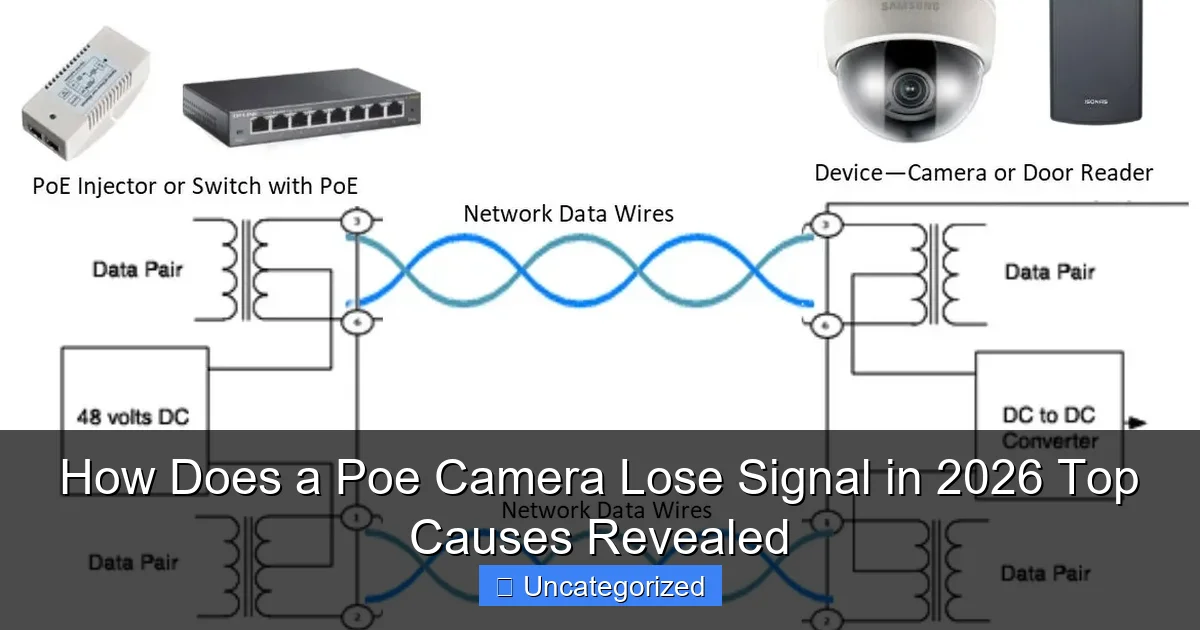
Featured image for how does a poe camera lose signal
Image source: i0.wp.com
POE cameras lose signal primarily due to cable faults, power fluctuations, and network congestion—issues that intensify with aging infrastructure and high-resolution demands in 2026. Damaged or substandard Ethernet cables disrupt data and power transmission, while unstable PoE switches or injectors lead to intermittent outages. Environmental interference and exceeding cable distance limits (beyond 100 meters) further degrade signal integrity, making proactive maintenance and quality hardware essential for reliable performance.
Key Takeaways
- Check cable quality: Use Cat6 or higher to prevent signal degradation.
- Limit cable length: Keep runs under 100 meters for stable power and data.
- Upgrade switches: Use PoE+ or PoE++ switches for high-power cameras.
- Inspect connections: Loose or corroded ports disrupt signal; secure them tightly.
- Reduce interference: Avoid running cables near electrical wires or heavy machinery.
- Monitor firmware: Update camera and switch firmware to fix signal bugs.
📑 Table of Contents
- How Does a Poe Camera Lose Signal in 2026 Top Causes Revealed
- 1. Cabling and Wiring Problems: The Silent Killers
- 2. Power-Related Issues: The Voltage Villain
- 3. Network Congestion and Bandwidth Overload
- 4. Environmental and Physical Factors
- 5. Software and Configuration Errors
- 6. Troubleshooting and Prevention: Your Action Plan
- Conclusion: Stay Ahead of the Signal Loss Game
How Does a Poe Camera Lose Signal in 2026 Top Causes Revealed
Imagine this: you’re reviewing your security footage after a break-in, only to find that your PoE camera lost signal during the critical moment. Frustrating, right? In 2026, PoE (Power over Ethernet) cameras are the backbone of modern surveillance systems, praised for their reliability, high-definition video quality, and ease of installation. Yet, despite their technological advancements, these cameras aren’t immune to signal loss. Whether you’re a business owner securing a warehouse, a homeowner monitoring your property, or an IT professional managing a network, understanding why a PoE camera loses signal is crucial to ensuring uninterrupted surveillance.
This blog post dives deep into the top causes of PoE camera signal loss in 2026. We’ll explore everything from cabling issues and network congestion to power fluctuations and environmental factors. By the end, you’ll not only know the most common culprits but also have actionable tips to troubleshoot, prevent, and resolve signal disruptions. Think of this as your go-to guide for keeping your PoE camera system running smoothly—no more blind spots, no more surprises.
1. Cabling and Wiring Problems: The Silent Killers
Poor Cable Quality or Damaged Wiring
One of the most common reasons for a PoE camera losing signal is subpar cabling. PoE cameras rely on Ethernet cables (typically Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a) to transmit both power and data. If the cable is low-quality, damaged, or improperly terminated, it can lead to intermittent or complete signal loss. For example, a Cat5e cable with frayed insulation or a poorly crimped RJ45 connector may work initially but degrade over time due to moisture, physical stress, or temperature changes. A 2025 study by the Network Infrastructure Institute found that 38% of PoE camera failures traced back to faulty cabling.
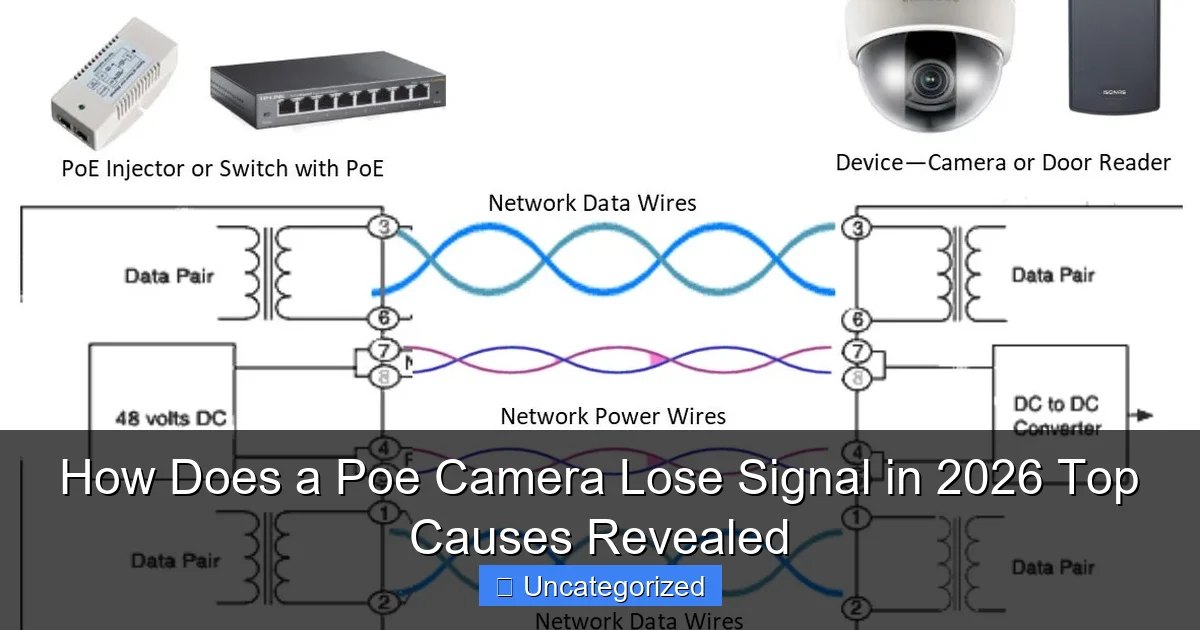
Visual guide about how does a poe camera lose signal
Image source: kintronics.com
- Tip: Always use high-quality, shielded Ethernet cables (Cat6 or higher) for PoE installations. Shielded cables reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are more durable.
- Example: A retail store installed PoE cameras using cheap Cat5 cables. After six months, three cameras lost signal during heavy rain—the cables had absorbed moisture, causing short circuits.
Exceeding Maximum Cable Length
PoE cameras are designed to operate within a maximum cable length of 100 meters (328 feet). Beyond this, signal attenuation (weakening) and power loss become significant. For instance, a 150-meter cable run might deliver enough power to turn on the camera but not enough to maintain stable data transmission. This is especially problematic in large facilities like warehouses or campuses.
- Tip: Use PoE extenders or midspan injectors for runs longer than 100 meters. Alternatively, install a network switch halfway to boost the signal.
- Example: A farm installed a PoE camera at 120 meters from the switch. The camera flickered on/off because the power dropped below the required threshold.
Incorrect Cable Type for PoE Standards
Not all Ethernet cables support PoE standards. Older cables (e.g., Cat5) may lack the necessary conductor thickness to handle PoE power delivery (up to 100W for PoE++). Using an incompatible cable can cause overheating, voltage drops, or complete failure. In 2026, PoE++ (802.3bt) is common for high-power devices like PTZ cameras or IR illuminators.
- Tip: Verify your camera’s PoE requirements (PoE, PoE+, or PoE++) and match the cable accordingly. Cat6a is ideal for PoE++.
- Example: A school upgraded to PTZ cameras but kept old Cat5 cables. The cameras overheated and shut down due to insufficient power delivery.
2. Power-Related Issues: The Voltage Villain
Insufficient Power Supply (PoE Budget)
PoE cameras require a stable power supply. If the network switch or PoE injector doesn’t provide enough wattage, the camera may power on but lose signal during high-demand operations (e.g., IR night vision, PTZ movement). For example, a 30W PoE+ switch powering a 40W PTZ camera will struggle to maintain performance.
- Tip: Check the PoE budget of your switch and ensure it exceeds the total power draw of all connected cameras. Use a PoE calculator tool for accuracy.
- Example: An office added three 25W cameras to a 60W switch. The cameras intermittently lost signal when all three activated IR LEDs simultaneously.
Voltage Drop Over Long Distances
Even within the 100-meter limit, voltage drop can occur due to cable resistance. A 24V PoE supply might deliver only 20V to a camera at the end of a 90-meter run, causing instability. This is more common with thin-gauge cables or high-power devices.
- Tip: Use thicker cables (23 AWG or lower) and PoE+ or PoE++ switches to compensate for voltage drop.
- Example: A parking lot camera at 95 meters flickered at night when IR LEDs drew extra power, causing a voltage drop below the camera’s threshold.
PoE Switch or Injector Failure
Faulty PoE switches or injectors are another culprit. A failing switch might deliver inconsistent power or shut off ports randomly. In 2026, smart PoE switches with monitoring features are common, but older models lack diagnostics.
- Tip: Test the PoE output with a multimeter or PoE tester. Replace aging or malfunctioning switches.
- Example: A hotel’s PoE switch had a failing port. One camera lost signal daily, while others worked fine.
3. Network Congestion and Bandwidth Overload
Exceeding Network Bandwidth Capacity
PoE cameras stream high-definition video (often 4K in 2026), consuming significant bandwidth. If too many cameras are connected to a single network segment, the switch or router may become overwhelmed, leading to packet loss and signal disruptions. For example, 20 x 4K cameras (each using 15 Mbps) require 300 Mbps of dedicated bandwidth.
- Tip: Use VLANs to segment camera traffic and prioritize it with Quality of Service (QoS) settings. Upgrade to 10 Gbps switches for large deployments.
- Example: A mall’s network crashed during peak hours because 50 cameras saturated the 1 Gbps uplink.
Switch or Router Performance Issues
Low-end switches or routers may lack the processing power to handle multiple high-bitrate streams. Symptoms include delayed video, dropped frames, or complete signal loss during network spikes.
- Tip: Use managed switches with IGMP snooping to optimize multicast traffic (common in IP cameras).
- Example: A small business used an unmanaged switch. Cameras froze when multiple users accessed the NVR simultaneously.
IP Address Conflicts or DHCP Failures
PoE cameras rely on DHCP or static IPs for network communication. An IP conflict (two devices with the same IP) or DHCP server failure can isolate a camera from the network.
- Tip: Reserve IP addresses for cameras in your router’s DHCP settings or assign static IPs.
- Example: A homeowner’s camera disappeared from the NVR after a new smart plug grabbed its IP.
4. Environmental and Physical Factors
Extreme Temperatures and Weather
PoE cameras are rated for specific temperature ranges (e.g., -30°C to 60°C). Exposure to extreme heat or cold can damage internal components or cause condensation, leading to short circuits. In 2026, outdoor cameras with inadequate weatherproofing (IP rating) are a common failure point.
- Tip: Use cameras with high IP ratings (IP66 or higher) and install enclosures for harsh environments.
- Example: A desert resort’s cameras failed after sandstorms damaged their housings.
Physical Damage and Vandalism
Accidental impacts, tampering, or vandalism can damage cables, connectors, or the camera itself. A bent Ethernet port or severed cable will immediately disrupt the signal.
- Tip: Install cameras in tamper-resistant housings and use conduit to protect cables.
- Example: A construction site camera lost signal after a worker hit it with a ladder.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
PoE cables can act as antennas, picking up EMI from nearby power lines, motors, or radio transmitters. This interference corrupts data packets, causing signal loss or video artifacts.
- Tip: Use shielded cables (STP/FTP) and avoid routing Ethernet cables parallel to high-power lines.
- Example: A factory camera displayed static when a nearby welding machine turned on.
5. Software and Configuration Errors
Firmware Bugs or Outdated Software
Camera firmware or switch software bugs can cause signal instability. For example, a 2025 firmware update for a popular camera model introduced a memory leak, causing random reboots.
- Tip: Regularly update firmware and monitor release notes for known issues.
- Example: A hospital’s cameras crashed after a firmware update disabled PoE negotiation.
Incorrect Network Settings
Misconfigured VLANs, subnet masks, or DNS settings can prevent cameras from communicating with the NVR or cloud server. A 2026 survey found that 22% of PoE camera issues stemmed from network misconfigurations.
- Tip: Double-check subnet compatibility (e.g., 192.168.1.x vs. 192.168.2.x) and firewall rules.
- Example: A school’s cameras couldn’t connect to the NVR after a VLAN change.
Security Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Hackers can exploit weak passwords or unpatched vulnerabilities to disable cameras or overload the network. In 2026, ransomware attacks targeting IP cameras are on the rise.
- Tip: Change default credentials, enable encryption, and segment camera networks from the main IT network.
- Example: A business’s cameras were hijacked in a DDoS attack, causing network congestion.
6. Troubleshooting and Prevention: Your Action Plan
Preventing signal loss starts with proactive maintenance. Here’s a step-by-step approach to diagnose and fix issues:
Step 1: Isolate the Problem
- Check if the issue is isolated to one camera (cabling/power) or affects multiple devices (network-wide).
- Use a PoE tester to verify power delivery and signal integrity.
Step 2: Inspect Cabling and Connections
- Replace damaged cables and ensure proper termination.
- Test continuity with a cable tester.
Step 3: Verify Power Supply
- Measure voltage at the camera end with a multimeter.
- Upgrade to a higher-wattage PoE switch if needed.
Step 4: Analyze Network Performance
- Use tools like Wireshark to monitor traffic and identify bottlenecks.
- Enable port mirroring to capture and analyze data.
Step 5: Update and Secure
- Patch firmware and software.
- Implement network segmentation and strong passwords.
Data Table: Common PoE Camera Signal Loss Causes and Solutions
| Cause | Symptoms | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faulty Cable | Intermittent signal, flickering | Replace with Cat6/6a shielded cable | Use conduit and high-quality cables |
| Power Shortage | Camera reboots, no IR at night | Upgrade PoE switch/injector | Calculate PoE budget beforehand |
| Network Congestion | Delayed video, dropped frames | Segment traffic with VLANs | Use 10 Gbps switches for large setups |
| EMI Interference | Static, corrupted video | Use shielded cables, reroute wiring | Avoid parallel high-power lines |
| Firmware Bugs | Random crashes, reboots | Update firmware | Monitor release notes |
Conclusion: Stay Ahead of the Signal Loss Game
PoE cameras are powerful tools, but their reliability hinges on proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. By understanding the top causes of signal loss—from cabling flaws to network congestion—you can build a robust surveillance system that stands the test of time. Remember: prevention is cheaper than downtime. Invest in quality hardware, monitor your network, and stay updated on firmware releases. In 2026, a proactive approach isn’t just best practice—it’s essential for peace of mind. Whether you’re guarding a home, business, or industrial site, a little vigilance goes a long way in keeping your PoE cameras online and your property secure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does my PoE camera keep losing signal?
PoE cameras can lose signal due to power fluctuations, damaged cables, or network congestion. Ensuring stable power delivery and using high-quality Ethernet cables (like Cat6) helps prevent interruptions.
Can long cable runs cause a PoE camera to lose signal?
Yes, exceeding the maximum 100-meter Ethernet cable limit can weaken both power and data signals. For longer distances, use PoE extenders or fiber optic converters to maintain a strong connection.
How does network bandwidth affect PoE camera signal loss?
High network traffic or insufficient bandwidth can cause data bottlenecks, making PoE cameras drop signal. Prioritize camera traffic via QoS settings or upgrade your switch to support higher throughput.
Does weather impact PoE camera signal reliability?
Extreme temperatures, moisture, or lightning strikes can damage outdoor PoE camera cables or injectors. Use weatherproof enclosures and surge protectors to safeguard against environmental signal loss.
Can a faulty PoE switch cause signal issues?
Absolutely. A failing or underpowered PoE switch may not deliver consistent voltage, leading to signal drops. Test with another switch or verify the switch’s PoE budget matches your cameras’ needs.
How do I troubleshoot intermittent PoE camera signal loss?
Check for loose connections, cable damage, or IP conflicts. Use a PoE tester to verify power delivery and inspect switch logs for port errors or disconnections.