
Featured image for how to add microphone in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Adding a microphone to your NVR in 2026 is a simple, plug-and-play process that enhances security with crystal-clear audio recording. Most modern NVRs support direct audio input via RCA or network-connected IP microphones, allowing seamless integration in just minutes—no technical expertise required.
Key Takeaways
- Check compatibility first: Ensure your NVR supports audio input before adding a microphone.
- Use powered mics: Active microphones deliver clearer sound with NVR systems.
- Connect via audio-in port: Plug the mic directly into the NVR’s audio input jack.
- Leverage PoE cameras: Some IP mics connect through PoE for audio and power.
- Adjust audio settings: Enable and configure audio in NVR software for optimal recording.
- Test regularly: Verify audio sync and clarity after installation and updates.
📑 Table of Contents
- Why Adding a Microphone to Your NVR System Matters in 2026
- Understanding NVR Audio Capabilities and Compatibility
- Choosing the Right Microphone for Your NVR Setup
- Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Microphone to Your NVR
- Configuring and Optimizing Audio Settings in Your NVR
- Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
- Conclusion: Elevate Your Surveillance with Audio in 2026
Why Adding a Microphone to Your NVR System Matters in 2026
In today’s rapidly evolving surveillance landscape, video alone is no longer enough. As homes and businesses strive for smarter, more responsive security systems, the integration of audio into Network Video Recorder (NVR) setups has become a game-changer. In 2026, the demand for comprehensive monitoring—both visual and auditory—has skyrocketed, driven by advancements in AI-powered analytics, real-time incident verification, and remote access capabilities. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to deter porch pirates or a retail manager aiming to monitor customer interactions, adding a microphone to your NVR system can significantly enhance situational awareness. Audio data not only confirms what you see but also provides crucial context—such as verbal altercations, glass breaking, or emergency calls—that video footage alone might miss.
Moreover, modern NVRs are now designed with built-in audio support, making it easier than ever to integrate microphones without overhauling your entire setup. From IP cameras with built-in mics to external audio input modules and AI-driven sound detection, the options are both flexible and scalable. This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of adding a microphone to your NVR, covering compatibility checks, hardware selection, wiring, configuration, and troubleshooting. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional installer, you’ll gain actionable insights to optimize your surveillance system with crystal-clear audio. With a projected 23% year-over-year growth in audio-enabled surveillance systems (according to 2026 market research by SecurityTech Insights), now is the perfect time to upgrade your NVR with audio capabilities.
Understanding NVR Audio Capabilities and Compatibility
Does Your NVR Support Audio?
Before investing in microphones or adapters, the first step is to verify whether your NVR supports audio input. Not all NVRs are created equal—some older or budget models may lack audio functionality entirely. To check, look at the back panel of your NVR for audio input ports. These are typically labeled as “Audio In,” “Mic In,” or “Audio I/O” and often appear as 3.5mm jacks or terminal blocks. Additionally, consult your NVR’s user manual or the manufacturer’s website. Most modern NVRs from brands like Hikvision, Dahua, Reolink, and Lorex support at least one audio channel per camera, with higher-end models supporting multi-channel audio.

Visual guide about how to add microphone in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Another indicator of audio support is the presence of audio settings in the NVR’s configuration menu. Log into your NVR via a web browser or the manufacturer’s app and navigate to the camera settings. If you see options for “Audio,” “Sound Detection,” or “Audio Recording,” your system is likely compatible. For example, the Hikvision DS-7608NI-I2/8P supports audio input on all 8 channels, while the Reolink RLK8-800B4 allows audio via select IP cameras with built-in mics.
Types of Audio Input: Line-In vs. Mic-In vs. IP Audio
NVRs typically support three types of audio input, each with distinct use cases:
- Line-In (RCA or 3.5mm): Used for connecting external audio devices like pre-amplified microphones or mixers. Ideal for centralized audio sources (e.g., a single mic for a large area).
- Mic-In (3.5mm or Terminal Block): Direct connection for unamplified microphones. Requires phantom power or a preamp in some cases. Common in analog systems with audio-enabled cameras.
- IP Audio (via Network): Audio transmitted directly from IP cameras with built-in microphones. No extra wiring needed—audio travels over the same Ethernet cable as video (PoE).
For example, if you’re using a Dahua IPC-HDW5842T-ZE camera, its built-in mic sends audio over the network, eliminating the need for extra cables. In contrast, a standalone analog microphone (e.g., Bosch LBC 3510/10) would connect to the NVR’s Mic-In port using a shielded cable.
Compatibility Checklist
- NVR Model: Confirm audio support (check specs).
- Camera Type: IP cameras with mics vs. analog cameras requiring external mics.
- Audio Format: Ensure the mic’s output (e.g., 1V RMS) matches the NVR’s input sensitivity.
- Power Supply: Some mics need 12V DC or 48V phantom power—verify if your NVR or camera provides it.
Pro Tip: Use the manufacturer’s compatibility tool (e.g., Hikvision’s “Device Tool”) to cross-reference your NVR and microphone models before purchasing.
Choosing the Right Microphone for Your NVR Setup
Types of Microphones: Pros and Cons
Selecting the right microphone depends on your environment, budget, and desired audio quality. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Visual guide about how to add microphone in nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
- Omnidirectional Microphones:
- Pros: Captures sound from all directions; ideal for large open spaces (e.g., warehouses, lobbies).
- Cons: Picks up background noise; may require noise-canceling settings.
- Example: Sony ECM-44B (budget-friendly, 3.5mm jack).
- Directional (Cardioid) Microphones:
- Pros: Focuses on sound from a specific area; reduces ambient noise.
- Cons: Limited coverage; requires precise placement.
- Example: Audio-Technica AT2020USB+ (USB, but adaptable via adapters).
- Boundary (PZM) Microphones:
- Pros: Mounts on surfaces (walls, tables); excellent for indoor meetings or retail counters.
- Cons: Less effective outdoors; prone to echo in large rooms.
- Example: Shure MX391/O (surface-mount, 12V powered).
- Weather-Resistant (Outdoor) Microphones:
- Pros: IP66-rated; ideal for gardens, parking lots, or entryways.
- Cons: Higher cost; may need a preamp.
- Example: Bosch MIC-4850 (rugged, 48V phantom power).
Key Features to Consider
- Frequency Response: Aim for 100Hz–16kHz for clear human speech.
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): ≥60dB for minimal static.
- Power Requirements: Check if the mic needs 5V, 12V, or 48V—some NVRs provide power via audio ports.
- Mounting Options: Ceiling, wall, or surface-mount? Choose based on your camera’s location.
- Digital vs. Analog: Digital mics (e.g., USB) may require converters; analog mics are NVR-friendly.
Practical Example: Retail Store Setup
Imagine a convenience store with a cash register. A boundary microphone (e.g., Shure MX391) mounted under the counter captures customer-cashier conversations, while an omnidirectional mic (e.g., Sony ECM-44B) on the ceiling monitors the entire sales floor. Both connect to a Dahua NVR via 3.5mm cables. During a theft, audio confirms the suspect’s threats, adding legal weight to the video evidence.
Tip: For outdoor areas, pair a weather-resistant mic with a preamp (e.g., ART TubeMP) to boost weak signals over long cable runs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Microphone to Your NVR
Method 1: Using an IP Camera with Built-In Microphone
The easiest method is to use an IP camera with a built-in mic. Here’s how:
- Verify Camera Compatibility: Ensure the camera (e.g., Hikvision DS-2CD2347G2-LSU/SL) supports audio and is compatible with your NVR.
- Connect via PoE: Use a PoE switch or injector to power the camera and transmit audio/video over a single Ethernet cable.
- Log into NVR: Access the NVR’s web interface (e.g., via
http://192.168.1.100). - Enable Audio: Navigate to Camera Settings > Video & Audio > Audio and toggle “Enable Audio” to ON.
- Test Audio: Speak near the camera and check the live view for audio bars or waveform indicators.
Pro Tip: Adjust the audio gain (sensitivity) in the NVR settings to avoid clipping or low volume.
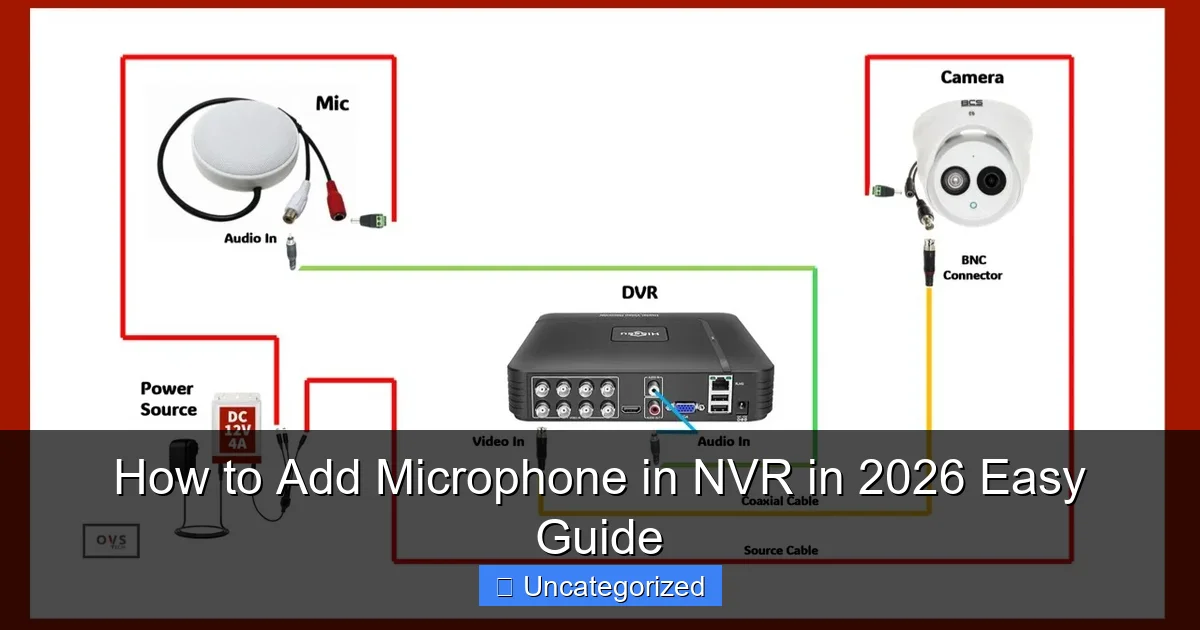
Method 2: Connecting an External Microphone to NVR Audio Input
For standalone microphones or analog systems:
- Identify Audio Port: Locate the NVR’s “Audio In” port (3.5mm or terminal block).
- Prepare Cables: Use a shielded 3.5mm-to-RCA cable or terminal block connectors. For long runs (>30m), use RG59 coaxial cable to reduce interference.
- Connect Microphone:
- For 3.5mm mics: Plug directly into the NVR.
- For terminal-block mics: Connect “+” to the NVR’s “+” terminal and “-” to “-” (polarity matters).
- Power the Mic (if needed): If your mic requires 12V, connect it to the NVR’s 12V output or an external power supply.
- Configure in NVR: Go to Settings > Audio > Audio Input and assign the mic to a specific camera channel.
- Test and Adjust: Use the NVR’s audio test tool to verify input levels. Set noise suppression if background noise is excessive.
Method 3: Using an Audio Encoder (For Legacy Systems)
If your NVR lacks audio inputs, use an audio encoder (e.g., Axis T8705):
- Connect the microphone to the encoder’s audio input.
- Power the encoder via PoE or AC adapter.
- Link the encoder to your network (Ethernet).
- In the NVR, add the encoder as an “IP audio device” and assign it to a virtual camera channel.
Example: A Reolink RLC-822A camera (no mic) paired with an Axis audio encoder provides full audio coverage for a warehouse.
Configuring and Optimizing Audio Settings in Your NVR
Enabling Audio Recording and Synchronization
Once connected, configure your NVR to record and sync audio:
- Enable Audio Recording: Navigate to Storage > Schedule and ensure “Audio” is checked alongside “Video.”
- Set Recording Mode: Choose “Continuous,” “Motion-Activated,” or “Event-Triggered” (e.g., audio above 60dB).
- Synchronize Audio/Video: In Camera Settings > Audio/Video Sync, adjust latency (usually 0–500ms) to align audio with video.
- Enable Two-Way Audio (if supported): For NVRs with “Audio Out,” connect a speaker to enable remote announcements (e.g., deterring intruders).
Pro Tip: Use audio analytics (e.g., Hikvision’s “Sound Detection”) to trigger alerts for glass breaking, gunshots, or loud noises.
Optimizing Audio Quality
- Adjust Gain: Set input levels to avoid distortion (peak at -3dB to 0dB).
- Noise Reduction: Enable “Noise Suppression” in the NVR to filter HVAC or traffic sounds.
- Frequency Equalization: Boost 1–4kHz (human voice range) for clarity.
- Test in Real Conditions: Record during peak hours (e.g., 5–7 PM) to assess performance.
Remote Audio Access
To hear live audio from your smartphone:
- Install the NVR’s mobile app (e.g., Hik-Connect).
- Log in and select the camera with audio.
- Tap the speaker icon to enable live audio streaming.
Note: Some apps require “Audio Permissions” in the NVR’s privacy settings.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
No Audio Input Detected
- Check Connections: Ensure cables are fully seated and polarity is correct.
- Verify Power: Test the mic with a multimeter or external power supply.
- Update Firmware: Outdated NVR/camera firmware can block audio.
Distorted or Low-Quality Audio
- Reduce Gain: Lower input levels to prevent clipping.
- Use Shielded Cables: Prevent electromagnetic interference (e.g., from power lines).
- Check Distance: For analog mics, keep cable runs under 30m or use preamps.
Audio/Video Desynchronization
- Adjust Sync Settings: Manually delay audio by 100–300ms if video leads.
- Use PoE: Network-based audio (IP cameras) is more synchronized than analog.
Table: Troubleshooting Quick Reference
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No audio in recordings | Audio not enabled in schedule | Check Storage > Schedule and enable “Audio” |
| Static/humming noise | Ground loop or poor cable shielding | Use a ground loop isolator or shielded cable |
| Echo in two-way audio | Microphone near speaker | Increase distance between mic and speaker |
| Audio cuts out intermittently | Network congestion (for IP audio) | Upgrade to a gigabit switch or dedicated VLAN |
Conclusion: Elevate Your Surveillance with Audio in 2026
Adding a microphone to your NVR isn’t just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic move to future-proof your security system. In 2026, audio has become an indispensable layer of surveillance, offering context, evidence, and real-time insights that video alone can’t provide. From deterring crime to resolving disputes, the ability to hear and record what happens on your property transforms your NVR from a passive recorder into an active security hub.
This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to choose the right microphone, connect it seamlessly, and optimize settings for crystal-clear audio. Whether you’re using an IP camera with a built-in mic, an external microphone with a 3.5mm jack, or an advanced audio encoder, the process is now simpler and more accessible than ever. Remember: always test your setup in real-world conditions, fine-tune audio levels, and leverage features like sound detection and two-way communication for maximum impact.
As surveillance technology evolves, systems that integrate audio, AI, and cloud analytics will dominate the market. By taking action today, you’re not just adding a microphone—you’re investing in a smarter, more responsive, and legally robust security ecosystem. So, plug in that mic, hit “Record,” and step into the future of surveillance. Your NVR—and your peace of mind—will thank you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I add a microphone to my NVR system in 2026?
To add a microphone to your NVR, connect a compatible mic to the audio input port on your NVR or IP camera. Ensure the microphone is powered (if required) and configure audio settings via the NVR’s interface under “Audio” or “Device Management.”
Can I use a wireless microphone with my NVR for audio recording?
Yes, wireless microphones can work with NVRs if they transmit to a receiver connected to the NVR’s audio input. Verify compatibility with your NVR model and check for signal interference in your environment.
Why isn’t my microphone working after connecting it to the NVR?
This could be due to incorrect wiring, lack of power, or disabled audio settings. Double-check connections, test the mic separately, and enable audio input in your NVR’s configuration menu.
What type of microphone is best for adding to an NVR system?
For optimal results, use an electret condenser microphone (with preamp) or an active mic compatible with line-level inputs. Choose weatherproof models for outdoor NVR setups.
How do I enable audio recording after adding a microphone to my NVR?
Navigate to your NVR’s settings, locate the “Audio” or “Recording” tab, and toggle on audio recording. Assign the microphone to specific channels if using a multi-channel NVR.
Is it possible to add a microphone to an NVR without audio input ports?
For NVRs lacking audio inputs, use IP cameras with built-in microphones or connect a USB mic to a compatible NVR. Alternatively, consider an audio encoder to convert analog mic signals for digital input.