Public health surveillance is a process. It helps us watch over the health of a community. This system collects, analyzes, and shares health data. It plays a key role in protecting public health. Understanding this process is important for everyone.

Why is Public Health Surveillance Important?
Public health surveillance helps in many ways:
- Detecting diseases: It helps find outbreaks early.
- Tracking health trends: It shows how health changes over time.
- Planning health programs: It helps leaders make better decisions.
- Informing the public: It keeps people aware of health risks.
How Does Public Health Surveillance Work?
The process of public health surveillance includes several steps:
1. Data Collection
Data comes from many sources. Hospitals, clinics, and labs provide information. Surveys and interviews also help collect data. This information is vital for understanding health issues.
2. Data Analysis
After collecting data, experts analyze it. They look for patterns and trends. This analysis helps identify health threats. It also shows which populations are at risk.
3. Interpretation
Interpreting data is crucial. It helps health officials understand what the data means. This step answers questions like:
- Is there an outbreak?
- Who is most affected?
- What actions should we take?
4. Dissemination
Once the data is analyzed and interpreted, it must be shared. Public health officials share findings with the community. They also inform policymakers and healthcare workers.
5. Action
The final step is taking action. Based on the findings, health officials implement programs. These programs aim to prevent disease and promote health.
Types of Public Health Surveillance
There are different types of public health surveillance. Each type has its own focus:
1. Passive Surveillance
This type relies on healthcare providers. They report cases of diseases to health departments. It is simple but may miss some cases.
2. Active Surveillance
In active surveillance, health officials seek out information. They contact healthcare providers regularly. This method helps find more cases.
3. Sentinel Surveillance
Sentinel surveillance watches specific health events. It focuses on a few key locations. This type can provide early warnings about outbreaks.
4. Syndromic Surveillance
Syndromic surveillance looks for symptoms, not just diseases. It helps identify outbreaks before lab tests confirm them. This method uses data from emergency rooms and clinics.
Examples of Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance has many real-life examples:
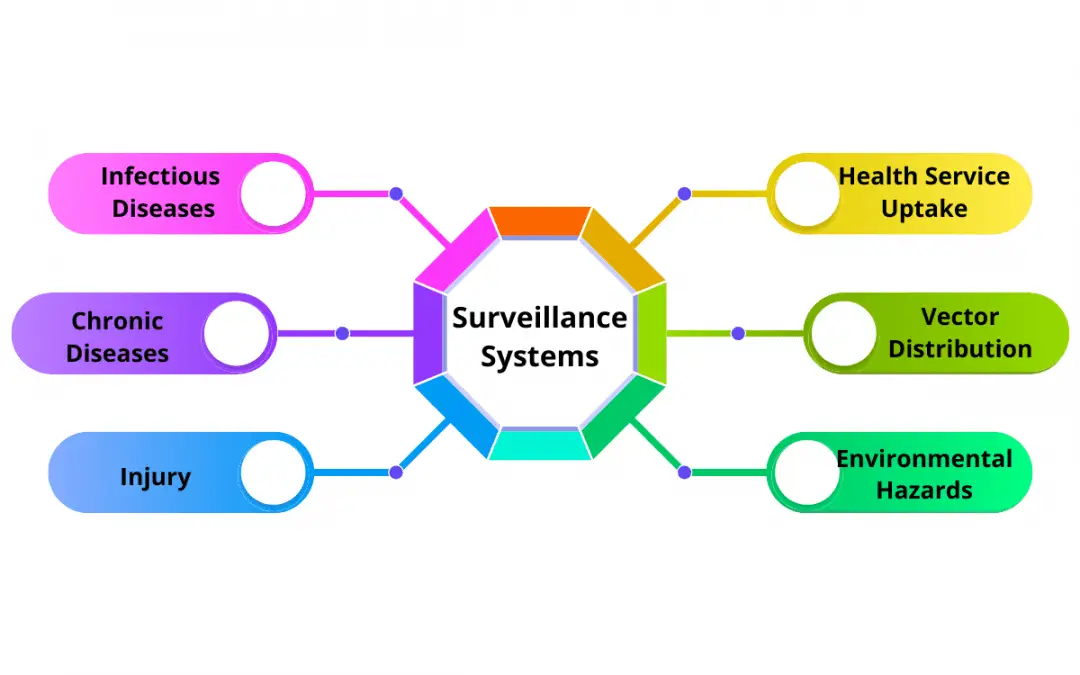
1. Tracking Infectious Diseases
Health departments track diseases like flu and COVID-19. They collect data on cases and deaths. This information helps guide responses to outbreaks.
2. Monitoring Chronic Diseases
Surveillance also tracks chronic diseases. Conditions like diabetes and heart disease are monitored. This helps identify trends and risk factors.
3. Environmental Health Surveillance
Public health officials monitor environmental factors. They study air and water quality. This helps identify health risks from pollution.
4. Behavioral Surveillance
This type looks at health behaviors. It studies smoking, drinking, and exercise habits. Understanding these behaviors helps promote healthier choices.
Challenges in Public Health Surveillance
While public health surveillance is helpful, it faces challenges:
1. Data Quality
Not all data is accurate. Some cases may go unreported. This can lead to gaps in information.
2. Privacy Concerns
Collecting health data raises privacy issues. People may worry about their personal information. Protecting privacy is essential in surveillance.
3. Limited Resources
Many health departments have limited funds. This can affect their ability to collect and analyze data. More resources are needed for effective surveillance.
4. Rapid Changes In Health Trends
Health trends can change quickly. New diseases may emerge unexpectedly. Surveillance systems need to adapt to these changes.
The Future of Public Health Surveillance
The future of public health surveillance looks promising. New technologies can improve data collection. For example, mobile apps can track health trends. Artificial intelligence can analyze data faster. These advancements can help detect outbreaks quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Public Health Surveillance?
Public health surveillance is the continuous, systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health data. It helps track diseases and health trends.
Why Is Public Health Surveillance Important?
It helps detect outbreaks, monitor health trends, and inform public health actions. This protects communities and improves health outcomes.
How Is Public Health Surveillance Conducted?
Health officials collect data from hospitals, clinics, and labs. They analyze this data to identify patterns and trends in health.
What Types Of Data Are Used In Surveillance?
Data can include disease reports, vaccination records, and health surveys. This information helps understand public health issues.
Conclusion
Public health surveillance is vital for community health. It helps detect diseases, track health trends, and inform the public. By collecting and analyzing data, health officials can take action. While challenges exist, advancements in technology can enhance surveillance systems. Understanding public health surveillance is important for everyone. It helps us stay safe and healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Public health surveillance monitors community health.
- It includes data collection, analysis, interpretation, and action.
- There are different types of surveillance methods.
- Challenges include data quality and privacy concerns.
- The future of surveillance looks bright with new technology.