We’re living in a world that’s becoming increasingly aware of the impact of greenhouse gases on our planet. One of the biggest culprits is methane, a potent greenhouse gas that traps far more heat than carbon dioxide. Methane emissions come from a variety of sources, from landfills to livestock and oil and gas production.
With so many sources, detecting methane leaks can be a daunting task, especially since the gas is colorless and odorless. But fear not, because in this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various methods and technologies that can be used to detect methane emissions. From traditional techniques like flame ionization detectors to newer technologies like optical gas imaging cameras, we’ll break down the pros and cons of each approach.
We’ll also dive into the regulatory landscape around methane emissions and discuss what the future looks like in terms of reducing these emissions. Whether you’re a concerned citizen, an environmental engineer, or a business owner looking to reduce your company’s environmental impact, this guide has something for you. Methane emissions are a serious problem, but with the right tools and knowledge, we can work towards a more sustainable future.
So, let’s get started and learn how to detect methane like the experts do.
Understanding Methane
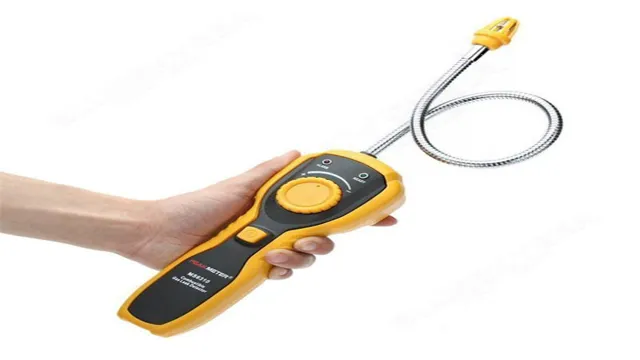
If you’re working in an industrial setting, it’s important to understand how to detect methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane is odorless, colorless, and tasteless, which makes it difficult to detect without the right tools. One way to detect methane is through the use of a handheld gas detector.
These devices are portable, easy to use, and provide instant readings of methane levels in the air. Another way to detect methane is through the use of infrared cameras, which can detect methane leaks from a distance. Additionally, companies can install methane sensors in areas where leaks are likely to occur, such as near storage tanks or pipelines.
Regular monitoring and maintenance of equipment can help prevent methane leaks and ensure the safety of workers and the environment. By understanding how to detect methane, we can work towards reducing emissions and mitigating the impact of climate change.
What is Methane?
Methane is a colorless, odorless gas that is primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms. It is a crucial part of the Earth’s atmosphere and is considered a potent greenhouse gas. Methane is naturally produced by microbes in environments with little oxygen, such as swamps, marshes, and the digestive tracts of animals.
It is also produced by human activities such as agriculture, landfills, and the production and transportation of fossil fuels. Methane is considered a major contributor to climate change due to its potency as a greenhouse gas and its ability to trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding methane and its role in the environment is critical in developing solutions to reduce its impact on the planet.
Methane Properties and Behavior
Methane is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas with the chemical formula CH It is the primary component of natural gas, and it is also present in other forms of fuels like coal and oil. Methane is a greenhouse gas that has a significant impact on global warming, as it has a much higher heat-trapping potential than carbon dioxide.
Methane is lighter than air, and it can ignite or explode when it reaches a concentration of about 5% to 15% in the air. Methane is produced naturally by anaerobic bacteria in wetlands, landfills, and digestive systems of animals like cows and sheep. Humans also produce methane through various industrial activities like agriculture, waste management, and oil and gas production.
Understanding the properties and behavior of methane is crucial in mitigating its impact on the environment and reducing the risks associated with its handling and use.
Methods for Methane Detection
If you’re looking to detect methane, there are several methods you can use depending on your needs. One commonly used method is the handheld combustible gas detector, which measures the levels of methane in the air. Another option is infrared cameras that detect methane leaks by identifying infrared radiation.
You can also use laser-based sensors that detect methane’s unique spectral signature. Furthermore, stationary sensors placed in strategic locations can detect methane leaks and alert operators in real-time. These methods are widely used in industries like oil and gas or landfill management, where the release of methane gas poses a potential safety hazard.
By utilizing these methods, you can detect methane leaks early, minimizing the risk of explosions, fires, and environmental damage.
Visual Observation
When it comes to detecting methane, visual observation can be a helpful method. Methane, being a colorless and odorless gas, is not easy to detect. However, there can be some instances where methane gas can change the environment around it, which can be identified visually.
For example, if there is a leak in a pipeline, the vegetation around the pipeline may start to wither or die off, which is an indication of a possible methane leak. Another sign of methane leakage is bubbling or seepage in wetlands, which can be observed visually. Visual observation of methane leaks can be helpful, but it is important to note that it is not a foolproof method.
Sometimes, a methane leak may not cause any visual changes, which is why it is essential to use other methane detection methods like gas sensors, infrared cameras, or spectral analysis.
Methane Sensor Technology
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes significantly to global warming. To mitigate its impact on the environment, it is crucial to detect and monitor methane emissions accurately. Methane sensor technology enables us to do so by detecting the presence of methane in the atmosphere.
These sensors use various methods to detect methane, such as infrared absorption, catalytic oxidation, and laser spectroscopy. Infrared absorption sensors measure the amount of methane by analyzing the light absorbed by methane molecules. Catalytic oxidation sensors detect methane by converting it into carbon dioxide and water through a catalytic reaction.
Laser spectroscopy sensors measure the concentration of methane by detecting the unique absorption properties of the gas in the infrared region. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific application and environmental condition. Overall, methane sensor technology is a powerful tool for monitoring and controlling methane emissions, which is essential to combat climate change.
Infrared Cameras
Infrared cameras are becoming increasingly popular for methane detection due to their high accuracy. One method for methane detection using infrared cameras is optical gas imaging (OGI). OGI involves using infrared cameras to detect methane emissions from oil and gas facilities, landfills and agricultural operations.
The infrared cameras are capable of detecting specific wavelengths of infrared light, which methane gas absorbs. The cameras then create an image of the gas plume, which typically appears as a cloud or smoke-like formation, enabling operators to visualize the location and concentration of gas emissions. OGI offers several advantages over other detection methods, including its ability to detect gas leaks from a distance, its ability to quickly locate and quantify leaks, and its ability to identify leaks that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Overall, infrared cameras are a highly effective method for detecting methane emissions and are rapidly becoming an essential tool for ensuring methane emission reductions in a variety of industries.
Using Technology to Detect Methane
If you’re wondering how to detect methane, technology has made it easier than ever before. Various devices and sensors have been developed to detect methane, which is a colorless and odorless gas that is highly flammable and explosive. These tools can be used in a wide range of applications, from monitoring gas leaks in industrial settings to detecting methane emissions from livestock or natural gas operations.
One common method of detecting methane is using infrared technology. Instruments with infrared detectors can detect the gas by measuring the way that methane molecules absorb infrared radiation. Another method is laser spectroscopy, which uses laser beams to detect methane by analyzing the way that light interacts with the gas.
Remote sensing technology can also be used for methane detection. Satellites equipped with sensors can scan wide areas to detect concentrations of methane in the atmosphere. This technology can be used to monitor methane emissions from sources like oil and gas fields, landfills, and agricultural facilities.
In addition to these technologies, there are also portable devices that can detect methane. These handheld devices work by sucking in air samples and analyzing the methane concentration. They are often used by gas companies, firefighters, and other professionals who need to detect methane quickly and easily.
In conclusion, there are a variety of technologies available that can be used to detect methane. Whether you need to monitor for gas leaks in an industrial setting or detect methane emissions from a natural gas facility, there are tools available to help you get the job done quickly and efficiently. By understanding the different technologies available, you can choose the right tool for your specific needs and ensure that you are able to detect methane in a safe and effective manner.
Portable Gas Detectors
Portable gas detectors are an essential tool for industries that deal with hazardous gases like methane. These detectors use advanced technologies to detect the presence of gas in the surrounding air. One technology that is becoming increasingly popular is infrared detection.
Infrared detectors work by sending out an infrared light that is absorbed by the gas molecules. The amount of light absorbed by the gas molecules is then measured and analyzed to determine the concentration of gas in the surrounding air. Other technologies, like catalytic bead sensors, electrochemical sensors, and photoionization sensors, are also used in portable gas detectors.
The use of such advanced technologies ensures that workers are protected from dangerous levels of gas exposure while working in confined spaces or hazardous environments. With the help of portable gas detectors, workers can confidently carry out their tasks without having to worry about their safety.
Fixed Gas Detectors
Fixed gas detectors are an essential safety measure in many industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment. These detectors use advanced technology to detect the presence of dangerous gases, such as methane, and provide early warning to operators. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that is 25 times more powerful than carbon dioxide, presenting a significant environmental and safety risk.
Fixed gas detectors use infrared sensors or catalytic bead sensors to detect methane and other gases in the air. These sensors are highly sensitive and can detect even small leaks, allowing operators to take proactive measures to prevent accidents and protect the environment. Overall, fixed gas detectors are a critical tool for ensuring the safety of workers and the environment in industrial settings.
Preventing Methane Leaks
If you’re looking to prevent methane leaks, the first step is to be able to detect the gas accurately. Methane is odorless and colorless, making it tough to spot without specialized equipment. The most common devices used to detect methane leaks are handheld gas detectors, which work by sensing the gas’s concentration in the air.
These detectors can be calibrated to alarm workers of dangerous methane levels, or continuously monitor for small leaks. Additionally, thermal imaging cameras can also detect the infrared radiation of methane, which helps locate leaks in pipelines or storage tanks. Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment can also help prevent methane leaks, as worn or damaged components increase the likelihood of leaks occurring.
By taking these preventative measures, companies can significantly reduce the risk of methane leaks and keep their facilities running safely.
Industry Best Practices
Methane leaks are one of the most significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions in the energy sector. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, about 30 times more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide. Therefore, preventing methane leaks is vital to minimizing the impact on climate change.
Several industry best practices exist to prevent methane leaks, including regular maintenance of equipment, advanced leak detection systems, and employee training. Maintenance involves checking valves, pipelines, and other equipment used to handle and transport natural gas. Leak detection systems can detect and alert operators of methane leaks as small as one percent of the pipeline’s flow rate.
Employee training is also essential to prevent human errors that could cause methane leaks. Overall, implementing these best practices is vital in the fight against climate change and reducing the carbon footprint of the energy industry.
Methane Detection System Maintenance
Preventing Methane Leaks Methane detection systems are used to detect any leaks of this flammable gas that could potentially cause explosions in confined spaces. However, it is important to regularly maintain these systems to ensure they are functioning properly and prevent any unexpected leaks. This can involve checking for any signs of wear and tear on the system’s components, such as sensors and valves, and repairing or replacing them as necessary.
Additionally, it’s important to thoroughly test the system’s response to possible leaks and calibrate it as needed. Preventing methane leaks through regular system maintenance not only ensures the safety of personnel working in confined spaces, but also the surrounding environment. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, so any leaks could have a significant impact on the planet.
By maintaining methane detection systems, companies can do their part in reducing the risk of harmful leaks and protecting the environment.
Conclusion
Well, if you want to detect methane, all you have to do is follow your nose! But for a more scientific approach, you can use a methane detector or simply look for signs like bubbling in water, presence of fire or flame, and sudden changes in air quality. Remember, methane may be odorless and colorless, but its impact on the environment and our health is anything but insignificant. So don’t let it slip under your nose – keep it on your radar and take action when necessary!”
FAQs
What is methane?
Methane is a colorless, odorless gas that is the primary component of natural gas.
What are some common sources of methane emissions?
Some common sources of methane emissions include natural gas production and transportation, animal and dairy farming, and decomposing organic matter in landfills.
How can methane be detected in the atmosphere?
Methane can be detected in the atmosphere using a variety of methods, including satellite and aircraft remote sensing, ground-based sensors, and drones.
Why is it important to detect methane emissions?
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes significantly to global warming. By detecting and reducing methane emissions, we can help mitigate the impacts of climate change.
What technologies are available to reduce methane emissions?
Technologies such as methane capture and utilization systems, leak detection and repair programs, and renewable energy development can help reduce methane emissions.
