Disease surveillance is very important for public health. It helps us know how diseases spread. It also helps us control outbreaks. This article explains why disease surveillance matters. We will look at its benefits and how it works.

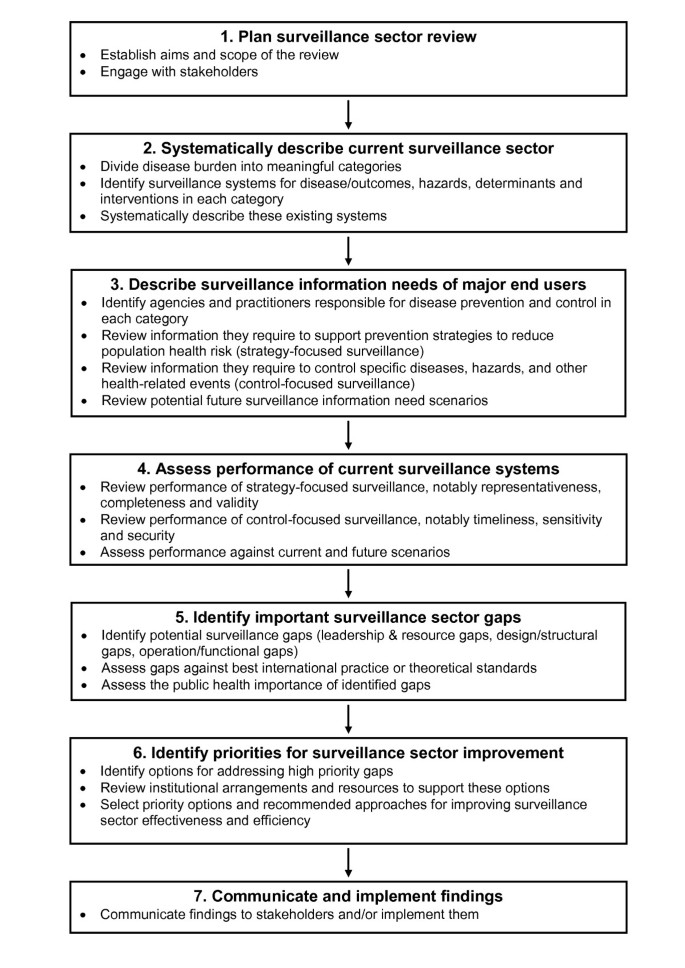
What is Disease Surveillance?
Disease surveillance means watching for diseases. It is a way to collect data about health. This data helps us understand health problems. There are many types of disease surveillance. Here are a few:
- Active Surveillance: Health workers actively look for cases.
- Passive Surveillance: Health workers wait for reports from hospitals.
- Syndromic Surveillance: This looks for symptoms of diseases.
Each type has its own purpose. They all help us keep track of diseases.
Why is Disease Surveillance Important?
Disease surveillance has many benefits. Here are some key reasons why it is important:
1. Early Detection
Early detection of diseases saves lives. When we find a disease early, we can act quickly. This can stop the disease from spreading. For example, if a new flu strain appears, we need to know fast. Early reports help health workers prepare. They can also inform the public about safety measures.
2. Understanding Disease Patterns
Disease surveillance helps us understand patterns. It shows how diseases spread in communities. This information helps health officials. They can create plans to control the disease. For instance, if a disease is common in one area, more help can be sent there.
3. Resource Allocation
Surveillance helps allocate resources. It tells us where to send doctors, nurses, and supplies. If an outbreak occurs, resources can be sent quickly. This ensures that people get the help they need. It also prevents shortages of medical supplies.
4. Evaluation Of Public Health Programs
Public health programs need evaluation. Surveillance helps us see what works. It shows if a program reduces disease rates. If a program is not effective, it can be changed. This allows for better public health strategies in the future.
5. Informing Public Policy
Good data informs public policy. Policymakers need accurate information. Surveillance provides the facts they need. This helps in making decisions about health laws and regulations. For example, if there is an increase in smoking-related diseases, new laws can be made to reduce smoking.
6. Outbreak Response
When outbreaks happen, quick response is crucial. Surveillance identifies outbreaks early. This allows health officials to control the situation. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, surveillance was key. It helped track cases and spread of the virus.
7. Global Health Security
Disease surveillance is also important for global health. Diseases do not stop at borders. What happens in one country affects others. Surveillance helps track diseases worldwide. This information helps prevent global pandemics.
How is Disease Surveillance Done?
Disease surveillance is a step-by-step process. Here are the main steps involved:
1. Data Collection
Data collection is the first step. Health workers collect information on diseases. This can come from hospitals, clinics, or labs. They look for reports on symptoms and diagnoses.
2. Data Analysis
After collecting data, it needs to be analyzed. This means looking for trends and patterns. Health experts study the data. They look for increases in certain diseases. They also check if diseases are spreading.
3. Data Reporting
Once data is analyzed, it must be reported. Reports go to public health officials. They use this information to make decisions. Reports can also go to the public. This helps keep everyone informed about health risks.
4. Response And Action
After reports are made, action is needed. Health officials create plans to respond. This might include providing vaccines or treatments. They may also advise the public on safety measures.
Challenges in Disease Surveillance
Despite its importance, disease surveillance has challenges. Here are some common issues:
1. Underreporting
Some diseases go unreported. This is called underreporting. People may not visit doctors for mild symptoms. This makes it hard to track diseases accurately.
2. Data Quality
Data quality can vary. Some reports may lack detail. This can lead to misunderstandings about disease spread. Good training for health workers can help improve data quality.
3. Resource Limitations
Many places have limited resources. Some countries may not have enough staff or technology. This makes effective surveillance difficult. International support can help improve these systems.
4. Privacy Concerns
Surveillance involves personal health data. This raises privacy concerns. People may not want their health information shared. It is important to handle data carefully and respectfully.
The Future of Disease Surveillance
The future of disease surveillance looks promising. Technology is improving quickly. Here are some ways it may change:
1. Use Of Technology
New technology can make surveillance easier. Mobile apps can help track symptoms. Wearable devices can monitor health in real-time. This can provide quick data to health officials.
2. Global Collaboration
Countries are working together more. Global collaboration helps share data. This is important for tracking diseases across borders. It ensures that everyone is prepared for outbreaks.
3. Increased Public Awareness
Public awareness about disease surveillance is growing. More people understand its importance. This can lead to better reporting of symptoms. Communities can work together to improve health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Disease Surveillance In Public Health?
Disease surveillance is the ongoing collection and analysis of health data. It helps monitor disease trends and outbreaks.
Why Is Disease Surveillance Important?
It is crucial for early detection of diseases. This helps control outbreaks and protect public health.
How Does Disease Surveillance Help Communities?
It identifies health risks, guides response efforts, and informs public health policies. Communities can respond effectively to health threats.
What Methods Are Used In Disease Surveillance?
Common methods include reporting systems, surveys, and laboratory tests. These methods help gather accurate health data.
Conclusion
Disease surveillance is crucial for public health. It helps detect diseases early. It allows us to understand how diseases spread. This information helps allocate resources effectively. It also plays a key role in outbreak response and global health security.
Despite challenges, the future looks bright. Technology and collaboration will enhance surveillance. By working together, we can improve public health for everyone. Remember, healthy communities start with good disease surveillance.
