any doorbell wiring. Understanding your system’s voltage empowers you to troubleshoot, repair, or upgrade your doorbell with confidence and, most importantly, safely. If you ever detect higher voltages or feel uncertain, don’t hesitate to contact a professional electrician.
🎥 Related Video: Safely Touching a live wire. #offgrid
📺 Retro Electric
Frequently Asked Questions
Are doorbell wires live, like regular household electricity?
Most traditional doorbell systems operate on low voltage, typically between 10-24 volts AC, which is significantly lower than the 120-240 volts found in standard household circuits. This means the wires are generally not “live” in the sense of posing a severe electrocution risk.
What voltage are doorbell wires usually?
Residential doorbell systems commonly use a step-down transformer to convert standard household voltage to a much lower range. You’ll typically find doorbell wiring carrying between 10 and 24 volts alternating current (AC), rather than high voltage.
Is it safe to touch doorbell wires if my doorbell isn’t working?
While doorbell wires are generally low voltage and usually won’t deliver a dangerous shock, it’s always best to exercise caution. To ensure safety, it’s recommended to turn off the power to your doorbell transformer at the breaker box before handling any wiring.
How can I tell if my doorbell wires are low voltage?
The simplest way to confirm low voltage is to locate your doorbell transformer, often found near your main electrical panel, furnace, or in an attic or basement. The transformer will have a label indicating its output voltage, which is what your doorbell wires carry. If you’re unsure, you can also use a multimeter to test the voltage.
Can doorbell wires give you a serious electric shock?
Due to their low voltage nature, doorbell wires are highly unlikely to deliver a serious or fatal electric shock. At most, you might feel a slight tingle if you come into contact with them while power is on. However, proper safety precautions should always be taken when working with any electrical wiring.
Do smart doorbells also use low voltage wiring?
Yes, the vast majority of smart doorbells are designed to integrate with existing low voltage doorbell wiring. They typically draw power from the same doorbell transformer, though some models may also incorporate an internal battery or require a specific power adapter for installation.