Featured image for how to add cctv camera in nvr
Image source: i.pinimg.com
Adding a CCTV camera to your NVR in 2026 is faster and easier than ever, thanks to plug-and-play compatibility and intuitive mobile apps. Simply connect the camera to the same network as your NVR, power it on, and let auto-detection do the rest—no complex configurations needed. Within minutes, you’ll have real-time monitoring and secure cloud backups.
Key Takeaways
- Verify compatibility: Ensure your camera and NVR support the same protocol before setup.
- Use PoE switches: Simplify power and data with a single Ethernet cable connection.
- Access NVR menu: Navigate to camera settings and select “Add Camera” to begin.
- Scan for devices: Let the NVR auto-detect cameras on the same network.
- Secure connections: Enable encryption and strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Update firmware: Always install the latest NVR and camera firmware for optimal performance.
📑 Table of Contents
- How to Add CCTV Camera in NVR in 2026: A Complete Guide
- Understanding the Basics: CCTV Cameras and NVRs
- Pre-Installation Planning and Network Setup
- Physical Installation of CCTV Cameras
- Adding Cameras to the NVR: Step-by-Step Configuration
- Advanced Settings and Optimization
- Conclusion: Securing Your Future with a Smart Surveillance System
How to Add CCTV Camera in NVR in 2026: A Complete Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of home and business security, the integration of CCTV cameras with Network Video Recorders (NVRs) has become a cornerstone of modern surveillance systems. As we step into 2026, advancements in IP camera technology, AI-powered analytics, and cloud integration have made setting up a robust surveillance network easier than ever. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to secure your property or a business owner aiming to protect assets and personnel, knowing how to add CCTV cameras to an NVR is a critical skill. Gone are the days of complex coaxial cabling and analog systems—today’s IP-based solutions offer plug-and-play convenience, remote access, and crystal-clear video quality.
This step-by-step guide is designed to walk you through the entire process of adding CCTV cameras to your NVR, from initial planning to final configuration and testing. We’ll cover everything from understanding compatibility and network setup to troubleshooting common issues. By the end of this guide, you’ll not only know how to physically and digitally connect your cameras but also how to optimize your system for maximum performance, reliability, and scalability. Whether you’re adding a single camera or expanding a multi-camera network, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge to do it right—safely, efficiently, and with confidence.
Understanding the Basics: CCTV Cameras and NVRs
What Is an NVR and How Does It Work?
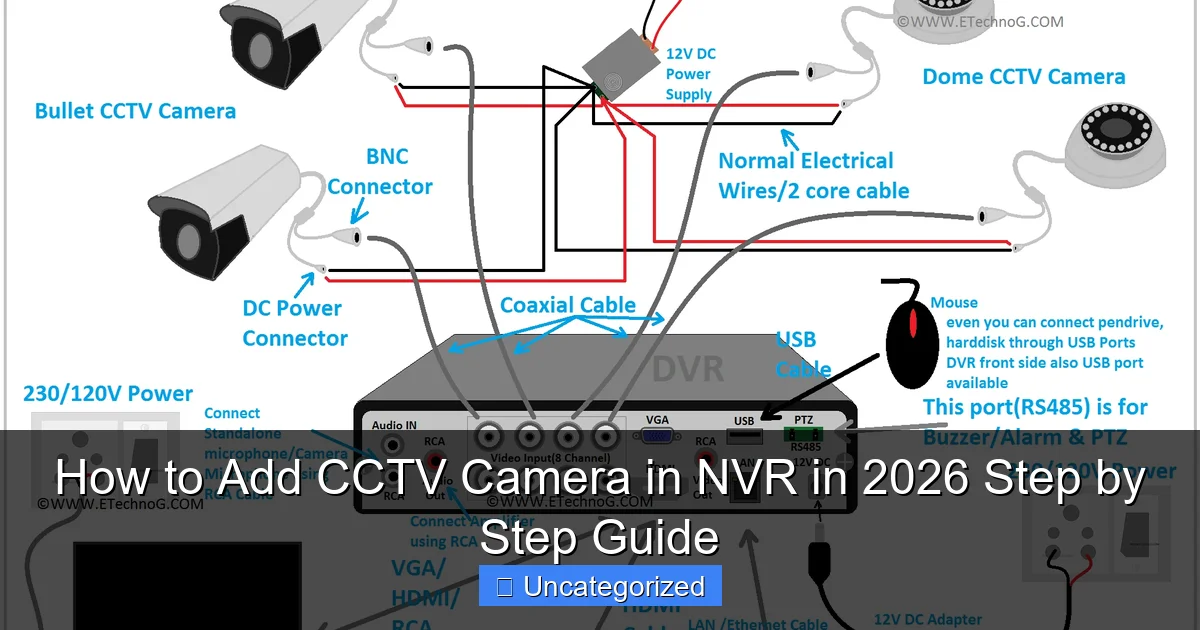
An NVR (Network Video Recorder) is a digital device that records and manages video streams from IP-based CCTV cameras. Unlike DVRs (Digital Video Recorders), which are designed for analog cameras and require coaxial cables, NVRs are built for networked IP cameras that transmit data over Ethernet or Wi-Fi. The NVR connects to your local network, receives video feeds from the cameras, stores them on internal or external hard drives, and allows you to access footage remotely via apps or web interfaces.
NVRs are typically more scalable and flexible than DVRs. They support higher-resolution cameras (up to 4K and beyond), offer better integration with smart home systems, and allow for advanced features like motion detection, facial recognition, and AI-based analytics. In 2026, most NVRs come with built-in PoE (Power over Ethernet) switches, reducing the need for separate power adapters and simplifying installation.
Types of CCTV Cameras Compatible with NVRs
When adding cameras to your NVR, it’s essential to choose the right type of camera based on your needs. The most common types include:
- Fixed Bullet Cameras: Ideal for monitoring specific areas like entrances or driveways. They offer a fixed field of view and are often weatherproof.
- Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Cameras: Allow remote control of direction and zoom. Great for large areas like parking lots or warehouses.
- Dome Cameras: Discreet and vandal-resistant, perfect for indoor and outdoor use in retail or office settings.
- Fisheye Cameras: Provide 360-degree panoramic views, ideal for open spaces like lobbies or conference rooms.
- Wireless IP Cameras: Connect via Wi-Fi, eliminating the need for Ethernet cables. Best for temporary setups or areas where cabling is difficult.
Tip: Always ensure your cameras are ONVIF-compliant (Open Network Video Interface Forum). This standard ensures interoperability between different brands, so you’re not locked into a single manufacturer. In 2026, over 95% of IP cameras support ONVIF Profile S and G, which cover basic and advanced video streaming and PTZ controls.
NVR and Camera Compatibility Checklist
Before purchasing or installing any equipment, verify the following:
- The NVR supports the camera’s resolution (e.g., 4K, 8MP, 12MP).
- The NVR has enough PoE ports for all cameras (if using PoE).
- The NVR firmware is up to date and supports the camera’s encoding (H.264, H.265, H.265+).
- The camera’s frame rate (e.g., 30fps) is supported by the NVR’s processing capacity.
- Both devices are ONVIF-compliant or from the same brand ecosystem (e.g., Hikvision, Dahua, Reolink).
Example: If you’re using a Hikvision DS-7608NI-I2 NVR, it supports up to 8 channels, 4K resolution, H.265+ encoding, and ONVIF Profile S. Pairing it with Hikvision DS-2CD2347G2-LSU/SL 4MP cameras ensures seamless integration.
Pre-Installation Planning and Network Setup
Assessing Your Surveillance Needs
Before adding any cameras, conduct a thorough site assessment. Identify key areas that require monitoring: entry/exit points, parking lots, server rooms, blind spots, etc. Sketch a layout of your property and mark camera positions. Consider:
- Field of View (FOV): Ensure cameras cover critical areas without overlapping unnecessarily.
- Lighting Conditions: Use IR night vision cameras for low-light areas and WDR (Wide Dynamic Range) for high-contrast scenes (e.g., backlit entrances).
- Weatherproofing: For outdoor cameras, ensure an IP66 or higher rating for dust and water resistance.
- Power and Data Access: Plan cable routes and power sources. PoE simplifies this by combining power and data in one cable.
Tip: Use tools like Hikvision’s iVMS-4200 or Reolink’s RLN8-410 software to simulate camera placement and test coverage before physical installation.
Setting Up Your Network Infrastructure
A stable, high-bandwidth network is crucial for smooth video streaming and remote access. Follow these steps:
- Upgrade Your Router: Use a Gigabit router (Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) to handle multiple high-resolution streams. Ensure it supports Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize video traffic.
- Use a Managed Switch (Optional but Recommended): For systems with 8+ cameras, a managed PoE switch (e.g., TP-Link TL-SG108PE) allows VLANs, QoS, and remote monitoring.
- Assign Static IPs: Configure your NVR and cameras with static IP addresses to prevent connection drops. Use your router’s DHCP reservation feature or set manually in the device settings.
- Enable Port Forwarding (for Remote Access): Open ports 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), and 554 (RTSP) on your router and forward them to the NVR’s IP. For security, use a non-standard port and enable HTTPS.
- Test Network Bandwidth: Use tools like iPerf to measure throughput. A 4K camera can use 8–16 Mbps per stream; ensure your upload speed exceeds the total camera bandwidth.
Example: For 6 x 4K cameras (12 Mbps each = 72 Mbps total), your internet upload speed should be at least 100 Mbps to allow for remote viewing and cloud backup.
Choosing the Right Cabling and Power Options
For wired systems, use Cat6 or Cat6a Ethernet cables for distances up to 100 meters. Cat6 supports 1 Gbps, while Cat6a handles 10 Gbps—ideal for future-proofing. For PoE, ensure cables are rated for PoE (e.g., 802.3af or 802.3at). For wireless cameras:
- Place them within 30–50 feet of the router or access point.
- Use Wi-Fi extenders or mesh networks for large properties.
- Test signal strength with tools like NetSpot or WiFi Analyzer.
Tip: Avoid daisy-chaining PoE switches. Use a central switch connected directly to the router for better performance and reliability.
Physical Installation of CCTV Cameras
Mounting Cameras Securely
Proper mounting ensures optimal coverage and durability. Follow these guidelines:
- Height: Mount cameras 8–10 feet high to prevent tampering but still capture facial details.
- Angle: Tilt cameras slightly downward (5–15 degrees) to reduce glare and improve visibility.
- Tools: Use a drill, level, and appropriate wall anchors. For outdoor installations, use stainless steel screws.
- Weatherproofing: Seal cable entries with silicone or conduit. Use junction boxes for exposed connections.
Example: For a bullet camera at a front gate, mount it on a corner wall at a 10-degree downward tilt, ensuring it covers the driveway and entrance without obstructions.
Connecting Cameras to the NVR
For wired PoE cameras:
- Run Ethernet cables from the NVR’s PoE ports to each camera.
- Plug one end into the NVR’s PoE port and the other into the camera’s Ethernet port.
- The NVR will automatically power the camera and establish a data connection.
For non-PoE cameras or wireless setups:
- Connect the camera to a separate PoE injector or power adapter.
- Link the camera to the network via Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Ensure the camera and NVR are on the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.1.x).
Tip: Label each cable at both ends (e.g., “Front Door – Camera 1”) for easy troubleshooting.
Testing Camera Functionality
After installation, power on the NVR and cameras. Check:
- Power LED: Should be solid or blinking (indicates power and network activity).
- Video Feed: Access the NVR’s local interface (via HDMI) or web app to verify the camera appears.
- Focus and Zoom: Adjust manually or via PTZ controls to ensure clarity.
- Night Vision: Cover the camera’s IR sensor to test auto-switch to night mode.
If a camera doesn’t appear, check cable connections, PoE status, and IP conflicts using the NVR’s network tools.
Adding Cameras to the NVR: Step-by-Step Configuration
Accessing the NVR Interface
There are three primary ways to access your NVR:
- Local Display: Connect a monitor and keyboard directly to the NVR via HDMI and USB.
- Web Browser: Enter the NVR’s IP address in a browser (e.g.,
https://192.168.1.100). Log in with admin credentials. - Mobile App: Use the manufacturer’s app (e.g., Hik-Connect, Reolink App) to scan the NVR’s QR code or enter IP manually.
Tip: Always change the default password and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for security.
Automatic Camera Discovery and Addition
Most modern NVRs support automatic discovery:
- Log in to the NVR interface.
- Navigate to Camera > Add Camera or Device Management > Search.
- The NVR will scan the local network for connected cameras.
- Select the cameras you want to add and click Add.
- The NVR will assign IP addresses (if not static) and begin streaming.
Example: On a Dahua NVR, go to Camera > IP Camera > Add, click Search, and select the desired cameras. Click Add to finalize.
Manual Camera Addition (For Non-ONVIF or Wireless Cameras)
If automatic discovery fails, add cameras manually:
- In the NVR interface, go to Camera > Manual Add.
- Enter the camera’s IP address, port (usually 80 or 8000), username, and password.
- Select the correct protocol (ONVIF, RTSP, or manufacturer-specific).
- Set the stream type (Main Stream for recording, Sub Stream for preview).
- Click Add and verify the video feed.
Tip: For RTSP streams, use the camera’s RTSP URL (e.g., rtsp://192.168.1.200:554/stream1).
Configuring Recording and Storage Settings
Once cameras are added, configure recording:
- Continuous Recording: Records 24/7. Requires large storage (e.g., 8TB for 10 days of 4K footage).
- Motion Detection Recording: Saves only when motion is detected. Reduces storage needs and speeds up playback.
- Schedule Recording: Set time-based rules (e.g., record only during business hours).
Storage Calculation Example:
| Camera Resolution | Bitrate (Mbps) | Storage per Day (GB) | Storage for 7 Days (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1080p (2MP) | 4 | 43.2 | 302.4 |
| 4K (8MP) | 12 | 129.6 | 907.2 |
| 5MP (3K) | 6 | 64.8 | 453.6 |
Use the formula: Storage (GB) = (Bitrate Mbps × 3600 × 24) / (8 × 1024).
Advanced Settings and Optimization
Enabling AI and Smart Features
In 2026, AI-powered features are standard. Enable:
- Motion Zones: Define areas where motion should trigger alerts (e.g., ignore trees but detect people).
- Face Recognition: Identify authorized personnel or flag unknown individuals.
- Vehicle Detection: Track cars in parking lots or driveways.
- Line Crossing: Alert when someone crosses a virtual line (e.g., perimeter breach).
Tip: Train AI models with sample footage for better accuracy. For example, upload images of delivery personnel to reduce false alerts.
Remote Access and Cloud Integration
Enable remote viewing via:
- P2P (Peer-to-Peer): Use the manufacturer’s app with a cloud account (e.g., Hik-Connect ID). No port forwarding needed.
- DDNS (Dynamic DNS): Set up a free DDNS service (e.g., No-IP) to access your NVR using a domain name.
- Cloud Storage: Subscribe to cloud plans (e.g., Reolink Cloud) for offsite backup and AI analysis.
Example: On a Reolink NVR, go to Settings > Network > P2P, enable P2P, and scan the QR code in the Reolink app to link your account.
System Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance ensures reliability:
- Update Firmware: Check for NVR and camera updates monthly.
- Clean Storage: Set automatic overwrite (e.g., keep 30 days of footage).
- Test Backups: Schedule weekly cloud or USB backups.
- Monitor Logs: Check system logs for errors or unauthorized access attempts.
Tip: Create a maintenance checklist and schedule reminders in your calendar.
Conclusion: Securing Your Future with a Smart Surveillance System
Adding CCTV cameras to an NVR in 2026 is no longer a complex, technical endeavor reserved for IT professionals. With intuitive interfaces, plug-and-play PoE technology, and AI-driven features, even beginners can build a powerful, scalable surveillance system. This guide has walked you through every critical step—from understanding camera types and network requirements to physical installation, configuration, and advanced optimization. By following these best practices, you’ll not only enhance the security of your property but also gain peace of mind knowing your system is future-ready.
Remember, the key to a successful setup lies in planning, compatibility, and maintenance. Invest in high-quality, ONVIF-compliant hardware, optimize your network for video traffic, and leverage AI to reduce false alarms and improve response times. Whether you’re securing a small home or a large enterprise, a well-configured NVR system is your first line of defense against threats. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive will ensure your surveillance network remains effective, efficient, and ahead of the curve.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I add a CCTV camera to my NVR for the first time?
To add a CCTV camera to your NVR, connect the camera to the same network as the NVR, then use the NVR’s interface to scan and auto-detect the camera. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the setup process in minutes.
Can I add an IP camera to an NVR without using a PoE switch?
Yes, you can add an IP camera to an NVR without a PoE switch by using a separate power adapter for the camera and connecting both devices via a router or network switch. Ensure the camera and NVR are on the same subnet for discovery.
How to add a wireless CCTV camera to an NVR in 2026?
For wireless cameras, connect the NVR and camera to the same Wi-Fi network, then use the NVR’s “Add Camera” wizard to locate and authenticate the camera. Most modern NVRs support plug-and-play setup for Wi-Fi-enabled models.
Why isn’t my NVR detecting the CCTV camera during setup?
If your NVR isn’t detecting the camera, check network connectivity, IP address conflicts, and firewall settings. Ensure the camera’s firmware is updated and compatible with your NVR model for seamless integration.
How to add an analog CCTV camera to an NVR?
Analog cameras require a coax cable connection to a hybrid NVR or a video encoder. Connect the camera to the NVR’s BNC port (or encoder), then use the NVR interface to enable analog channel support and configure video settings.
Do I need to manually add each CCTV camera in the NVR settings?
Most modern NVRs auto-discover cameras on the network, but manual addition is possible if needed. Enter the camera’s IP address, username, and password in the NVR’s “Camera Management” menu to complete the process.