Featured image for how to set up ethernet poe security cameras
Image source: perle.com
Setting up Ethernet PoE security cameras is a fast, reliable way to power and connect your surveillance system using a single cable. With plug-and-play PoE switches or NVRs, you can install cameras in minutes—no separate power outlets or complex wiring needed. Just connect via Cat5e/Cat6 cable, and your cameras are live, delivering high-definition video with minimal downtime.
Key Takeaways
- Plan camera placement first: Choose optimal spots for coverage and PoE cable access.
- Use a PoE switch/injector: Ensures power and data over a single Ethernet cable.
- Run cables neatly: Secure and conceal wires to prevent damage and tampering.
- Connect via NVR: Link cameras to a Network Video Recorder for centralized management.
- Test before finalizing: Verify live feeds and adjust angles or settings as needed.
- Secure network access: Enable encryption and strong passwords to prevent hacking.
📑 Table of Contents
- How to Set Up Ethernet PoE Security Cameras in Minutes
- Understanding Ethernet PoE Security Cameras: The Basics
- Essential Equipment and Tools for PoE Camera Setup
- Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Network Configuration and Remote Access
- Troubleshooting Common Issues and Maintenance
- Data Table: Recommended PoE Camera Systems
- Conclusion
How to Set Up Ethernet PoE Security Cameras in Minutes
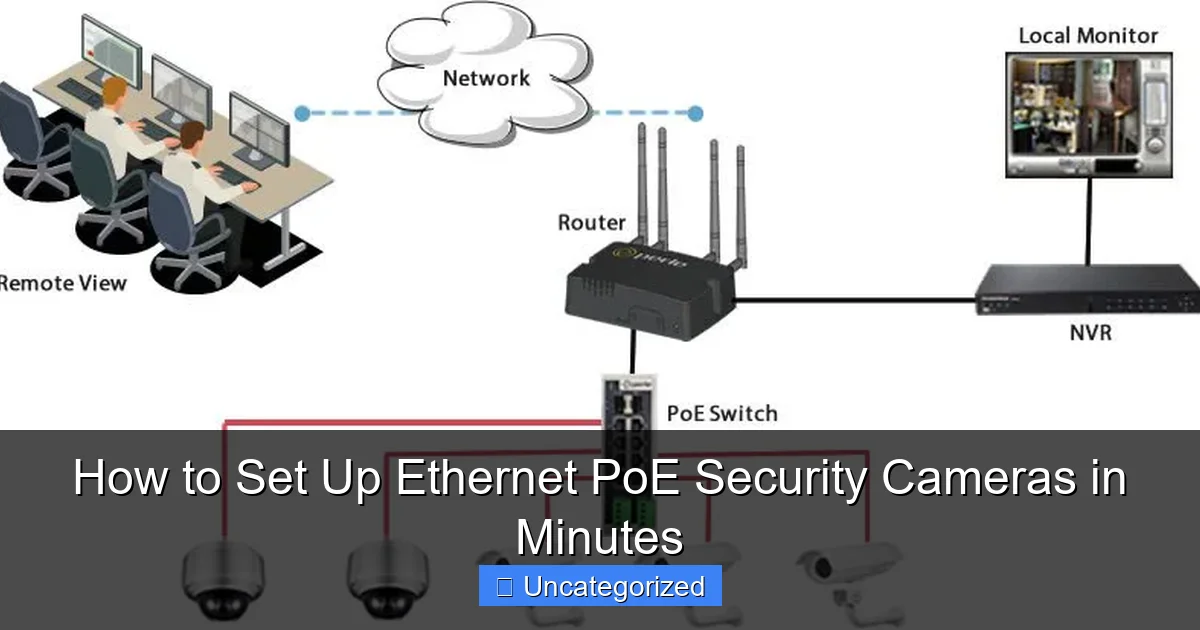
Imagine coming home to find your front porch light on, your garage door securely shut, and your backyard undisturbed—thanks to a reliable security camera system that’s always on duty. In today’s world, home and business security are no longer optional luxuries but essential investments. Among the many types of surveillance systems available, Ethernet Power over Ethernet (PoE) security cameras stand out for their reliability, high-quality video transmission, and ease of installation. Unlike traditional analog cameras or Wi-Fi-based systems, PoE cameras deliver both power and data through a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power outlets and reducing clutter.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast looking to protect your family or a business owner aiming to secure your premises, setting up PoE cameras can be simpler than you think. With the right tools, a clear plan, and a few minutes of focused effort, you can have a robust surveillance system up and running. This guide walks you through every step—from choosing the right equipment to configuring your network and troubleshooting common issues. By the end, you’ll not only understand how to set up Ethernet PoE security cameras efficiently but also appreciate why they’re one of the most effective security solutions available today.
Understanding Ethernet PoE Security Cameras: The Basics
Before diving into installation, it’s crucial to understand what makes Ethernet PoE security cameras unique and why they’re increasingly popular among homeowners and professionals alike. At their core, these cameras use standard Ethernet cables (typically Cat5e or Cat6) to transmit both data (video, audio, control signals) and electrical power from a central source—usually a PoE switch or injector. This dual functionality simplifies wiring, reduces installation time, and enhances system reliability.

Visual guide about how to set up ethernet poe security cameras
Image source: platinumcctv.com
How PoE Works
Power over Ethernet technology follows IEEE 802.3af (PoE), 802.3at (PoE+), and 802.3bt (PoE++) standards. These standards define how much power can be safely delivered over Ethernet cables:
- PoE (802.3af): Delivers up to 15.4 watts per port (12.95W usable), ideal for standard HD cameras.
- PoE+ (802.3at): Provides up to 30 watts (25.5W usable), suitable for PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras and those with heaters or IR illuminators.
- PoE++ (802.3bt): Offers up to 60W (Type 3) or 100W (Type 4), used for advanced cameras with multiple features or long-distance runs.
This means your camera doesn’t need a nearby wall outlet—just a single Ethernet cable connected to a PoE-enabled device. For example, a 4K bullet camera with night vision and motion detection can draw power and stream video simultaneously over a single Cat6 cable running 100 meters (328 feet).
Advantages Over Other Camera Types
Compared to Wi-Fi or analog (CCTV) systems, PoE cameras offer several key benefits:
- Stable, high-bandwidth connection: Unlike Wi-Fi, which can suffer from interference, latency, or signal drops, Ethernet provides a dedicated, high-speed data path. This ensures smooth 4K video streaming and real-time alerts.
- Simplified wiring: One cable handles both power and data, reducing cable clutter and minimizing points of failure.
- Remote power cycling: If a camera freezes, you can reboot it remotely via the network, avoiding physical access.
- Scalability: Adding more cameras is as simple as plugging into the PoE switch and extending the network.
- Enhanced security: Wired connections are less vulnerable to hacking than Wi-Fi signals, making PoE systems more secure.
For instance, a small business with four outdoor cameras can avoid installing four separate power outlets by using a single PoE switch. The result? Cleaner installation, lower labor costs, and improved reliability.
Essential Equipment and Tools for PoE Camera Setup
Setting up a PoE security camera system doesn’t require a degree in networking—just the right gear and a few basic tools. Below is a comprehensive list of everything you’ll need to get started, along with practical tips to avoid common pitfalls.
Core Components
- PoE Security Cameras: Choose models with the features you need—resolution (1080p, 4K), field of view, weather resistance (IP66/IP67), night vision, audio, and motion detection. Brands like Reolink, Hikvision, Lorex, and Ubiquiti offer reliable options.
- PoE Switch or PoE NVR: This is the heart of your system. A PoE switch powers and connects multiple cameras directly. A PoE Network Video Recorder (NVR) does the same while also recording and managing footage. For 4–8 cameras, a 8-port PoE+ switch (e.g., Netgear GS308PP) or a PoE NVR (e.g., Lorex 8-Channel 4K NVR) is ideal.
- Ethernet Cables (Cat5e/Cat6): Use Cat5e for shorter runs (up to 100m) and Cat6 for longer distances or future-proofing. Pre-terminated cables are convenient, but custom lengths (via bulk cable and crimps) reduce waste and cost.
- Network Video Recorder (NVR) or Cloud Storage: If using a PoE switch, you’ll need a standalone NVR to record footage. Alternatively, some cameras support microSD cards or cloud storage (e.g., Reolink’s cloud plans).
- Router/Modem: Connects your system to the internet for remote viewing via smartphone apps or web portals.
Tools and Accessories
- Ethernet Crimping Tool: For creating custom-length cables with RJ45 connectors.
- Drill and Drill Bits: For mounting cameras and running cables through walls or soffits.
- Fish Tape or Cable Puller: Helps route cables through tight spaces.
- Wire Strippers and Snips: For preparing cables.
- Zip Ties and Cable Clips: To secure and organize wiring.
- Power Tester or PoE Tester: Verifies that power and data are being delivered correctly (optional but recommended).
- Smartphone or Tablet: For initial setup and configuration via camera manufacturer’s app.
Pro Tips for Choosing Equipment
- Match PoE standards: Ensure your switch or NVR supports the same PoE standard as your cameras (e.g., PoE+ for PTZ cameras).
- Check power budget: A 8-port PoE+ switch may have a total power budget of 60W. If each camera needs 7W, you can support up to 8 cameras. Exceeding this limit can cause cameras to shut down.
- Use shielded cables outdoors: Shielded Cat6 (STP) reduces interference from power lines or weather.
- Plan for future expansion: Buy a switch with 2–3 extra ports for future cameras.
Example: A homeowner installing 6 outdoor cameras might opt for a 8-port PoE+ switch (70W budget), Cat6 cables, and a 4K NVR. This setup allows room for two additional cameras later without upgrading the switch.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Now that you have your equipment, it’s time to install. Follow this step-by-step guide to set up your Ethernet PoE security cameras efficiently—whether you’re wiring a single camera or an entire network.
1. Plan Camera Locations
Before drilling any holes, map out where each camera will go. Consider:
- Coverage areas: Entry points (doors, windows), driveways, backyards, garages.
- Height and angle: Install cameras 8–10 feet high to avoid tampering but low enough to capture faces.
- Cable routing: Identify the shortest path from each camera to the central PoE switch/NVR. Use attic spaces, basements, or soffits to hide cables.
- Weather protection: Ensure outdoor cameras are under eaves or use weatherproof junction boxes.
Tip: Use a laser distance measurer to calculate cable lengths and avoid overbuying.
2. Mount the Cameras
- Mark drill points using the camera’s mounting template.
- Drill pilot holes and insert wall anchors (for masonry or stucco).
- Secure the camera’s mounting bracket with screws.
- Attach the camera to the bracket and adjust the viewing angle.
Pro Tip: Test camera positioning before final mounting by holding it in place and checking the live view on your phone app.
3. Run Ethernet Cables
- Start at the PoE switch/NVR and run cables to each camera location.
- Use fish tape to pull cables through walls, attics, or soffits. For outdoor runs, use weatherproof conduit or bury cables 6–12 inches deep (if allowed by local codes).
- Leave 1–2 feet of slack at both ends for adjustments.
- Terminate cables with RJ45 connectors (if using bulk cable) or use pre-made cables.
Example: For a camera in the backyard, run a Cat6 cable from the basement switch, up through a soffit, and down to the camera. Secure with clips every 18–24 inches.
4. Connect to the PoE Switch/NVR
- Plug one end of each Ethernet cable into the PoE switch/NVR.
- Connect the other end to the camera.
- Power on the switch/NVR. Most PoE devices automatically detect and power the cameras.
Note: If using a PoE injector (for non-PoE switches), connect the injector between the camera and switch, and plug the injector into a power outlet.
5. Configure Cameras and NVR
- Download the camera manufacturer’s app (e.g., Reolink App, Hik-Connect).
- Follow in-app instructions to add cameras to the network. Most systems auto-detect new devices.
- Assign names to each camera (e.g., “Front Door,” “Driveway”) for easy identification.
- Set recording schedules, motion detection zones, and alerts.
Pro Tip: Enable ONVIF compatibility if using third-party NVRs or apps for broader integration options.
6. Test the System
- Check live views on the app and NVR interface.
- Verify motion detection by walking through coverage areas.
- Test night vision and audio (if available).
- Review recorded footage to ensure clarity and storage.
Example: After setup, a homeowner tests the “Front Door” camera by triggering motion detection. The app sends a real-time alert, and the NVR records a 15-second clip—confirming the system works as expected.
Network Configuration and Remote Access
Once your cameras are installed, the next step is configuring your network to enable remote viewing, secure access, and reliable performance. This section covers essential network settings and best practices.
Connect to Your Router
Link your PoE switch or NVR to your home/business router using an Ethernet cable. This connects your security system to the internet, enabling:
- Remote live viewing via smartphone apps.
- Cloud storage and backup.
- Firmware updates and alerts.
Tip: Use a dedicated port on the router to avoid bandwidth competition with other devices.
Set Up Remote Viewing
- In the camera/NVR app, enable remote access.
- Create a strong, unique password (use a password manager).
- For NVRs, configure DDNS (Dynamic DNS) if your internet provider uses dynamic IP addresses. This ensures you can always access your system via a fixed URL (e.g., “myhome.ddns.net”).
- Port forwarding (if required): Some systems need specific ports (e.g., 80, 443, 554) opened on the router. Use UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) if supported, or manually forward ports (check your router’s manual).
Example: A business owner uses DDNS to access their 12-camera system from a laptop while traveling. They log in via the NVR’s web portal using their DDNS address and a two-factor authentication app.
Optimize Network Performance
- Bandwidth management: High-resolution cameras (e.g., 4K) consume significant bandwidth. Limit remote streaming to 1080p or use motion-triggered alerts to reduce data usage.
- QoS (Quality of Service): Prioritize camera traffic on your router to prevent lag during peak hours.
- VLANs (Virtual LANs): For advanced users, isolate cameras on a separate VLAN to enhance security and reduce network congestion.
Pro Tip: Use a network monitoring tool (e.g., PRTG, Wireshark) to identify bandwidth hogs or connection issues.
Ensure Security
- Firmware updates: Regularly update camera and NVR firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
- Strong passwords: Use 12+ characters with symbols, numbers, and mixed cases. Avoid default credentials.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for remote access.
- Disable UPnP if not needed, as it can expose your network to external attacks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues and Maintenance
Even the best PoE systems can encounter issues. Here’s how to diagnose and fix common problems, plus tips for ongoing maintenance.
No Power or Video
- Check PoE compatibility: Ensure the switch/NVR and camera support the same PoE standard.
- Test the cable: Use a PoE tester or swap with a known-working cable. Look for damaged connectors or kinks.
- Inspect power budget: If the switch’s power budget is exceeded, cameras may not power on. Reduce load or upgrade to a higher-budget switch.
Intermittent Connection
- Replace damaged cables: Long runs or outdoor exposure can degrade cable integrity.
- Use shielded cables in areas with electrical interference (e.g., near power lines).
- Check for IP conflicts: Ensure each camera has a unique IP address. Use DHCP or static IPs.
Poor Video Quality
- Adjust resolution settings: Lower resolution (e.g., 1080p instead of 4K) if bandwidth is limited.
- Clean camera lenses: Dust, rain, or spider webs can blur footage.
- Optimize lighting: Add IR illuminators or external lights for dark areas.
Maintenance Best Practices
- Monthly checks: Inspect cameras for damage, misalignment, or obstructions.
- Firmware updates: Schedule quarterly updates.
- Test backup power: If using a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), test it annually.
- Review footage: Regularly check recordings to ensure clarity and storage integrity.
Example: A homeowner notices their “Garage” camera has no night vision. After troubleshooting, they discover a loose cable connection—fixed in minutes with a re-crimped connector.
Data Table: Recommended PoE Camera Systems
| System Type | Best For | PoE Standard | Max Cameras | Key Features | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reolink 8-Channel 4K NVR | Homeowners (4–8 cameras) | PoE+ (802.3at) | 8 | 4K recording, AI detection, 2TB HDD, remote access | $350–$450 |
| Hikvision DS-7608NI-I2/8P | Small businesses | PoE+ | 8 | 4K, ONVIF, 2TB, motion detection, cloud storage | $400–$500 |
| Ubiquiti UniFi Protect G4 Pro | Tech-savvy users | PoE++ (802.3bt) | 30+ (scalable) | 4K, AI detection, cloud management, no monthly fees | $600+ (base + cameras) |
| Lorex 4K PoE System | Budget-conscious | PoE | 4 | 4K, 1TB HDD, night vision, mobile alerts | $250–$350 |
| Netgear GS308PP Switch + NVR | Custom setups | PoE+ | 8 | 70W power budget, VLAN support, plug-and-play | $200 (switch) + NVR cost |
Conclusion
Setting up Ethernet PoE security cameras doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With the right equipment, a clear plan, and this guide, you can have a high-performance surveillance system installed and configured in minutes—not days. From understanding PoE standards and selecting reliable gear to running cables, configuring networks, and troubleshooting issues, every step has been designed to empower you with a secure, scalable, and user-friendly solution.
The beauty of PoE systems lies in their simplicity and robustness. No more worrying about Wi-Fi dropouts, power outlet shortages, or complex wiring. Instead, enjoy crisp 4K video, real-time alerts, and remote access from anywhere in the world. Whether you’re protecting your home, monitoring a business, or ensuring the safety of loved ones, PoE cameras offer peace of mind with minimal effort. So grab your tools, follow the steps, and take control of your security today. Your future self—and your property—will thank you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I set up Ethernet PoE security cameras for the first time?
To set up Ethernet PoE security cameras, connect the camera to a PoE switch or injector using an Ethernet cable, then link the switch to your router. Most systems auto-detect the camera, allowing configuration via a mobile app or web interface.
What equipment do I need for a PoE security camera setup?
You’ll need PoE cameras, a PoE switch/injector, Ethernet cables (Cat 5e or higher), and a router. Ensure your NVR (if used) supports PoE for seamless integration with your Ethernet PoE security cameras.
Can I power PoE cameras without a PoE switch?
Yes, use a PoE injector between a non-PoE switch and the camera. The injector delivers power over the Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for a dedicated PoE switch in smaller setups.
How far can I run an Ethernet cable for PoE security cameras?
Ethernet cables can reliably transmit power and data up to 100 meters (328 feet) for Ethernet PoE security cameras. Beyond that, use extenders or fiber converters to avoid signal degradation.
Do PoE cameras work with Wi-Fi routers?
Yes, but only if the router is connected to a PoE switch/injector. PoE cameras require wired Ethernet for power, but the router can still handle Wi-Fi for remote viewing via apps.
How do I troubleshoot a PoE camera not powering on?
Check cable connections, ensure the PoE switch/injector is functional, and verify the camera’s compatibility with your PoE standard (e.g., 802.3af/at). Test with a shorter cable if needed.