Featured image for how to add a new ip camera to your nvr
Image source: 2.bp.blogspot.com
Adding a new IP camera to your NVR in 2026 is faster and easier than ever, thanks to plug-and-play compatibility and AI-driven auto-detection features. Simply connect the camera to your network, power it on, and let your NVR’s smart scanning system locate, authenticate, and configure it automatically—no manual IP entry required.
Key Takeaways
- Verify compatibility first: Ensure your NVR supports the camera’s resolution and protocol.
- Use PoE for simplicity: Power and connect the camera via a single Ethernet cable.
- Access NVR settings: Navigate to the IP camera addition menu in your NVR interface.
- Scan for cameras automatically: Let the NVR detect new IP cameras on the network.
- Secure with strong credentials: Change default login details immediately after setup.
- Update firmware: Install the latest NVR and camera firmware for optimal performance.
📑 Table of Contents
- The Future of Surveillance: Why Adding IP Cameras to Your NVR Matters in 2026
- Understanding the Core Components: IP Cameras and NVRs
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Add a New IP Camera to Your NVR
- Advanced Integration: Smart Features and Automation
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Comparing NVR and IP Camera Brands in 2026
- Conclusion: Building a Future-Proof Surveillance System
The Future of Surveillance: Why Adding IP Cameras to Your NVR Matters in 2026
In the rapidly evolving world of security technology, IP cameras and Network Video Recorders (NVRs) have become the gold standard for both residential and commercial surveillance systems. As we step into 2026, the demand for high-resolution, intelligent, and remotely accessible security systems continues to grow. Whether you’re upgrading an existing setup or installing a new one, knowing how to add a new IP camera to your NVR is a critical skill. With advancements in AI-powered analytics, cloud integration, and 4K+ video streaming, modern NVRs are more powerful than ever—capable of managing dozens of cameras, detecting anomalies, and even automating responses.
Adding a new IP camera to your NVR isn’t just about plugging in a device and calling it a day. It’s a process that involves careful planning, network configuration, and optimization to ensure seamless integration, maximum performance, and long-term reliability. From choosing the right camera to troubleshooting connection issues, this guide will walk you through every step of the process. Whether you’re a DIY homeowner, a small business owner, or an IT professional managing enterprise-grade systems, mastering this process will future-proof your surveillance infrastructure and enhance your overall security posture.
Understanding the Core Components: IP Cameras and NVRs
What Is an IP Camera?
An IP camera (Internet Protocol camera) is a digital video camera that transmits data over a network, typically via Ethernet or Wi-Fi. Unlike traditional analog CCTV cameras, IP cameras send video streams directly to a network, enabling remote access, higher resolution (up to 12MP or more), and advanced features like motion detection, facial recognition, and two-way audio. In 2026, most IP cameras support H.265+ encoding, which reduces bandwidth usage by up to 50% compared to older standards, making them ideal for large-scale deployments.

Visual guide about how to add a new ip camera to your nvr
Image source: electricaltechnology.org
Modern IP cameras come in various forms: bullet, dome, PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom), fisheye, and even thermal or AI-powered models. They often include built-in storage (via microSD), night vision (IR or color), and weather resistance for outdoor use. For example, the Hikvision AcuSense 4K Dome Camera uses AI to distinguish between humans, vehicles, and animals—reducing false alarms by up to 90%.
What Is an NVR?
A Network Video Recorder (NVR) is the central hub that receives, processes, and stores video streams from IP cameras. Unlike DVRs (Digital Video Recorders), which are designed for analog systems, NVRs are built for digital, networked environments. They connect to cameras via a local network (LAN) or the internet and can support multiple camera feeds simultaneously.
Modern NVRs in 2026 are packed with features: AI-powered video analytics, cloud backup, mobile app integration (iOS/Android), and support for ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) standards. They also offer robust storage solutions, with models supporting up to 64TB of internal HDD capacity and RAID configurations for redundancy. For instance, the Dahua XVR5104HS-4K supports up to 32 IP cameras and includes smart motion detection and facial search capabilities.
How IP Cameras and NVRs Work Together
When you add a new IP camera to your NVR, the two devices communicate over your network using protocols like RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) or ONVIF. The camera captures video, compresses it (using H.264/H.265), and streams it to the NVR, which stores the footage on internal or external drives. The NVR also provides a user interface (via web browser or app) to view live feeds, playback recordings, and configure settings.
Key benefits of this integration include:
- Centralized management: Control all cameras from one interface.
- Scalability: Add more cameras without rewiring (as long as network bandwidth allows).
- Remote access: View your system from anywhere using a smartphone or tablet.
- Smart features: Use AI to detect intruders, track objects, or trigger alerts.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Add a New IP Camera to Your NVR
Step 1: Prepare Your Network and Equipment
Before adding a new IP camera, ensure your network and NVR are ready. Here’s what to check:

Visual guide about how to add a new ip camera to your nvr
Image source: platinumcctv.com
- Network bandwidth: Each camera consumes bandwidth based on resolution and frame rate. For example, a 4K camera at 30fps may use 12-16 Mbps. Use a network speed test tool to confirm your LAN can handle the load.
- PoE switch or injector: If your camera uses Power over Ethernet (PoE), ensure your switch or injector supports the required power (usually 802.3af or 802.3at). For non-PoE cameras, have a power adapter ready.
- NVR capacity: Verify your NVR has enough channels (e.g., 8, 16, 32) and storage space. Most NVRs allow you to add cameras up to their max channel count.
- ONVIF compatibility: Check that both your camera and NVR support ONVIF Profile S (for video streaming) and Profile G (for recording). This ensures seamless integration.
Pro Tip: Use a dedicated VLAN (Virtual LAN) for your security cameras to isolate them from your main network and improve performance.
Step 2: Physically Install the IP Camera
Mount your camera in the desired location, ensuring:
- It has a clear line of sight to the area you want to monitor.
- It’s protected from weather (for outdoor models) and tampering.
- Wiring is secure and hidden (if possible). Use conduit for outdoor runs.
For PoE cameras, connect the Ethernet cable directly to your PoE switch or injector. For non-PoE, connect the camera to a power outlet and the network. Power on the camera and wait 1-2 minutes for it to boot up.
Step 3: Connect the Camera to the NVR
There are two primary methods to add the camera:
Method 1: Auto-Discovery (Plug-and-Play)
- Log in to your NVR’s web interface (via IP address in a browser) or use the manufacturer’s app.
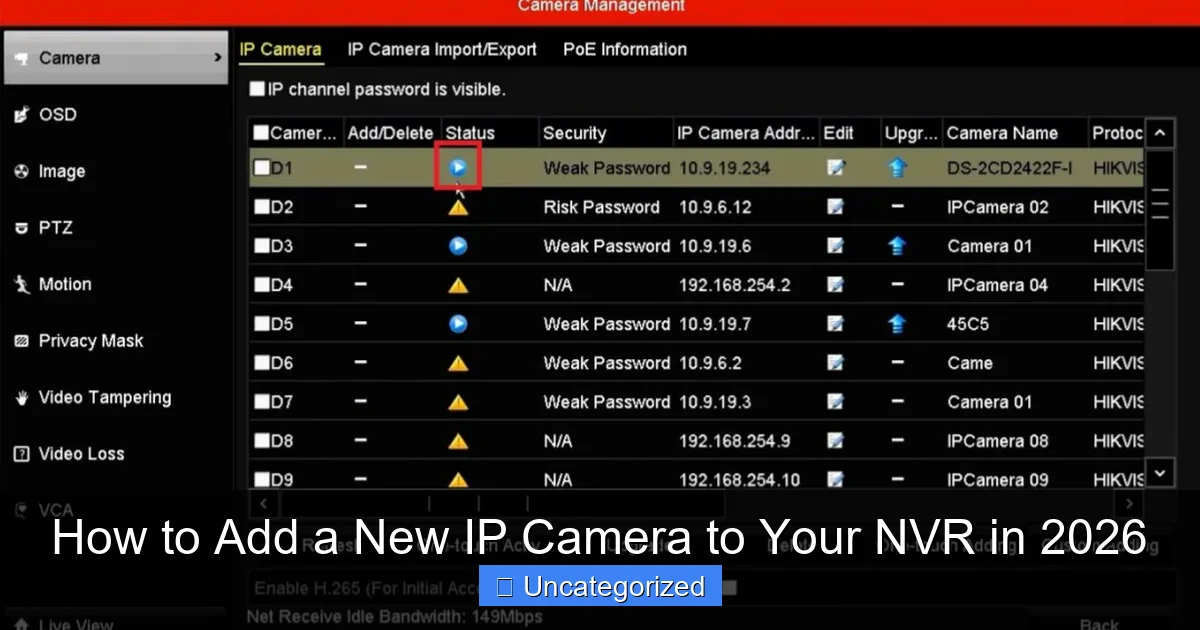
- Navigate to Camera Management > Add Camera.
- Click Auto Search or Discover. The NVR will scan the network for ONVIF-compliant cameras.
- Select your new camera from the list and click Add.
Method 2: Manual IP Address Entry
- If auto-discovery fails, manually enter the camera’s IP address, username, and password.
- To find the camera’s IP, use the manufacturer’s IP scanner tool (e.g., Hikvision iVMS-4200, Dahua ConfigTool) or check your router’s connected devices list.
- Enter the details in the NVR’s camera settings and click Add.
Example: Adding a Reolink RLC-811A camera to a Synology Surveillance Station NVR using manual entry: Enter the camera’s IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100), port 80, username “admin,” and password. Enable ONVIF and save.
Step 4: Configure Camera Settings
After adding the camera, optimize its settings:
- Resolution and frame rate: Set to 4K@30fps for high detail, or lower (e.g., 1080p@15fps) to save bandwidth.
- Video encoding: Use H.265+ if supported for better compression.
- Motion detection: Adjust sensitivity and set detection zones to avoid false alerts (e.g., from moving trees).
- Storage: Choose continuous recording or event-based (motion-triggered). Set retention period (e.g., 30 days).
- AI features: Enable person/vehicle detection, facial recognition, or license plate recognition (if available).
Pro Tip: Use the NVR’s “Test” feature to verify the camera feed and adjust focus/zoom remotely.
Step 5: Test and Troubleshoot
After configuration, test the system:
- View the live feed on your NVR or mobile app.
- Trigger motion (e.g., wave at the camera) to test detection and recording.
- Check storage: Ensure the NVR is recording and storing footage.
Common issues and fixes:
- Camera not found: Verify IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Reboot the camera.
- No video feed: Check network cables, PoE power, and firewall settings.
- Poor video quality: Reduce resolution, enable H.265, or upgrade network switches.
Advanced Integration: Smart Features and Automation
AI-Powered Analytics
In 2026, AI is a game-changer for surveillance. Modern NVRs and cameras can:
- Detect intruders: Ignore false alarms from animals or shadows.
- Count people: Useful for retail stores to track foot traffic.
- Track vehicles: Identify license plates or suspicious behavior.
- Facial recognition: Grant access to authorized personnel.
For example, the Axis Q1615-LE uses deep learning to classify objects with 95% accuracy. To enable these features, navigate to your NVR’s Analytics tab and configure rules (e.g., “Send email alert if a person is detected after 10 PM”).
Cloud Integration and Remote Access
Most NVRs now support cloud services for off-site backup and remote viewing:
- Cloud storage: Upload critical footage to platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or manufacturer-specific services (e.g., Hik-Connect, Reolink Cloud).
- Mobile apps: Use apps like Blue Iris or Surveillance Station to monitor your system on the go.
- Push notifications: Receive alerts on your phone when motion is detected.
Pro Tip: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your NVR’s cloud account to prevent unauthorized access.
Automation with Smart Home Systems
Integrate your NVR with smart home platforms (e.g., Google Home, Apple HomeKit, IFTTT):
- Turn on smart lights when motion is detected.
- Lock doors automatically if an intruder is spotted.
- Sync with voice assistants (e.g., “Show me the backyard camera” via Alexa).
For example, using IFTTT, you can create an applet that triggers a siren if a camera detects a vehicle in a restricted zone.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Network Congestion and Bandwidth Issues
Adding too many high-resolution cameras can overwhelm your network. Symptoms include:
- Laggy video feeds
- Dropped frames
- Camera disconnections
Solution: Use a managed PoE switch with QoS (Quality of Service) to prioritize camera traffic. For large deployments, consider a separate VLAN or dedicated network for surveillance.
Security Vulnerabilities
IP cameras are vulnerable to hacking if not secured properly. Risks include:
- Weak default passwords
- Outdated firmware
- Unencrypted video streams
Solution:
- Change default usernames/passwords immediately.
- Enable HTTPS and SSL encryption.
- Update firmware regularly (check manufacturer websites monthly).
- Disable UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) on your router.
Storage Management
Running out of storage is a common issue. To avoid this:
- Use motion-based recording instead of continuous.
- Enable smart encoding (e.g., H.265+).
- Schedule regular backups to external drives or the cloud.
- Monitor storage usage via your NVR’s dashboard.
Comparing NVR and IP Camera Brands in 2026
Choosing the right hardware is crucial for a reliable system. Below is a comparison of top brands and their key features:
| Brand | NVR Model Example | Max Cameras | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hikvision | DS-7608NI-K2/8P | 8 | 4K recording, AcuSense AI, PoE ports | Mid-sized businesses |
| Dahua | XVR5104HS-4K | 32 | Facial recognition, 4K decoding, RAID support | Large enterprises |
| Reolink | RLN8-410 | 8 | Plug-and-play, 12TB storage, free cloud | Homeowners |
| Axis | Q615-E Mk II | 32 | Deep learning analytics, 360° coverage | High-security facilities |
| Synology | Surveillance Station (DS1621+) | 40 | AI detection, cloud sync, mobile app | Tech-savvy users |
Note: Always verify ONVIF compatibility between your camera and NVR before purchasing.
Conclusion: Building a Future-Proof Surveillance System
Adding a new IP camera to your NVR in 2026 is more than just a technical task—it’s a strategic investment in security, intelligence, and peace of mind. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure seamless integration, optimal performance, and long-term reliability. From choosing the right hardware to leveraging AI-powered analytics and cloud integration, modern surveillance systems offer capabilities that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
Remember, the key to success lies in preparation, attention to detail, and ongoing maintenance. Regularly update firmware, monitor storage, and test your system to catch issues before they escalate. Whether you’re securing your home, office, or warehouse, a well-configured NVR and IP camera setup will provide 24/7 protection, actionable insights, and remote access—no matter where you are. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will keep your surveillance system ahead of the curve.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I add a new IP camera to my NVR for the first time?
To add a new IP camera to your NVR, connect the camera to the same network as your NVR, then use the NVR’s interface to scan for and auto-detect the camera. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the setup, ensuring both devices are powered and firmware is up to date.
Why can’t my NVR detect my new IP camera?
This often happens due to network mismatches, firewall settings, or incompatible protocols. Verify that the camera and NVR are on the same subnet and that ONVIF or your manufacturer’s plug-and-play protocol is enabled on both devices.
Can I add an IP camera to my NVR without using PoE?
Yes, you can use a separate power adapter for the camera or connect it via Wi-Fi if supported. However, for reliable performance, a PoE switch or injector is recommended to deliver both power and data over a single cable.
How do I manually add an IP camera to my NVR if auto-discovery fails?
In your NVR’s camera management menu, select “Manual Add” and enter the camera’s IP address, port, username, and password. Ensure the camera’s protocol (e.g., ONVIF, RTSP) matches what the NVR supports for seamless integration.
Do all IP cameras work with every NVR?
Not always. While many IP cameras and NVRs support ONVIF for cross-compatibility, older or proprietary systems may require matching brands. Always check the manufacturer’s compatibility list before purchasing to avoid issues when adding an IP camera to your NVR.
How do I secure my IP camera after adding it to the NVR?
Change the default camera login credentials immediately and enable encryption (e.g., HTTPS, WPA3). Regularly update firmware on both the camera and NVR to patch vulnerabilities and protect against unauthorized access.