
Featured image for how to access lts nvr outside of network
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Access your LTS NVR remotely in 2026 by enabling cloud connectivity or setting up secure port forwarding through your router, ensuring real-time surveillance from anywhere. With end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication, modern LTS systems offer both convenience and robust protection for off-site access.
Key Takeaways
- Enable port forwarding: Configure your router to allow external access to the NVR.
- Use LTS Connect app: Securely connect to your NVR remotely via the official app.
- Verify DDNS settings: Ensure dynamic DNS is active for consistent remote access.
- Update firmware regularly: Keep your NVR updated to fix security and access issues.
- Check firewall rules: Confirm no local or network firewalls block remote connections.
- Use strong passwords: Protect remote access with complex, unique credentials.
📑 Table of Contents
- Why Remote Access to Your LTS NVR Matters
- Understanding LTS NVR Remote Access: The Basics
- Method 1: Using LTS Connect Cloud for Hassle-Free Remote Access
- Method 2: Port Forwarding for Direct NVR Access
- Method 3: Dynamic DNS (DDNS) for Dynamic IP Addresses
- Method 4: VPN Access for Maximum Security
- Comparing Remote Access Methods: Which One Is Right for You?
- Conclusion: Stay Connected, Stay Secure in 2026
Why Remote Access to Your LTS NVR Matters
In today’s fast-paced, interconnected world, security is no longer confined to physical premises. Whether you’re monitoring a retail store, a warehouse, or your own home, the ability to access your LTS NVR (Network Video Recorder) from anywhere in the world is not just a convenience—it’s a necessity. With advancements in IP surveillance technology and cloud integration, LTS has made significant strides in enabling remote access, ensuring that users can monitor their security systems in real time, no matter where they are. As we move into 2026, remote NVR access is no longer a luxury reserved for tech-savvy professionals; it’s a standard feature expected by users across industries and personal applications.
However, accessing your LTS NVR outside your local network can be a daunting task for many, especially for those unfamiliar with networking protocols, port forwarding, or cloud-based solutions. Misconfigurations can lead to failed connections, security vulnerabilities, or even system lockouts. The good news? With the right tools, knowledge, and step-by-step guidance, remote access to your LTS NVR is not only possible but also secure and reliable. This guide will walk you through the most effective, up-to-date methods to access your LTS NVR remotely in 2026—ensuring you stay in control of your surveillance system, whether you’re across town or on the other side of the globe.
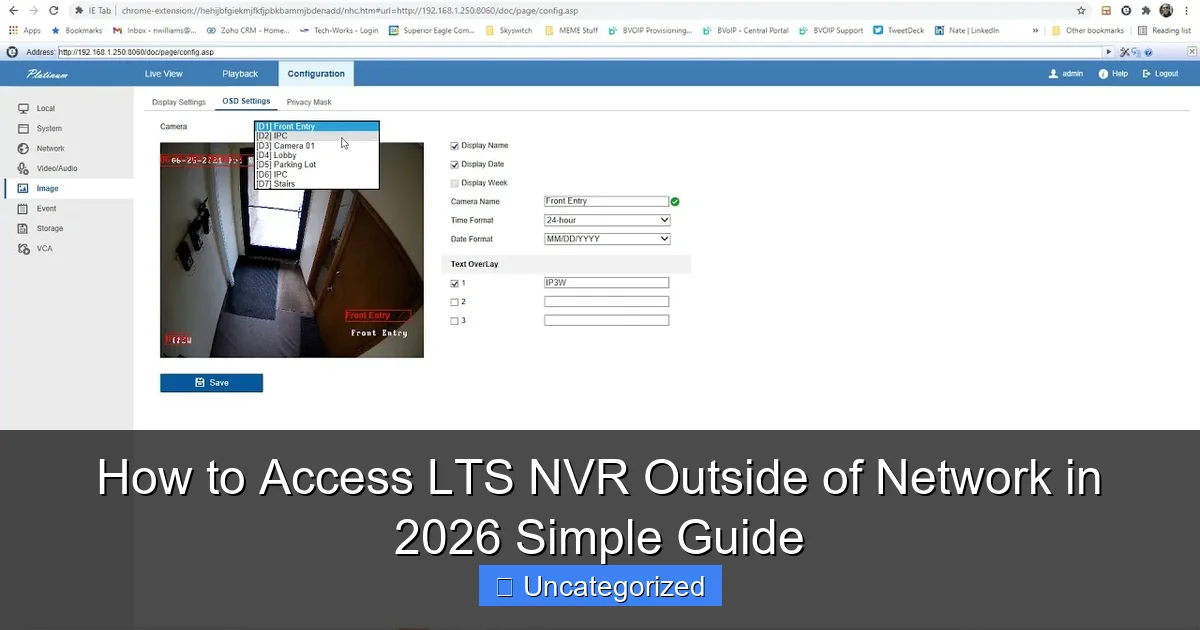
Understanding LTS NVR Remote Access: The Basics
Before diving into the technical setup, it’s essential to understand what remote access to an LTS NVR entails. At its core, remote access allows you to view live camera feeds, playback recorded footage, adjust system settings, and receive alerts—all from a device outside your local network (e.g., smartphone, tablet, or laptop). This requires your NVR to be accessible over the internet, which can be achieved through several methods, each with its own advantages and security considerations.

Visual guide about how to access lts nvr outside of network
Image source: ltsecurityinc.zendesk.com
How LTS NVRs Communicate Over the Internet
LTS NVRs use IP-based communication to transmit video data. When you access the NVR locally, your device and the NVR are on the same network (e.g., via Wi-Fi or Ethernet). For remote access, the NVR must be reachable via a public IP address. This can be done through:
- Port Forwarding: Opening specific ports on your router to allow external traffic to reach the NVR.
- Cloud-Based Services: Using LTS’s cloud platform (e.g., LTS Connect) to create a secure tunnel.
- Dynamic DNS (DDNS): Mapping a domain name to your changing public IP address, ideal for residential connections with dynamic IPs.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Creating a secure, encrypted connection to your local network as if you were on-site.
Each method has its trade-offs. For instance, port forwarding offers direct access but can expose your NVR to potential cyber threats if not properly secured. In contrast, cloud-based solutions are easier to set up but may involve subscription fees. Understanding these options helps you choose the best method based on your technical comfort, security needs, and network environment.
Prerequisites for Remote Access
Before attempting remote access, ensure the following:
- Your LTS NVR is connected to the internet via a stable broadband connection.
- The NVR firmware is up to date (check LTS’s official website for the latest version).
- You have administrative access to your router (for port forwarding or DDNS).
- Your ISP does not block common surveillance ports (e.g., HTTP port 80, RTSP port 554, or custom ports).
- You have a smartphone or computer with the LTS mobile app (LTS Connect) or web client installed.
For example, if you’re using a residential internet connection, your public IP address may change periodically (dynamic IP), which complicates direct access. In such cases, DDNS or cloud services are highly recommended.
Method 1: Using LTS Connect Cloud for Hassle-Free Remote Access
LTS’s official cloud-based solution, LTS Connect, is one of the simplest and most secure ways to access your NVR remotely in 2026. Unlike traditional port forwarding, this method requires no technical configuration and works seamlessly across devices. It leverages a secure peer-to-peer (P2P) connection, ensuring data privacy while maintaining high performance.
Visual guide about how to access lts nvr outside of network
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Step-by-Step Setup with LTS Connect
- Register for an LTS Connect Account: Visit https://connect.ltscctv.com and create a free account. Use a strong, unique password and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Add Your NVR to the Cloud: On your NVR’s local interface (via monitor or web browser), navigate to Network > Cloud Service. Enable cloud access and log in with your LTS Connect credentials. The NVR will generate a unique QR code or device ID.
- Pair Devices via Mobile App: Download the LTS Connect app (available on iOS and Android). Log in with your account and scan the QR code displayed on the NVR or manually enter the device ID. The NVR will appear in your device list.
- Test Remote Access: Disconnect from your local Wi-Fi and use mobile data to access the app. You should now see live feeds, playback options, and system alerts.
Tip: For multi-site management, you can add multiple NVRs to a single LTS Connect account. Use custom labels (e.g., “Home Garage,” “Warehouse East”) to organize devices.
Advantages of LTS Connect
- No Port Forwarding: Eliminates the need to configure your router, making it ideal for non-technical users.
- Encrypted Connection: Uses TLS 1.3 encryption for secure data transmission.
- Cross-Platform Support: Access via mobile app, web browser, or desktop client.
- Push Notifications: Receive real-time alerts for motion detection, camera tampering, or system errors.
Example Use Case: A small business owner uses LTS Connect to monitor two store locations. From her phone, she receives a motion alert from the back door camera at 2 AM. She logs into the app, reviews the footage, and confirms a false alarm (a raccoon triggered the sensor). She then disables the alarm remotely and checks camera angles—all without leaving her home.
Limitations and Troubleshooting
While LTS Connect is user-friendly, it may face issues such as:
- Connection Timeouts: Caused by unstable internet or NVR overload. Ensure your NVR has sufficient processing power and bandwidth.
- Device Offline: Check if the NVR is powered on and connected to the internet. Restart the NVR and router if needed.
- App Crashes: Update the app to the latest version or reinstall it.
For enterprise users, LTS offers a premium cloud tier with advanced features like AI-powered analytics, 4K streaming, and multi-user access controls.
Method 2: Port Forwarding for Direct NVR Access
For users who prefer full control over their network or require direct access (e.g., for integration with third-party software), port forwarding remains a viable option. This method routes external traffic to your NVR through specific ports on your router. While it offers low latency and high reliability, it requires careful configuration to avoid security risks.
Step-by-Step Port Forwarding Setup
- Assign a Static IP to Your NVR: On your router, set a static (reserved) IP address for the NVR (e.g., 192.168.1.100). This prevents the IP from changing and breaking remote access.
- Identify NVR Ports: Check your NVR’s network settings for the following default ports:
- HTTP/HTTPS: 80/443 (for web interface)
- RTSP: 554 (for video streaming)
- Custom Port: Often 37777 (for remote access)
- Configure Port Forwarding on Your Router:
- Log in to your router (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Navigate to Advanced > Port Forwarding.
- Create rules: Forward external ports (e.g., 8080, 5554, 37777) to the NVR’s internal IP and ports. Use TCP/UDP protocols.
- Test External Access: From an external network (e.g., mobile data), open a browser and enter
http://[Your_Public_IP]:8080. If configured correctly, you’ll see the NVR’s login page.
Tip: Avoid using default ports (e.g., 80, 443) for security. Use non-standard ports like 8080 or 8443 to reduce automated attacks.
Security Best Practices
Port forwarding exposes your NVR to the internet, making it a potential target for hackers. Follow these security measures:
- Change Default Credentials: Use a strong, unique password for the NVR admin account.
- Enable HTTPS: Encrypt web traffic by enabling SSL/TLS in the NVR settings.
- Use a Firewall: Configure your router’s firewall to block unauthorized IP addresses.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Patch vulnerabilities by updating the NVR firmware quarterly.
Example Use Case: A homeowner sets up port forwarding to integrate their LTS NVR with a smart home system (e.g., Home Assistant). They forward port 37777 and use a custom script to trigger lights when motion is detected.
Common Pitfalls and Fixes
- Port Blocked by ISP: Contact your ISP to unblock ports or use a non-standard range (e.g., 8080-8090).
- Dynamic Public IP: Pair port forwarding with DDNS (see next section) to handle IP changes.
- NAT Loopback Failure: Some routers block internal access to forwarded ports. Test from an external network or use the NVR’s local IP internally.
Method 3: Dynamic DNS (DDNS) for Dynamic IP Addresses
Many residential internet connections use dynamic public IP addresses, which change periodically. This makes port forwarding unreliable unless paired with Dynamic DNS (DDNS). DDNS links a domain name (e.g., yourhome.ddns.net) to your changing IP, allowing seamless remote access.
Setting Up DDNS with LTS NVR
- Choose a DDNS Provider: Popular free options include No-IP, DuckDNS, and FreeDNS. LTS also offers a built-in DDNS service (check your NVR’s network settings).
- Register a Domain: Sign up for a DDNS account and claim a domain (e.g.,
mysecurity.ltscctv.net). - Configure DDNS on Your NVR:
- Go to Network > DDNS on the NVR interface.
- Select your provider, enter the domain, and log in with your DDNS credentials.
- Pair with Port Forwarding: Use the DDNS domain instead of your public IP in remote access URLs (e.g.,
http://mysecurity.ltscctv.net:8080).
Tip: Enable automatic IP updates in your DDNS settings. Most NVRs update the IP every 5-10 minutes.
Advantages and Use Cases
- Cost-Effective: Free DDNS services eliminate the need for a static IP (which often costs extra).
- Scalable: Manage multiple NVRs with unique domain names (e.g.,
store1.ltscctv.net,store2.ltscctv.net). - Reliability: Ideal for users with unstable internet connections.
Example Use Case: A remote worker uses DDNS to access their home security system while traveling. They enter homecam.ltscctv.net:8080 into their phone’s browser to check if the dog walker arrived.
Method 4: VPN Access for Maximum Security
For users prioritizing security and privacy, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is the gold standard. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your remote device and your local network, making it appear as if you’re on-site. This method is ideal for businesses, sensitive locations, or users in high-risk environments.
Setting Up a Site-to-Site or Client-to-Site VPN
- Choose a VPN Solution:
- Router-Based VPN: Use a router that supports OpenVPN (e.g., ASUS, Netgear, or pfSense).
- Dedicated VPN Server: Set up a VPN server on a local computer (e.g., using WireGuard or SoftEther).
- Configure the VPN on Your Router/Server: Follow the provider’s instructions to set up the VPN. Assign a subnet (e.g., 192.168.2.0/24) for VPN clients.
- Connect Remotely: Install the VPN client on your device (e.g., OpenVPN Connect or WireGuard app). Log in and connect to your network.
- Access the NVR: Once connected, use the NVR’s local IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100) in the LTS Connect app or web interface.
Tip: Use split tunneling to route only NVR traffic through the VPN, reducing bandwidth usage.
Security and Performance Benefits
- End-to-End Encryption: Protects data from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- No Port Exposure: The NVR remains hidden from the public internet.
- Multi-User Support: Grant access to employees or family members with individual credentials.
Example Use Case: A hospital uses a WireGuard VPN to allow doctors to remotely access surveillance footage from patient monitoring cameras. All traffic is encrypted, ensuring HIPAA compliance.
Comparing Remote Access Methods: Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing the best method depends on your needs, technical expertise, and security requirements. Below is a comparison table to help you decide:
| Method | Ease of Setup | Security Level | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTS Connect Cloud | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | Free (Premium: $5/month) | Home users, small businesses |
| Port Forwarding | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | Free | Tech-savvy users, integrations |
| DDNS + Port Forwarding | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | Free | Dynamic IP users |
| VPN | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | Free (Hardware: $100+) | Businesses, high-security needs |
For most users, LTS Connect Cloud offers the best balance of simplicity, security, and functionality. However, if you require direct access or have specific integration needs, port forwarding or DDNS may be more suitable. For maximum security, a VPN is unmatched.
Conclusion: Stay Connected, Stay Secure in 2026
Accessing your LTS NVR outside your local network has never been easier or more secure. Whether you choose the user-friendly LTS Connect Cloud, the customizable port forwarding method, the flexible DDNS approach, or the ultra-secure VPN solution, the key is to match the method to your unique requirements. In 2026, remote surveillance is not just about convenience—it’s about peace of mind, operational efficiency, and proactive security.
Remember, no method is foolproof. Always prioritize security best practices: update firmware, use strong passwords, enable encryption, and monitor for suspicious activity. With the right setup, your LTS NVR becomes a powerful tool for real-time monitoring, remote management, and rapid response—no matter where life takes you.
Take action today: pick a method, follow the steps, and gain full control of your security system. The future of remote surveillance is here, and it’s in your hands.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I access my LTS NVR outside of network securely?
To access your LTS NVR remotely, enable port forwarding on your router and use the LTS mobile app or web client with your public IP address. Always ensure strong passwords and firmware updates for security.
Is there a way to access LTS NVR remotely without port forwarding?
Yes, use LTS Cloud or P2P services like the LTS Connect app, which bypass port forwarding by connecting through a secure server. This simplifies setup and reduces network vulnerabilities.
What’s the easiest method to access LTS NVR outside of network in 2026?
The easiest method is using LTS’s mobile app (LTS Smart or LTS Connect) with QR code pairing. It auto-configures remote access without manual router settings.
Can I use a DDNS service to access my LTS NVR remotely?
Yes, set up a DDNS (Dynamic DNS) service through your router or NVR settings to link your changing public IP to a static domain name. This simplifies remote access if your ISP doesn’t provide a static IP.
Why can’t I access my LTS NVR outside my local network?
Common issues include incorrect port forwarding, firewall blocks, or ISP restrictions. Verify your NVR’s IP/port settings and test connectivity using a mobile hotspot to isolate network issues.
Does LTS NVR support VPN for remote access?
Yes, you can connect to your home/office network via VPN (e.g., OpenVPN) and access the NVR as if you were local. This is ideal for advanced users prioritizing security.