Featured image for how to add ip camera in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Adding an IP camera to your NVR in 2026 is faster and easier than ever, thanks to plug-and-play compatibility and intuitive mobile apps. Simply connect the camera to the same network as your NVR, scan the QR code, and auto-sync within seconds—no manual IP configuration needed. This streamlined process ensures secure, high-resolution surveillance with minimal setup time.
Key Takeaways
- Verify compatibility: Ensure your IP camera and NVR support the same protocols (e.g., ONVIF).
- Use PoE switches: Simplify setup by powering cameras and transmitting data via one cable.
- Access NVR interface: Navigate to the camera management section to begin adding devices.
- Scan for cameras: Let the NVR auto-detect IP cameras on the same network segment.
- Manually add if needed: Enter camera IP, port, and credentials if auto-discovery fails.
- Update firmware: Keep NVR and camera firmware current to avoid compatibility issues.
- Test live view: Confirm camera feed appears and adjust settings like resolution or motion detection.
📑 Table of Contents
- Why Adding IP Cameras to Your NVR Matters in 2026
- Understanding the Basics: IP Cameras vs. NVRs and Compatibility
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Add IP Camera in NVR
- Advanced Configuration: Optimizing Performance and Security
- Common Troubleshooting: Solving Connection and Quality Issues
- Data Table: Recommended NVR and IP Camera Combinations (2026)
- Conclusion: Building a Future-Proof Surveillance System
Why Adding IP Cameras to Your NVR Matters in 2026
In today’s rapidly evolving security landscape, integrating IP cameras into Network Video Recorders (NVRs) is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re securing a small retail shop, monitoring a large corporate campus, or simply keeping an eye on your home, the flexibility, scalability, and high-definition clarity of IP camera systems make them the go-to solution in 2026. Unlike traditional analog systems, IP cameras transmit digital video over a network, offering superior image quality, remote access, and advanced analytics like facial recognition, motion detection, and license plate reading. But the real power lies in how these cameras communicate with your NVR—centralized storage and management that transforms raw video into actionable intelligence.
However, despite their advantages, many users—both homeowners and IT professionals—struggle with the initial setup. The process of how to add IP camera in NVR can seem daunting, especially with the growing complexity of network configurations, cybersecurity threats, and diverse camera brands. This comprehensive guide cuts through the confusion. We’ll walk you through every step, from choosing compatible hardware to troubleshooting common pitfalls, ensuring your system is up and running efficiently, securely, and with minimal downtime. By the end, you’ll have a fully functional, high-performance surveillance system tailored to your needs.
Understanding the Basics: IP Cameras vs. NVRs and Compatibility
What Is an IP Camera?
An IP camera (Internet Protocol camera) is a digital video camera that sends and receives data via a network connection, typically using Ethernet or Wi-Fi. Unlike analog CCTV cameras, which rely on coaxial cables and DVRs, IP cameras capture high-resolution video (ranging from 2MP to 12MP or more in 2026), support Power over Ethernet (PoE), and can be accessed remotely via web browsers or mobile apps. Modern IP cameras often include features like:

Visual guide about how to add ip camera in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
- Wide dynamic range (WDR) for low-light and backlit scenes
- AI-powered motion detection and object classification
- Two-way audio and built-in microphones
- Onboard storage (microSD) as a backup
For example, the Hikvision DS-2CD2143G0-I is a popular 4MP dome camera with PoE, night vision, and H.265+ compression—ideal for indoor and outdoor use.
What Is an NVR and Why Use It?
A Network Video Recorder (NVR) is a software-based system that records video footage from IP cameras. Unlike a DVR (Digital Video Recorder), which processes analog signals, an NVR works with digital streams over a network. The NVR handles:
- Video encoding and compression (H.264, H.265, H.265+)
- Storage management (RAID, NAS, or local hard drives)
- Remote access and live viewing
- Motion-triggered alerts and event-based recording
For instance, the Synology Surveillance Station or Reolink RLN8-410 are NVRs that support up to 8 or 16 channels, respectively, with intuitive interfaces and cloud integration.
Ensuring Compatibility Between IP Cameras and NVRs
One of the most critical steps in learning how to add IP camera in NVR is verifying compatibility. Not all IP cameras work with every NVR. Here are key factors to consider:
- ONVIF Conformance: Look for ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) certification. This global standard ensures interoperability between brands. For example, a Dahua NVR can often support Axis or Bosch IP cameras if both are ONVIF Profile S or G compliant.
- RTSP Support: Real-Time Streaming Protocol allows manual camera integration when ONVIF isn’t available. You’ll need the camera’s RTSP URL (e.g.,
rtsp://192.168.1.100:554/stream1). - Resolution and Bandwidth: Ensure your NVR can handle the camera’s resolution and bitrate. A 4K camera (3840×2160) may require 8–12 Mbps per stream, while 1080p uses 2–4 Mbps.
- Firmware Updates: Always update both camera and NVR firmware to the latest version to avoid bugs and security vulnerabilities.
Pro Tip: Use the ONVIF Device Manager (free software) to scan your network and verify ONVIF compatibility before purchasing.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Add IP Camera in NVR
Step 1: Physical and Network Setup
Before adding a camera, ensure your network infrastructure supports it:

Visual guide about how to add ip camera in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
- Connect the IP Camera: Use an Ethernet cable (Cat 5e or Cat 6) to connect the camera to your PoE switch or injector. If using Wi-Fi, ensure strong signal strength (minimum -65 dBm).
- Power the Camera: Most IP cameras use PoE (802.3af/at), eliminating the need for separate power cables. For non-PoE cameras, use a 12V/24V adapter.
- Connect NVR to Network: Link your NVR to the same network as the camera via Ethernet. Avoid Wi-Fi for the NVR to ensure stable, high-bandwidth recording.
- Assign Static IP (Optional): Assign static IPs to both camera and NVR (e.g., 192.168.1.100 for camera, 192.168.1.200 for NVR) to prevent IP conflicts.
Example: In a home setup, connect a Reolink RLC-820A (PoE) to a PoE switch (TP-Link TL-SG108PE), then link the switch to your router and NVR (Reolink RLN8-410).
Step 2: Access the NVR Interface
Power on the NVR and connect it to a monitor via HDMI/VGA. Log in using the default credentials (often admin/admin or admin/password). Change the password immediately for security.
- Web Interface: Access via browser using the NVR’s IP address (e.g.,
http://192.168.1.200). - Mobile App: Install the manufacturer’s app (e.g., Hik-Connect, Reolink App) and scan the NVR’s QR code.
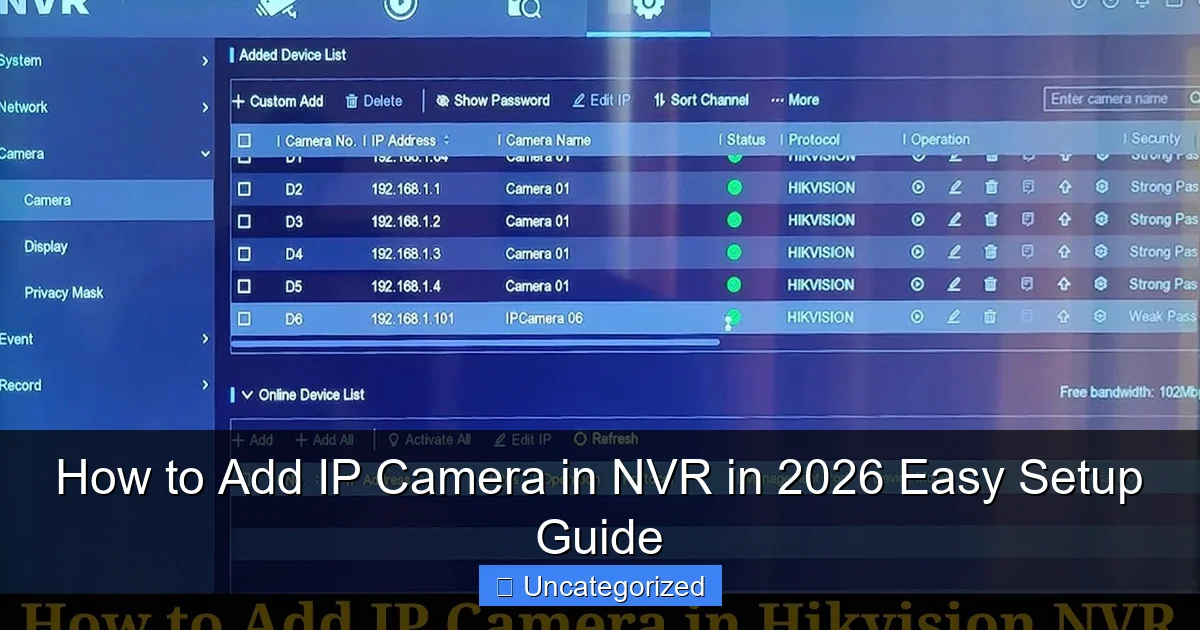
Step 3: Discover and Add the Camera
Most NVRs offer automatic camera discovery:
- Navigate to Camera Management or Channel Settings.
- Click Auto Search or Scan. The NVR will list all ONVIF-compliant cameras on the network.
- Select the camera(s) and click Add.
- Enter the camera’s username and password (default is often
admin/123456).
Tip: If the camera isn’t detected, verify:
- The camera is powered and connected.
- The camera and NVR are on the same subnet.
- Firewalls aren’t blocking ONVIF ports (typically 80, 554, 8000).
Step 4: Manual Camera Addition (When Auto-Fail)
If auto-discovery fails, add the camera manually:
- Obtain the camera’s IP address (via router DHCP list or IP scanner like Angry IP Scanner).
- In the NVR, go to Manual Add and enter:
- IP Address: e.g., 192.168.1.100
- Port: Usually 80 (HTTP) or 8899 (RTSP)
- Protocol: ONVIF or RTSP
- Stream Type: Main (high-res) or Sub (low-res for monitoring)
- Enter credentials and click Connect.
Example: To add a non-ONVIF camera via RTSP:
rtsp://192.168.1.100:554/user=admin_password=123456_channel=1_stream=0.sdp
Step 5: Configure Video and Recording Settings
After adding the camera:
- Set Resolution and Frame Rate: Balance quality and storage. For 24/7 recording, use 1080p at 15 fps. For motion-only, 4K at 10 fps.
- Enable Motion Detection: Define detection zones to reduce false alarms (e.g., ignore trees swaying).
- Schedule Recording: Use continuous, motion-triggered, or event-based schedules.
- Adjust Bitrate: Lower bitrate (e.g., 2048 kbps) saves space; higher (e.g., 4096 kbps) improves clarity.
Advanced Configuration: Optimizing Performance and Security
Bandwidth and Storage Management
High-resolution cameras consume significant bandwidth and storage. Optimize with:
- Dual-Stream Technology: Use the main stream (high-res) for recording and the sub-stream (low-res) for live monitoring.
- Compression: Use H.265+ instead of H.264 to reduce file size by 50% without quality loss.
- Storage Calculation: Use online calculators (e.g., Hikvision Storage Calculator) to estimate HDD needs. For example:
Example Calculation:
- 4K Camera (8 MP) at 30 fps, H.265: ~12 Mbps
- 8 Cameras × 12 Mbps = 96 Mbps total
- Daily storage: (96 Mbps × 86400 seconds) / 8 = 103.68 GB/day
- 30-day retention: 103.68 × 30 = 3.11 TB → Use 4TB HDD
Cybersecurity Best Practices
IP cameras are vulnerable to hacking. Protect your system:
- Change Default Credentials: Never use
admin/123456. Use strong, unique passwords. - Enable HTTPS/SSL: Encrypt data between camera and NVR.
- Update Firmware: Patch vulnerabilities. For example, a 2025 exploit in Dahua cameras allowed remote code execution—fixed in firmware v2.7.1.
- Isolate the Surveillance Network: Use a VLAN or separate subnet to prevent lateral movement if breached.
- Disable UPnP: Universal Plug and Play can expose cameras to the internet.
Pro Tip: Use a firewall (e.g., pfSense) to block inbound traffic to camera IPs unless from the NVR.
Remote Access and Mobile Integration
Access your cameras from anywhere:
- Port Forwarding: Forward ports (e.g., 8000 for Hikvision) in your router. Caution: Risky without SSL.
- Cloud Services: Use manufacturer cloud (e.g., Hik-Connect Cloud, Reolink Cloud) for encrypted remote access.
- DDNS: Set up Dynamic DNS (e.g., No-IP) if you have a dynamic public IP.
Common Troubleshooting: Solving Connection and Quality Issues
Camera Not Detected
- Check Network: Ping the camera’s IP. If unreachable, verify cables, PoE, and switch.
- Verify Subnet: Ensure camera and NVR are on the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.1.x).
- Disable Firewall: Temporarily disable Windows Firewall or router firewall to test.
Blurry or Pixelated Video
- Adjust Focus: Use the camera’s web interface to focus manually.
- Check Bitrate: Increase bitrate if compression artifacts appear.
- Clean Lens: Smudges or dirt degrade image quality.
Playback or Recording Failures
- HDD Health: Use S.M.A.R.T. tools to check for failing drives.
- Storage Full: Set overwrite mode to delete oldest footage when full.
- Firmware Bugs: Update NVR firmware—some 2025 models had recording glitches fixed in v3.2.0.
Audio Issues (If Supported)
- Enable Audio Stream: In camera settings, ensure audio is enabled.
- Check Cables: For external microphones, verify 3.5mm jack connections.
Data Table: Recommended NVR and IP Camera Combinations (2026)
| NVR Model | Max Channels | Max Resolution | ONVIF Support | Recommended IP Cameras | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reolink RLN8-410 | 8 | 4K | Profile S | Reolink RLC-820A, Dahua IPC-HDW5442TM | Small homes/retail |
| Hikvision DS-7608NI-I2 | 8 | 12MP | Profile S/G | Hikvision DS-2CD2387G2-L, Axis Q1656 | Large businesses |
| Synology Surveillance Station | 16 | 8K | Profile S/G | Bosch NBN-73023BA, Axis M3066 | Enterprise/IT |
| Amcrest NV4108E-HS | 8 | 5MP | Profile S | Amcrest IP8M-2496EW, Lorex LNE8962AB | Budget setups |
Conclusion: Building a Future-Proof Surveillance System
Mastering how to add IP camera in NVR in 2026 is about more than just plug-and-play setup. It’s about creating a robust, secure, and scalable surveillance ecosystem. From verifying ONVIF compatibility to optimizing bandwidth and hardening cybersecurity, each step ensures your system performs reliably—whether you’re monitoring a single room or an entire facility. The integration of AI, cloud access, and high-resolution imaging in modern IP cameras and NVRs makes this technology more powerful than ever, but it also demands careful planning and maintenance.
Remember: Compatibility, configuration, and security are the three pillars of a successful setup. Start with a clear plan, document your network topology, and always prioritize firmware updates and strong passwords. With this guide, you’re equipped to handle everything from basic installations to advanced troubleshooting. As surveillance technology continues to evolve—think 8K cameras, edge AI processing, and blockchain-based data integrity—the fundamentals you’ve learned here will remain your foundation. Now go build a smarter, safer environment with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I add an IP camera to my NVR for the first time?
To add an IP camera to your NVR, connect both devices to the same network, then use the NVR’s camera management menu to search for and add the camera. Most modern NVRs auto-detect compatible IP cameras on the network in 2026.
Why can’t my NVR detect my IP camera during setup?
This often happens due to network segmentation or incompatible protocols. Ensure both devices are on the same subnet, and verify the camera’s ONVIF or RTSP compatibility with your NVR’s specifications.
How to add an IP camera in NVR manually using its IP address?
Access your NVR’s camera settings, select “Manual Add,” then enter the camera’s IP address, port, username, and password. This method works when auto-discovery fails or for cross-brand setups.
Can I add wireless IP cameras to a wired NVR system?
Yes, as long as the wireless camera connects to the same network as the NVR. Configure the camera’s Wi-Fi settings first, then add it to the NVR via auto-discovery or manual entry.
What are the steps to add multiple IP cameras to one NVR?
Connect all cameras to the same network, then batch-add them through the NVR’s “Multi-Add” or “Auto-Scan” feature. Assign unique channels and adjust bandwidth settings to avoid network congestion.
Do I need to update firmware before adding IP cameras to my NVR?
Yes, outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues. Check your NVR manufacturer’s website for 2026 updates, as newer firmware often includes improved IP camera support and security patches.