
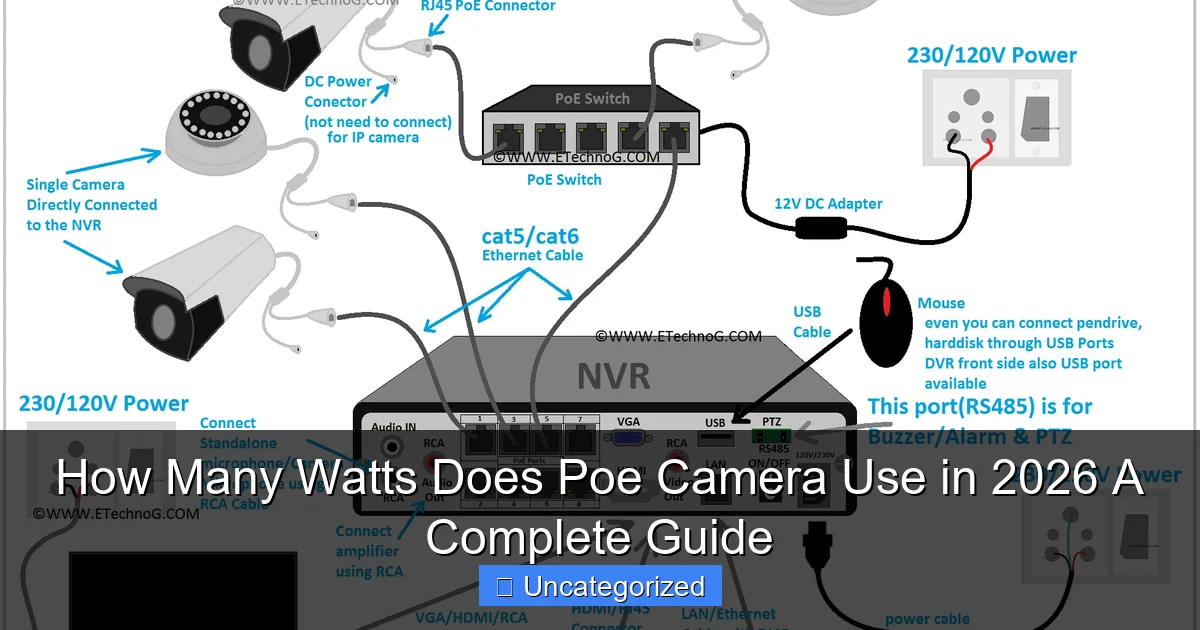
Featured image for how many wats does poe.camera use
Image source: securitycamcenter.com
POE cameras in 2026 typically use between 5 to 25 watts, depending on model, resolution, and features like infrared night vision or pan-tilt-zoom motors. Most standard HD POE cameras consume under 12 watts, making them energy-efficient and ideal for continuous 24/7 surveillance using Power over Ethernet technology.
Key Takeaways
- POE cameras use 5–30 watts depending on model and features.
- Check camera specs to confirm exact power needs before installation.
- Use IEEE 802.3af/at/bt standards to match power supply safely.
- High-resolution and IR models consume more power—plan accordingly.
- Efficient POE switches reduce energy waste and support multiple cameras.
📑 Table of Contents
- The Power Behind the Lens: Understanding Poe Camera Wattage in 2026
- Understanding PoE Standards and Their Impact on Camera Wattage
- Real-World Power Consumption: Breaking Down the Numbers
- Calculating Your System’s Total Power Requirements
- Energy Efficiency Innovations in 2026 PoE Cameras
- Optimizing Power Use: Practical Strategies for Installers
- Future Trends: What’s Next for PoE Camera Power in 2027+
The Power Behind the Lens: Understanding Poe Camera Wattage in 2026
As smart surveillance systems continue to evolve, Power over Ethernet (PoE) cameras have become the cornerstone of modern security infrastructure. From bustling city streets to suburban homes, these compact devices deliver high-resolution video while simplifying installation through a single cable solution. But as energy efficiency and sustainability concerns grow, one question dominates conversations: How many watts does a PoE camera use in 2026? The answer isn’t as simple as checking a spec sheet – it involves understanding power standards, environmental factors, and real-world usage patterns that shape energy consumption across different models and scenarios.
In today’s connected world, where every watt counts toward carbon footprints and electricity bills, knowing your PoE camera’s power draw is crucial. Whether you’re a business owner planning a 100-camera deployment or a homeowner upgrading to 4K surveillance, wattage impacts everything from infrastructure costs to long-term sustainability. This comprehensive guide explores the nuances of PoE camera power consumption, breaking down technical standards, usage patterns, and optimization strategies to help you make informed decisions. By the end, you’ll not only understand the numbers but also how to balance performance with energy efficiency in your security setup.
Understanding PoE Standards and Their Impact on Camera Wattage
IEEE 802.3af (PoE) – The Legacy Baseline
The original IEEE 802.3af standard, introduced in 2003, remains the foundation for most PoE cameras in 2026. This protocol delivers up to 15.4W per port at the source, with approximately 12.95W reaching the device after cable losses. While older HD cameras (720p-1080p) typically consume 3-5W, the extra headroom accommodates features like IR illumination (adding 1-2W) and basic PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) motors. For example, the Axis M3044-V uses 4.8W in normal operation but spikes to 7.2W when its IR cut filter activates at night.
Visual guide about how many wats does poe.camera use
Image source: i.pinimg.com
IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) – The Performance Booster
For 4K cameras and advanced models, PoE+ (802.3at) provides up to 30W source power, with 25.5W available to devices. This standard became essential for cameras with:
- High-resolution sensors (4K/8K)
- Motorized lenses and full PTZ mechanisms
- Heaters for cold climates (-30°C operation)
- Integrated microphones and speakers
A Hikvision DS-2DE4425IW-DE 4K PTZ camera, for instance, uses 8W for basic operation but draws 22W during continuous 360° rotation with simultaneous audio streaming.
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++/4PPoE) – The Future-Proof Solution
Emerging PoE++ standards (802.3bt) offer two tiers:
- Type 3 (60W source/51W device): Supports cameras with AI processors (e.g., Bosch NBN-73023BA using 45W for edge analytics)
- Type 4 (100W source/71W device): For specialty cameras with integrated thermal imaging or 360° fisheye lenses
While adoption remains limited to enterprise deployments in 2026, these standards enable next-gen features like real-time object recognition without external power.
Real-World Power Consumption: Breaking Down the Numbers
Typical Wattage Ranges by Camera Type
Actual power draw varies dramatically based on camera capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of average consumption in 2026:
| Camera Type | Basic Operation (W) | Peak Load (W) | Key Features Impacting Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1080p Fixed | 3.5-5.2 | 6-8 | IR LEDs, motion detection |
| 4K Fixed | 6-8 | 10-12 | HDR processing, WDR sensors |
| PTZ (Indoor) | 7-10 | 18-25 | Motorized movement, optical zoom |
| PTZ (Outdoor) | 9-12 | 25-35 | Heater, defroster, weatherproofing |
| AI-Enabled | 12-18 | 40-55 | Edge processing, analytics |
| Thermal/Fisheye | 15-22 | 65-75 | Specialized sensors, cooling systems |
Environmental and Operational Factors
Three key variables dramatically alter power consumption:
- Temperature: Outdoor cameras in freezing climates can double power use due to heater activation. A Dahua SD50225U-HNI draws 11W normally but 22W when maintaining -30°C operation.
- Usage Patterns: A camera recording 24/7 uses ~15% more power than one with motion activation. The Reolink RLC-822A shows 7.2W continuous vs. 6.1W motion-triggered.
- Firmware Features: Enabling advanced video analytics (e.g., facial recognition) can add 3-5W. The Hanwha XNV-8082R consumes 8W for basic streaming but 13W with full AI processing.
Calculating Your System’s Total Power Requirements
Step-by-Step Power Budgeting
To avoid overloading your PoE switch, follow this calculation process:
- List all camera models and their peak wattage (check specs)
- Add 20% buffer for cable losses and future upgrades
- Account for environmental factors (e.g., +30% for heated outdoor cameras)
- Calculate total: (Sum of all peak loads × 1.2 × environmental factor) + 15W per switch port for overhead
Example: A system with 10 indoor 4K cameras (peak 12W each) and 5 outdoor PTZs (peak 35W each):
- Indoor: 10 × 12W = 120W
- Outdoor: 5 × 35W × 1.3 (heater factor) = 227.5W
- Subtotal: 347.5W
- With 20% buffer: 417W
- Switch overhead (15 ports × 15W): 225W
- Total required: 642W → Need a 750W PoE++ switch
Infrastructure Considerations
Key infrastructure factors affecting power delivery:
- Cable length: 100m CAT6 cable causes ~15% voltage drop, requiring higher source wattage
- Switch efficiency: 80 Plus Platinum switches waste only 10% power vs. 30% on basic models
- Power sourcing equipment (PSE): Midspan injectors add ~5W per port overhead
- Redundancy: Dual power supplies add 20-25W but prevent outages
Pro Tip: Use PoE calculators like Ubiquiti’s Power Calculator or Microchip’s PoE Tool to model complex deployments with multiple cable runs and switch tiers.
Energy Efficiency Innovations in 2026 PoE Cameras
Smart Power Management Features
Modern cameras employ sophisticated power-saving techniques:
- Dynamic IR: Axis Q1656 reduces IR LED power by 40% using adaptive brightness
- Motion-based processing: Hikvision AcuSense disables analytics when no motion detected
- Thermal throttling: AI cameras like Bosch NBN-832 reduce clock speed when overheating
- Scheduled power modes: Outdoor cameras enter sleep mode during low-activity periods
The Hanwha PNV-A9081R exemplifies these features, cutting nighttime power from 18W to 9.5W using adaptive IR and AI motion filtering.
Hardware Efficiency Breakthroughs
2026’s most efficient cameras leverage:
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) power supplies: 95% efficiency vs. 80% for traditional silicon
- H.266/VVC encoding: 50% bandwidth reduction cuts processing power
- Low-power image sensors: Sony’s STARVIS 2 sensors use 30% less power than 2020 models
- Modular designs: Swappable sensor modules allow upgrading without replacing entire camera
The Axis P1465-LE uses these innovations to maintain 4K/30fps while consuming only 5.8W – 40% less than comparable 2020 models.
Optimizing Power Use: Practical Strategies for Installers
Right-Sizing Your PoE Infrastructure
Follow these best practices to avoid over-provisioning:
- Use PoE+ switches (30W ports) for 4K/AI cameras instead of PoE++ to save costs
- Segment networks: Group high-power cameras on dedicated switches
- Implement power scheduling: Use VLANs to disable non-essential cameras during off-hours
- Choose efficient cabling: CAT6A with 23 AWG reduces losses vs. thinner cables
- Monitor with SNMP: Track real-time power use to identify inefficiencies
Case Study: A retail chain reduced power use by 22% by replacing 100 legacy PoE switches with 802.3at models featuring per-port scheduling.
Maintenance and Monitoring Tips
Ongoing optimization requires proactive management:
- Quarterly power audits: Measure actual vs. rated consumption
- Firmware updates: New releases often include power efficiency improvements
- Thermal management: Ensure proper airflow to prevent overheating-induced power spikes
- Load balancing: Distribute high-power cameras across multiple switch ports
- Energy Star compliance: New 2026 models must meet strict efficiency benchmarks
Pro Tip: Use PoE Manager software (like Fluke Networks’ LinkRunner) to create power usage reports and predict infrastructure needs.
Future Trends: What’s Next for PoE Camera Power in 2027+
Emerging Power Standards and Technologies
Three developments will reshape PoE camera wattage:
- IEEE 802.3cg (10BASE-T1L): Enables 10W over 1km single-pair Ethernet, ideal for remote cameras
- USB-C Power Delivery integration: Hybrid PoE/USB power for temporary deployments
- Solar-PoE hybrids: Cameras with integrated solar panels reduce grid dependence
Early adopters like Axis Communications already offer 802.3cg prototypes for agricultural monitoring, using just 8W over 800m cable runs.
Sustainability and Regulatory Impacts
Global energy regulations will drive innovation:
- EU Ecodesign Directive 2027: Mandates <5W standby power for all surveillance cameras
- California Title 20: Requires 30% power reduction for 4K cameras by 2028
- Carbon labeling: Manufacturers will publish CO2e per camera-hour metrics
- Recycled materials: Power supply components using 75% post-consumer materials by 2030
These changes will push manufacturers toward zero-standby-power designs and AI-driven energy optimization as standard features.
Understanding PoE camera wattage isn’t just about reading spec sheets – it’s about making informed choices that balance security needs with energy efficiency. As we’ve seen, power consumption ranges from 3W for basic HD cameras to over 70W for specialty models, with real-world usage patterns dramatically altering these numbers. The key takeaway for 2026 is that smart power management through right-sized infrastructure, efficient hardware, and proactive monitoring delivers the best results. Whether deploying a single camera or a city-wide surveillance network, calculating total power needs while accounting for environmental factors and usage patterns prevents costly overloads and downtime.
Looking ahead, the industry’s shift toward sustainability will make energy efficiency a primary differentiator. Cameras that leverage innovations like GaN power supplies, H.266 encoding, and AI-driven processing will lead the market while reducing environmental impact. For installers and end-users, this means focusing on total cost of ownership rather than just upfront prices – an efficient 8W camera may cost more initially but save thousands in electricity over its lifetime. As PoE standards evolve and regulations tighten, staying informed about power consumption trends will remain essential for building effective, future-proof surveillance systems that protect both property and the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many watts does a PoE camera use on average in 2026?
Most PoE cameras in 2026 consume between **5 to 15 watts** per device, depending on resolution, features like night vision, and PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) functionality. High-end models with AI analytics may use up to 20 watts under peak load.
Can I power multiple PoE cameras with a single PoE switch without overloading it?
Yes, but you must check the total power budget of your PoE switch. For example, a 150W switch can safely power 10 cameras using 15 watts each, leaving room for other devices.
Does the wattage of a PoE camera affect my electricity bill significantly?
Not usually. Even if you run four 15-watt PoE cameras 24/7, they’ll cost roughly $5–$7 per month in electricity (based on $0.12/kWh), making them energy-efficient for surveillance.
How many watts does a PoE camera use during motion-triggered recording?
During active recording, a PoE camera may use **10–20% more power** than idle mode due to processing and storage demands. For example, a 10-watt camera could spike to 12 watts temporarily.
Are PoE cameras more energy-efficient than traditional wired cameras?
Yes, PoE cameras eliminate the need for separate power cables and often use **Power over Ethernet (PoE) standards like IEEE 802.3af/at**, which optimize energy use. This reduces overall power waste compared to AC-powered systems.
What happens if my PoE camera exceeds the switch’s power budget?
The switch may automatically shut down or reduce power to lower-priority devices. To avoid this, calculate the total wattage of all PoE devices and choose a switch with a 20–30% higher power budget than needed.