Featured image for how to access my nvr
Image source: resource.fs.com
Access your NVR in 2026 securely and efficiently using encrypted login credentials and multi-factor authentication via the official web portal or mobile app. Whether you’re on-site or remote, ensure your firmware is updated and your network is protected with a firewall to maintain uninterrupted, high-definition video access and real-time monitoring from any device.
Key Takeaways
- Verify compatibility: Ensure your NVR supports 2026 network standards before setup.
- Use strong passwords: Secure access with unique, complex credentials to prevent breaches.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of security for remote logins.
- Update firmware regularly: Patch vulnerabilities and improve performance with latest updates.
- Configure port forwarding: Access NVR remotely by setting correct router ports.
- Bookmark the IP address: Save the local IP for quick, reliable internal access.
📑 Table of Contents
- Understanding Your NVR and Its Importance in Modern Security
- Preparing Your NVR for Access: Initial Setup and Network Configuration
- Accessing Your NVR Locally: Methods and Tools
- Remote Access: Connecting to Your NVR from Anywhere
- Advanced Access Methods and Integrations
- Troubleshooting Common NVR Access Issues
- Conclusion: Mastering NVR Access in 2026 and Beyond
Understanding Your NVR and Its Importance in Modern Security
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, surveillance systems have become more sophisticated, reliable, and accessible than ever before. At the heart of most modern security setups lies the Network Video Recorder (NVR), a critical component that stores, manages, and enables remote access to video footage captured by IP cameras. Whether you’re a homeowner securing your property, a small business owner monitoring operations, or a facility manager overseeing a large campus, knowing how to access your NVR is essential for real-time monitoring, evidence retrieval, and system management. As we move into 2026, NVR technology continues to integrate advanced features such as AI-powered analytics, cloud synchronization, and mobile-first access, making remote and local access more seamless—but also more complex for the uninitiated.
Imagine arriving at your office only to discover an unauthorized entry the night before. Without access to your NVR, you’re left in the dark. Or picture receiving a motion alert on your phone while on vacation—being able to instantly pull up live or recorded footage from your NVR can mean the difference between a false alarm and a critical security breach. The ability to access your NVR from anywhere, at any time, not only enhances peace of mind but also empowers proactive decision-making. This guide will walk you through the step-by-step processes, tools, and best practices to access your NVR in 2026, whether you’re using a local network, the cloud, or a mobile app. From initial setup to troubleshooting, we’ll cover everything you need to know to stay connected to your security system.
Preparing Your NVR for Access: Initial Setup and Network Configuration
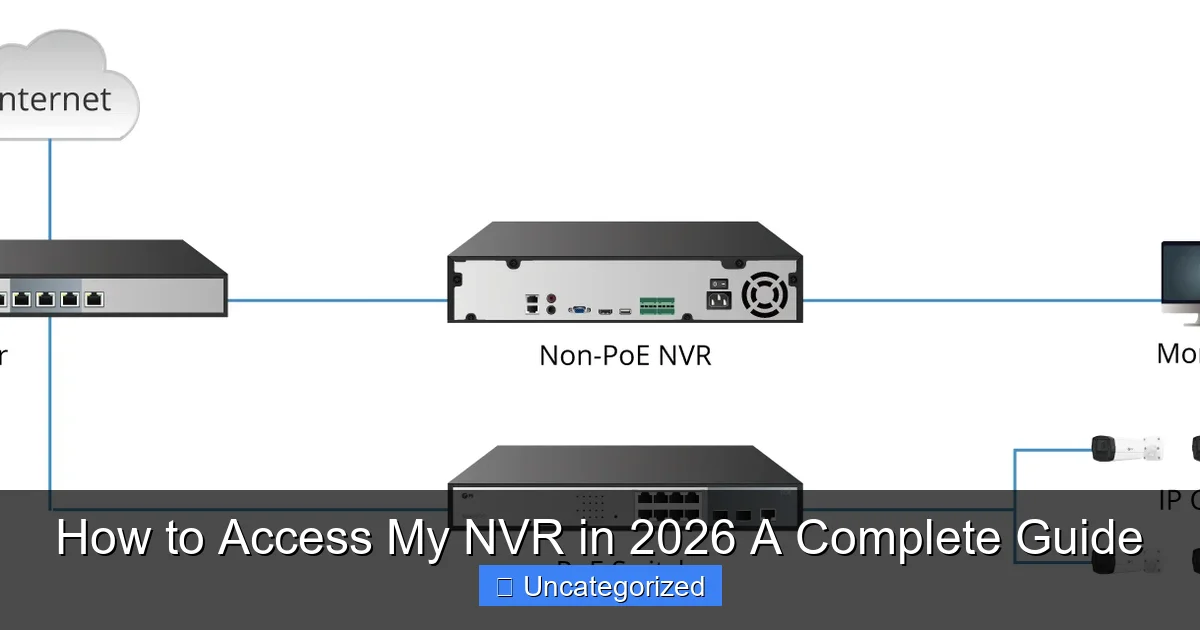
Connecting Your NVR to the Network
Before you can access your NVR, it must be properly connected to your network. The first step is physical setup: connect your NVR to your router or switch using an Ethernet cable. While some newer NVR models support Wi-Fi (especially compact or hybrid models), a wired Ethernet connection is recommended for stability, speed, and reduced latency—especially when handling multiple high-resolution camera streams. Ensure your NVR is powered on and that all IP cameras are properly connected and recognized by the system. Most NVRs will auto-detect cameras on the same network segment, but manual IP assignment may be required in larger deployments.
Visual guide about how to access my nvr
Image source: cucctv.co.uk
Next, assign a static IP address to your NVR. This prevents the NVR from changing IP addresses due to DHCP lease renewals, which can disrupt remote access. To do this, access your router’s admin panel (usually via 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1), locate the DHCP reservation or static IP section, and assign a fixed IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100) to the NVR’s MAC address. This ensures your NVR always has the same local address, simplifying port forwarding and mobile app configuration later.
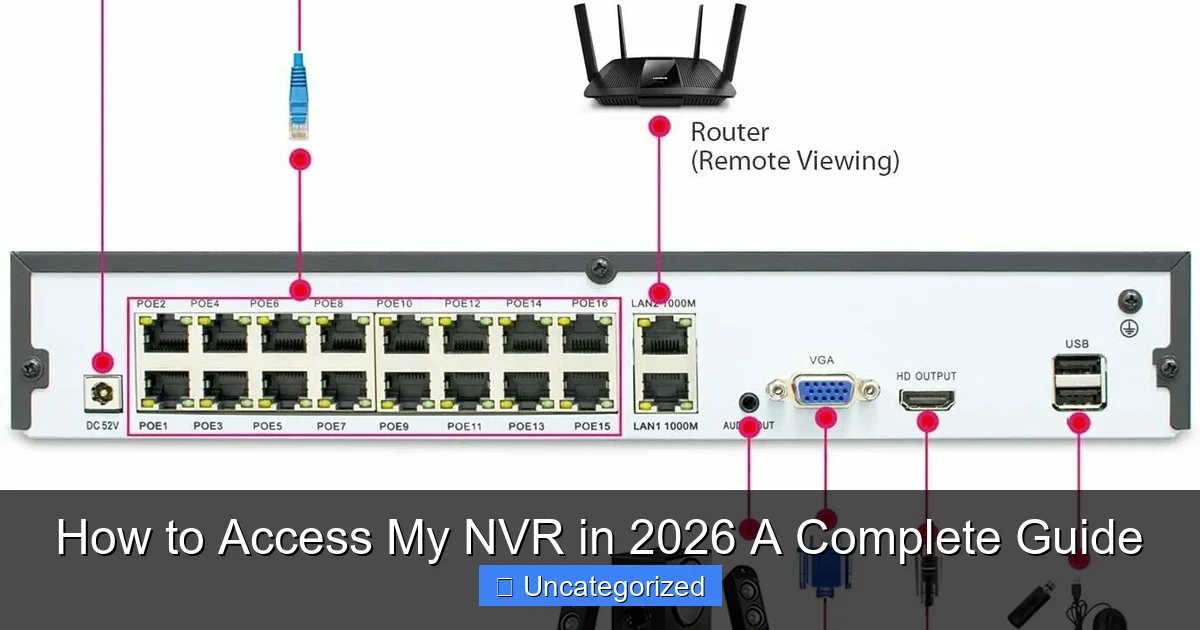
Configuring Port Forwarding for Remote Access
To access your NVR from outside your local network (e.g., from a smartphone on a different Wi-Fi network or while traveling), you’ll need to set up port forwarding on your router. This process directs external traffic to your NVR’s internal IP address. Common ports used by NVRs include:
- HTTP: 80
- HTTPS: 443
- RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol): 554
- Custom NVR Port: 37777 (common for Dahua, Hikvision, etc.)
- Mobile App Port: 34567 (varies by manufacturer)
For example, if your NVR is at 192.168.1.100 and uses port 37777, you would forward external port 37777 to internal IP 192.168.1.100 on port 37777. Caution: Exposing your NVR to the internet via port forwarding increases security risks. Always use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) if available, and consider using a VPN as a safer alternative (discussed later).
Enabling UPnP and P2P (Optional but Convenient)
Many modern NVRs support Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) or Peer-to-Peer (P2P) technology, which simplifies remote access. UPnP automatically configures port forwarding on compatible routers. P2P, on the other hand, uses a cloud-based relay server (managed by the NVR manufacturer) to connect your device to the NVR without manual port forwarding. For example, Hikvision’s “iVMS-4500” app uses P2P by scanning a QR code on the NVR. While P2P is user-friendly, it may introduce latency and depends on the manufacturer’s cloud infrastructure. Evaluate your needs: P2P for ease of use, port forwarding or VPN for reliability and security.
Accessing Your NVR Locally: Methods and Tools
Using the NVR’s Web Interface
One of the most direct ways to access your NVR is through its web-based management interface. Open a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, or Edge) and enter the NVR’s local IP address (e.g., http://192.168.1.100). You’ll be prompted to log in with admin credentials (default usernames and passwords are often admin/admin or admin/123456—change these immediately for security).

Visual guide about how to access my nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
The web interface typically provides full access to:
- Live camera feeds
- Playback and search functions
- User management and permissions
- System settings (date/time, network, storage)
- AI analytics (e.g., facial recognition, vehicle detection)
For example, a Dahua NVR offers a responsive web UI with drag-and-drop camera layout customization, while Hikvision’s iVMS-4200 desktop software (also accessible via browser) provides advanced event filtering and alarm management. Ensure your browser supports the NVR’s required plugins (e.g., ActiveX for older systems) or use HTML5-based interfaces (standard in 2026).
Using Desktop Management Software
Many manufacturers provide dedicated desktop software for Windows and macOS. For instance, Hikvision’s iVMS-4200, Dahua’s SmartPSS, or Axis Camera Station offer richer features than web interfaces, including:
- Multi-site management
- Advanced playback with timeline zoom
- Integration with access control systems
- Customizable dashboards and alerts
To use this method, download and install the software from the manufacturer’s official website, then add your NVR by entering its IP address, port, and login credentials. Some software supports automatic network discovery, which scans your local subnet for connected NVRs.
Direct HDMI/Display Connection
For quick local access without a network, connect a monitor or TV to your NVR via HDMI or VGA. This method is ideal for:
- Initial setup and configuration
- On-site troubleshooting
- Presenting footage to law enforcement or stakeholders
The on-screen display (OSD) menu allows you to navigate cameras, playback recordings, and adjust settings using a mouse or remote control. While not suitable for remote access, it remains a vital tool for hands-on management.
Remote Access: Connecting to Your NVR from Anywhere
Mobile App Access (iOS and Android)
In 2026, mobile access is the most popular method for checking your NVR on the go. Most manufacturers offer dedicated apps such as:
- Hik-Connect (Hikvision)
- DMSS (Dahua)
- Reolink App
- UniFi Protect (Ubiquiti)
To set up remote access:
- Download the app from the App Store or Google Play.
- Create an account or log in with your NVR’s credentials.
- Scan the QR code on your NVR (for P2P setup) or manually add the NVR by entering its public IP address and port.
- Enable push notifications for motion detection or alarm events.
Pro Tip: Use two-factor authentication (2FA) within the app to prevent unauthorized access. For example, the DMSS app supports 2FA via SMS or authenticator apps like Google Authenticator.
Cloud-Based Access and Hybrid Systems
Cloud-connected NVRs (e.g., Reolink, Lorex, or Eufy) store footage on remote servers, enabling access via the manufacturer’s cloud portal. Benefits include:
- No need for port forwarding
- Automatic firmware updates
- Redundant backup (if cloud storage is enabled)
- Access from any device with internet
To use cloud access:
- Register your NVR with the manufacturer’s cloud service (e.g., Reolink Cloud).
- Subscribe to a storage plan if required (e.g., $3.99/month for 7-day cloud storage).
- Log in to the cloud dashboard via web or app.
Example: A Reolink RLK16-410 NVR with cloud subscription allows you to view live feeds and download recordings from any browser using https://reolink.com/cloud.
Using a VPN for Secure Remote Access
For maximum security, especially in enterprise environments, use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to access your NVR. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and your home/office network, making your NVR appear as if you’re on the local network. This eliminates the need for port forwarding and reduces exposure to cyber threats.
Popular VPN solutions include:
- OpenVPN (self-hosted, highly secure)
- WireGuard (faster, modern protocol)
- Tailscale (user-friendly, zero-config)
- Commercial services like NordVPN or ExpressVPN (with split tunneling)
Once connected to the VPN, access your NVR using its local IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100:80) as if you were on-site. This method is ideal for IT administrators managing multiple NVRs across locations.
Advanced Access Methods and Integrations
Third-Party Software and VMS Platforms
For users with multiple NVR brands or advanced requirements, Video Management Software (VMS) platforms like Milestone XProtect, Genetec Security Center, or Blue Iris can unify access to disparate systems. These platforms:
- Support ONVIF-compliant cameras and NVRs
- Offer centralized control across sites
- Integrate with access control, alarms, and analytics
- Provide custom reporting and audit trails
For example, a retail chain might use Genetec to monitor 50 stores, each with a different NVR model, from a single dashboard. Setup involves adding NVRs as “cameras” in the VMS using RTSP URLs or manufacturer-specific plugins.
Smart Home and IoT Integration
In 2026, NVRs are increasingly integrated with smart home ecosystems. Platforms like:
- Google Home (via ONVIF or manufacturer apps)
- Apple HomeKit (with compatible NVRs like Eufy)
- Amazon Alexa (for voice commands like “Show me the front door”)
enable voice and automation control. For instance, an Alexa-enabled NVR can trigger a camera feed on your Echo Show when motion is detected. To set this up, link your NVR’s cloud account to the smart home platform and configure routines.
API and Automation for Developers
For tech-savvy users, many NVRs offer RESTful APIs or webhooks for custom integrations. For example:
- Automatically save clips to Google Drive when a facial recognition event occurs.
- Send SMS alerts via Twilio when the NVR goes offline.
- Integrate with Slack or Microsoft Teams for team notifications.
Refer to your NVR’s API documentation (e.g., Hikvision’s ISAPI, Dahua’s SDK) to build custom scripts or use tools like Node-RED or IFTTT.
Troubleshooting Common NVR Access Issues
Network Connectivity Problems
If you can’t access your NVR, first check:
- Is the NVR powered on and connected to the network?
- Can you ping the NVR’s IP address from another device on the same network?
- Is the router’s firewall blocking NVR traffic?
- Are you using the correct IP and port?
Tip: Use ping 192.168.1.100 in Command Prompt or Terminal to test connectivity.
Authentication and Login Failures
Common causes include:
- Forgotten password: Use the manufacturer’s password reset tool (e.g., Hikvision’s “Password Recovery” tool).
- Account lockout: Wait 15–30 minutes or contact support.
- Browser compatibility: Try a different browser or clear cache.
Remote Access Not Working
Checklist:
- Is port forwarding correctly configured?
- Is your public IP address dynamic? Use a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service like No-IP or DynDNS to map a domain name to your changing IP.
- Is your ISP blocking inbound ports? Contact your ISP or switch to P2P/cloud.
Data Table: Common NVR Access Methods Compared
| Method | Security Level | Ease of Setup | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web Interface (Local) | Medium | Easy | Quick on-site checks | Requires local network |
| Port Forwarding | Low (without 2FA) | Medium | Full remote control | Exposes NVR to internet |
| P2P/Cloud | Medium (depends on provider) | Very Easy | Beginners, small setups | Latency, subscription fees |
| VPN | High | Hard | Enterprise, high security | Complex setup, slower speed |
| Mobile App | Medium (with 2FA) | Easy | On-the-go monitoring | Limited features vs desktop |
Conclusion: Mastering NVR Access in 2026 and Beyond
Accessing your NVR in 2026 is no longer a technical hurdle reserved for IT professionals. With a range of options—from simple mobile apps to advanced VPNs and cloud integrations—there’s a solution for every user, regardless of technical skill or security needs. The key is to balance convenience with security: while P2P and cloud access offer plug-and-play simplicity, methods like VPNs and local network access provide greater control and protection. Always prioritize strong passwords, enable 2FA, keep firmware updated, and monitor access logs regularly.
As technology advances, expect even smarter NVRs with AI-driven access controls, biometric authentication, and seamless integration with broader IoT ecosystems. Whether you’re checking in on your home while traveling, managing a business’s security remotely, or building a custom surveillance system, understanding how to access your NVR empowers you to take full advantage of your investment. By following the steps, tools, and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll ensure that your security system remains accessible, reliable, and ready for whatever the future holds.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I access my NVR remotely using a web browser?
To access your NVR remotely, open a web browser and enter your NVR’s public IP address or domain name, followed by the port number (e.g., 80 or 443). Ensure port forwarding is configured on your router and use the correct login credentials for your NVR system.
What’s the easiest way to access my NVR from a smartphone or tablet?
Download the official mobile app (like Hik-Connect, iVMS-4500, or Dahua DMSS) and scan the NVR’s QR code or manually add the device using its IP and login details. This lets you monitor cameras in real time from anywhere using your NVR’s network.
Can I access my NVR over the internet without port forwarding?
Yes, many modern NVRs support cloud P2P services—simply enable P2P in your NVR settings and connect via the manufacturer’s app or portal. This method simplifies how to access my NVR without exposing your network to public IP risks.
Why can’t I access my NVR on the local network?
This often occurs due to incorrect IP settings, firewall blocks, or the NVR being on a different subnet. Verify the NVR and your computer are on the same network and that the correct local IP address is used when trying to access my NVR.
How do I find my NVR’s IP address to access it?
Use the manufacturer’s IP scanner tool (e.g., SADP for Hikvision) or check your router’s connected devices list to locate your NVR. The NVR may also display its IP on a connected monitor via its local interface.
Is it safe to access my NVR remotely, and how can I improve security?
Remote access is safe if you use HTTPS, strong passwords, and two-factor authentication. Avoid default ports and enable encryption to protect your data when you access your NVR over the internet in 2026.