
Featured image for how to add nvr to blue iris
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Integrating an NVR with Blue Iris in 2026 is faster and more reliable than ever, thanks to updated ONVIF support and streamlined network discovery. Simply add your NVR as an IP camera source in Blue Iris, authenticate, and map streams—no complex configurations needed for seamless multi-camera management.
Key Takeaways
- Verify compatibility: Ensure your NVR supports ONVIF or RTSP for seamless Blue Iris integration.
- Use static IPs: Assign fixed IP addresses to NVR and cameras to prevent connection drops.
- Add via camera tab: Navigate to Blue Iris’s Camera tab to add NVR-connected cameras individually.
- Optimize bandwidth: Adjust substream settings in Blue Iris to reduce network load from NVR feeds.
- Enable remote access: Configure port forwarding or cloud services for off-site NVR monitoring in Blue Iris.
- Regularly update firmware: Keep NVR and Blue Iris software current to fix bugs and improve stability.
📑 Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics: Why Integrate an NVR with Blue Iris?
- Preparing for Integration: Prerequisites and System Requirements
- Step-by-Step Guide: Adding NVR Cameras to Blue Iris
- Optimizing Performance: Bandwidth, Storage, and AI Features
- Troubleshooting Common Issues and Advanced Tips
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Understanding the Basics: Why Integrate an NVR with Blue Iris?
As surveillance technology continues to evolve, the demand for flexible, scalable, and powerful video management systems (VMS) has never been higher. Blue Iris, a leading Windows-based VMS, stands out for its robust features, real-time alerts, motion detection, and support for a vast array of IP cameras. However, as your security needs grow—whether for a large home, business, or multi-site operation—relying solely on direct camera connections can become unwieldy. This is where integrating a Network Video Recorder (NVR) with Blue Iris becomes a game-changer.
An NVR is a dedicated hardware device designed to record and manage IP camera feeds. When paired with Blue Iris, it acts as a centralized hub, reducing the load on your primary server, improving bandwidth efficiency, and enabling seamless management of multiple cameras across different locations. In 2026, with the rise of AI-powered analytics, 4K streaming, and cloud integration, combining an NVR with Blue Iris allows you to future-proof your surveillance setup. Whether you’re upgrading from a basic camera system or building a new enterprise-grade network, this integration offers unparalleled control, redundancy, and performance.
Preparing for Integration: Prerequisites and System Requirements
Hardware and Software Compatibility
Before diving into the setup process, it’s essential to ensure your hardware and software are compatible. Blue Iris runs exclusively on Windows (10/11 and Windows Server 2016+), while most modern NVRs support RTSP, ONVIF, and H.264/H.265 streaming protocols. Here’s what you need:
- Blue Iris Version 5.9.9.0 or later (as of 2026, the latest stable build)
- A Windows PC or server with at least 8GB RAM (16GB+ recommended for 16+ cameras)
- An ONVIF-compliant NVR from brands like Hikvision, Dahua, Reolink, or Lorex
- IP cameras connected to the NVR (preferably via PoE for stability)
- Stable network (Gigabit Ethernet recommended)
- At least 2TB of dedicated storage (SSD for OS, HDD for recordings)
Network Configuration and IP Addressing
Proper network setup is critical to avoid latency, dropped feeds, or authentication errors. Follow these best practices:
- Ensure the NVR and Blue Iris PC are on the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.1.x).
- Assign static IP addresses to the NVR and critical cameras to prevent DHCP conflicts.
- Enable ONVIF protocol on the NVR (Settings > Network > ONVIF).
- Open ports on your router/firewall if accessing remotely (typically 80/443 for HTTP/HTTPS, 554 for RTSP).
- Use VLANs or QoS settings to prioritize video traffic if your network handles heavy data loads.
Security Best Practices
Security is paramount. Never expose your NVR or Blue Iris server directly to the internet without safeguards. Recommended steps:
- Change default NVR credentials immediately (use strong, unique passwords).
- Enable HTTPS and disable outdated protocols (e.g., Telnet, FTP).
- Use a firewall to restrict access to the Blue Iris port (default: 81).
- Regularly update firmware on both the NVR and cameras.
- Consider a VPN (e.g., OpenVPN, WireGuard) for remote access instead of port forwarding.
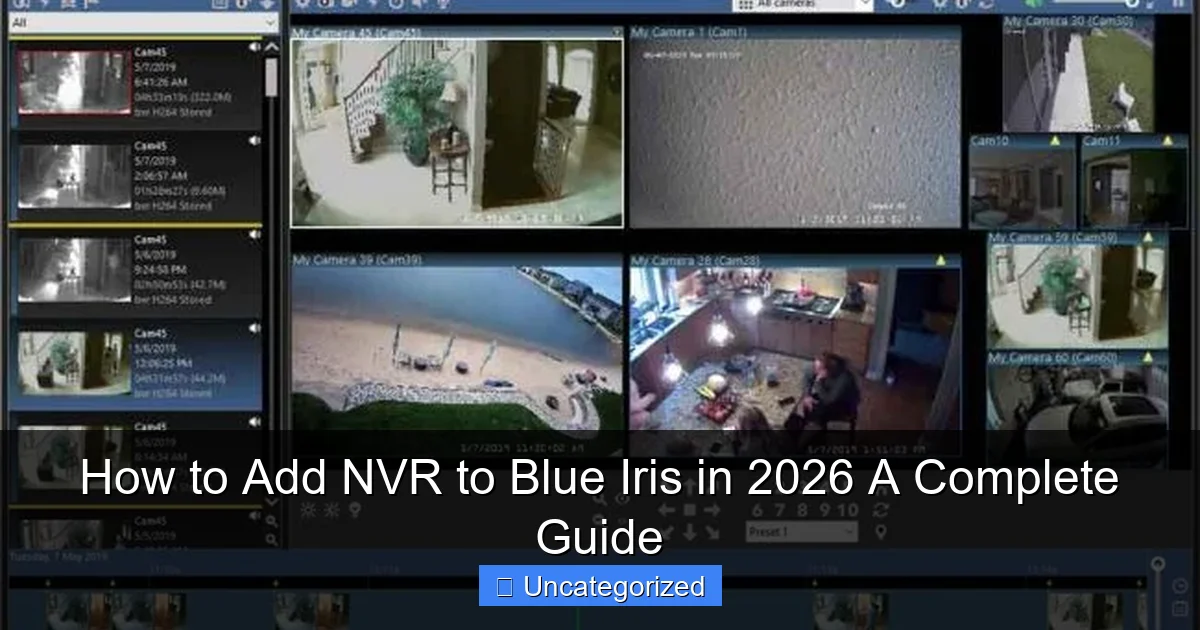
Step-by-Step Guide: Adding NVR Cameras to Blue Iris
Step 1: Access Your NVR’s Camera Feeds
First, log in to your NVR’s web interface or local GUI. Navigate to the camera management section and note the following for each camera:
Visual guide about how to add nvr to blue iris
Image source: nvripc.com
- Camera name or ID (e.g., “Front Door,” “Cam 03”)
- IP address or hostname (e.g., 192.168.1.105)
- RTSP URL (e.g.,
rtsp://192.168.1.105:554/Streaming/Channels/101) - ONVIF port (usually 80 or 8080)
- Username and password (if not using NVR credentials)
Tip: Test the RTSP URL in VLC Media Player to confirm it works before adding it to Blue Iris.
Step 2: Configure Blue Iris for NVR Integration
Open Blue Iris and follow these steps:
- Click the Cameras tab in the top-left.
- Click Add (or right-click in the camera list > Add Camera).
- Select Network (IP) Camera > Next.
- Choose ONVIF as the camera type. Click Discover.
- Blue Iris will scan the network for ONVIF devices. Select your NVR or its connected cameras.
- If discovery fails, enter the NVR’s IP manually. Click Test to verify the connection.
Note: Some NVRs (e.g., Hikvision) require you to enable “Allow third-party software to access” in ONVIF settings.
Step 3: Customize Stream Settings
After connecting, configure the camera’s streams for optimal performance:
- Main Stream (Primary): Set to 4K or 1080p at 15-30 FPS. Use H.265 if supported.
- Sub Stream (Secondary): Set to 720p or lower at 5-10 FPS for alerts and low-bandwidth monitoring.
- Bitrate: Use VBR (Variable Bitrate) with a cap of 4096 Kbps for 4K, 2048 Kbps for 1080p.
- Motion Detection: Enable in Blue Iris (not the NVR) for advanced analytics.
Pro Tip: Disable the NVR’s built-in motion detection to avoid duplicate alerts and reduce CPU load on the NVR.
Step 4: Set Up Recording and Alerts
Blue Iris offers flexible recording options:
- Continuous Recording: Record 24/7 to the NVR’s internal storage.
- Motion-Based Recording: Trigger recordings only when motion is detected (saves storage).
- Scheduled Recording: Define time blocks (e.g., business hours).
To configure alerts:
- Go to the Alerts tab in the camera’s settings.
- Set sensitivity, mask zones (e.g., ignore trees), and trigger actions (email, push notifications, sound).
- Link alerts to the NVR’s storage for backup (optional).
Optimizing Performance: Bandwidth, Storage, and AI Features
Bandwidth Management
Streaming 16+ 4K cameras can overwhelm your network. Use these strategies:
- Use Substreams for Monitoring: Display substreams (low-res) in Blue Iris’s live view; record main streams.
- Adjust FPS Dynamically: Set cameras to 5 FPS during low-traffic periods (e.g., nights).
- Enable Multicast (if supported): Reduces bandwidth by sending one stream to multiple destinations.
- QoS (Quality of Service): Prioritize camera traffic on your router.
Storage Solutions and Redundancy
Blue Iris can record to local drives, NAS, or the NVR itself. For redundancy:
- Local + NVR Recording: Record to both the NVR and Blue Iris (e.g., for backup or legal compliance).
- Cloud Backup: Use Blue Iris’s cloud upload feature (requires subscription) or sync with services like Google Drive.
- RAID Configuration: Use RAID 5/6 on the NVR for drive failure protection.
Storage Calculator: Estimate needs using this formula:
Total Storage (GB) = (Bitrate in Mbps × 3600 seconds × Hours) ÷ 8,192
Leveraging AI and Smart Detection
In 2026, AI is standard. Blue Iris integrates with:
- DeepStack AI: Free open-source tool for person/vehicle detection (reduces false alerts).
- Frigate NVR: Docker-based AI for real-time object recognition (works alongside Blue Iris).
- Cloud-Based AI: Services like AWS Rekognition for facial recognition (privacy considerations apply).
Example: Configure DeepStack to ignore pets but alert on humans. Set Blue Iris to trigger recordings only for “person” detections.
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Advanced Tips
Common Problems and Fixes
- Camera Not Detected: Verify ONVIF is enabled on the NVR. Check firewall rules.
- Laggy Streams: Reduce FPS/bitrate. Upgrade to Gigabit Ethernet.
- Authentication Errors: Re-enter credentials in Blue Iris. Ensure the NVR allows external access.
- Recording Gaps: Check disk health. Disable Windows sleep mode.
- High CPU Usage: Limit the number of simultaneous streams. Use hardware decoding (NVIDIA NVENC).
Advanced Configurations
- Multi-Site Monitoring: Use Blue Iris’s “Remote” feature to connect to NVRs at different locations.
- Failover Systems: Set up a secondary Blue Iris server for redundancy.
- Custom Triggers: Link cameras to smart devices (e.g., turn on lights when motion is detected).
- API Integration: Use Blue Iris’s JSON API to automate tasks (e.g., arm/disarm system via Home Assistant).
Firmware and Software Updates
Always keep systems updated:
- Check for Blue Iris updates monthly (Settings > About > Check for updates).
- Update NVR firmware quarterly (Settings > System > Maintenance).
- Subscribe to security bulletins for your NVR brand (e.g., Hikvision’s PSIRT).
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Case Study 1: Small Business Surveillance
A retail store uses a 16-channel Hikvision NVR with 8 4K cameras. By integrating with Blue Iris:
- Bandwidth reduced by 40% using substreams for monitoring.
- Motion detection tuned to ignore shelves but alert on aisles.
- Cloud backups enabled for insurance claims.
Case Study 2: Residential Smart Home
A homeowner connects a 12-camera Reolink NVR to Blue Iris:
- AI filters out wildlife but alerts on human activity.
- Cameras trigger smart lights via IFTTT.
- Remote access via Blue Iris mobile app.
Data Table: NVR vs. Direct Camera Connection
| Feature | NVR Integration | Direct Camera Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | High (supports 32+ cameras) | Medium (limited by server CPU) |
| Bandwidth | Lower (centralized processing) | Higher (direct streams to server) |
| Redundancy | High (NVR + Blue Iris backups) | Low (single point of failure) |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate (requires NVR config) | Low (plug-and-play) |
| AI Features | Advanced (via Blue Iris + external AI) | Basic (camera-dependent) |
Integrating an NVR with Blue Iris in 2026 is not just about convenience—it’s about building a resilient, intelligent surveillance ecosystem. By following this guide, you’ll unlock the full potential of your security setup: from bandwidth optimization and AI-driven alerts to multi-site management and failover redundancy. Whether you’re a tech-savvy homeowner or an IT professional, this integration future-proofs your system against evolving threats and technological advancements. Remember, the key to success lies in meticulous planning, regular maintenance, and leveraging the synergy between your NVR and Blue Iris. Now, go ahead and take your surveillance to the next level—your security deserves nothing less.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I add an NVR to Blue Iris for centralized camera management?
To add an NVR to Blue Iris, go to the “Cameras” tab, click “Add,” and select “IP Camera.” Enter your NVR’s RTSP or ONVIF stream URL, along with login credentials. Blue Iris will detect connected cameras and allow you to manage them centrally.
Can I integrate my existing NVR with Blue Iris without losing footage?
Yes, you can integrate your NVR with Blue Iris without losing stored footage by configuring it as an IP camera source. Blue Iris accesses the NVR’s live stream and recordings via RTSP, leaving original data intact on the NVR.
What’s the best way to add multiple cameras from an NVR to Blue Iris at once?
Use the “Scan Network” feature in Blue Iris to detect all cameras connected to your NVR automatically. Alternatively, manually add each camera using the NVR’s RTSP URL format, replacing the camera ID to batch-add streams efficiently.
How do I ensure my NVR works with Blue Iris using ONVIF?
Enable ONVIF on your NVR and verify the credentials in its settings. In Blue Iris, select “ONVIF Camera” during setup, enter the NVR’s IP and credentials, and let Blue Iris discover and add connected cameras.
Why won’t Blue Iris recognize my NVR when I try to add it?
This often occurs due to incorrect RTSP/ONVIF settings, firewall blocks, or authentication issues. Double-check the NVR’s port settings, ensure RTSP is enabled, and confirm Blue Iris has network access to the NVR’s IP.
Is it possible to use Blue Iris as a backup for my NVR recordings?
Yes, by adding your NVR as a camera source in Blue Iris, you can configure recording schedules and alerts. Blue Iris will store secondary copies of footage, providing redundancy alongside your NVR’s primary recordings.
