Public health surveillance is very important. It helps us keep track of diseases. It also helps us understand health trends. This article will explain public health surveillance. We will look at examples. These examples show how surveillance works in real life.
What is Public Health Surveillance?
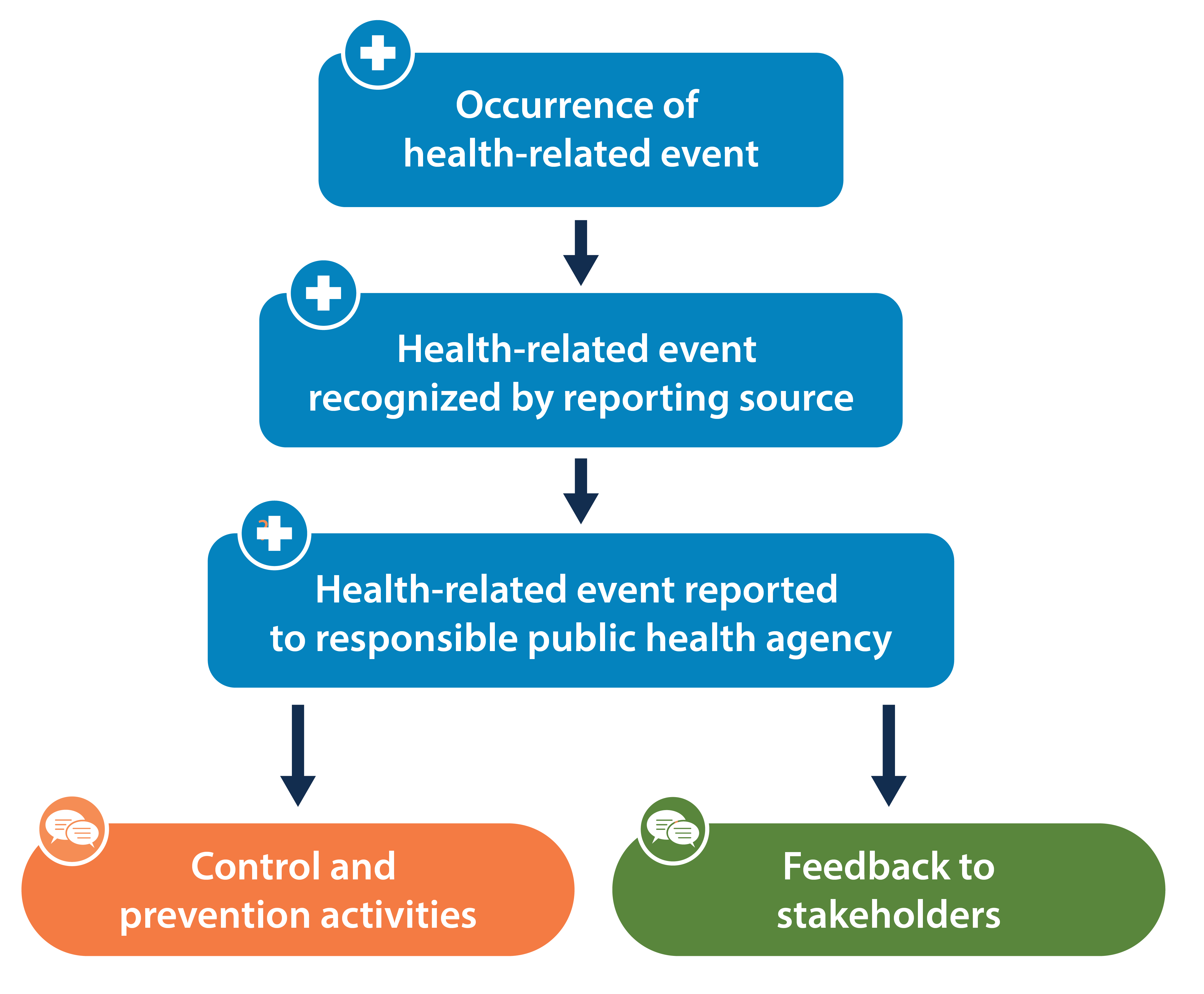
Public health surveillance is the process of monitoring health data. It helps health officials see how diseases spread. It also helps them find out who is affected. By collecting data, we can understand health threats. This knowledge helps us take action.
Surveillance can be done in many ways. Health workers use reports from hospitals. They also use surveys and lab tests. This information is collected over time. The goal is to spot trends and outbreaks.
Why is Public Health Surveillance Important?
Public health surveillance is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Detection: It helps find diseases early.
- Control Outbreaks: It helps control disease outbreaks.
- Resource Allocation: It shows where to send resources.
- Policy Making: It helps make informed health policies.
Now let’s look at some examples of public health surveillance.
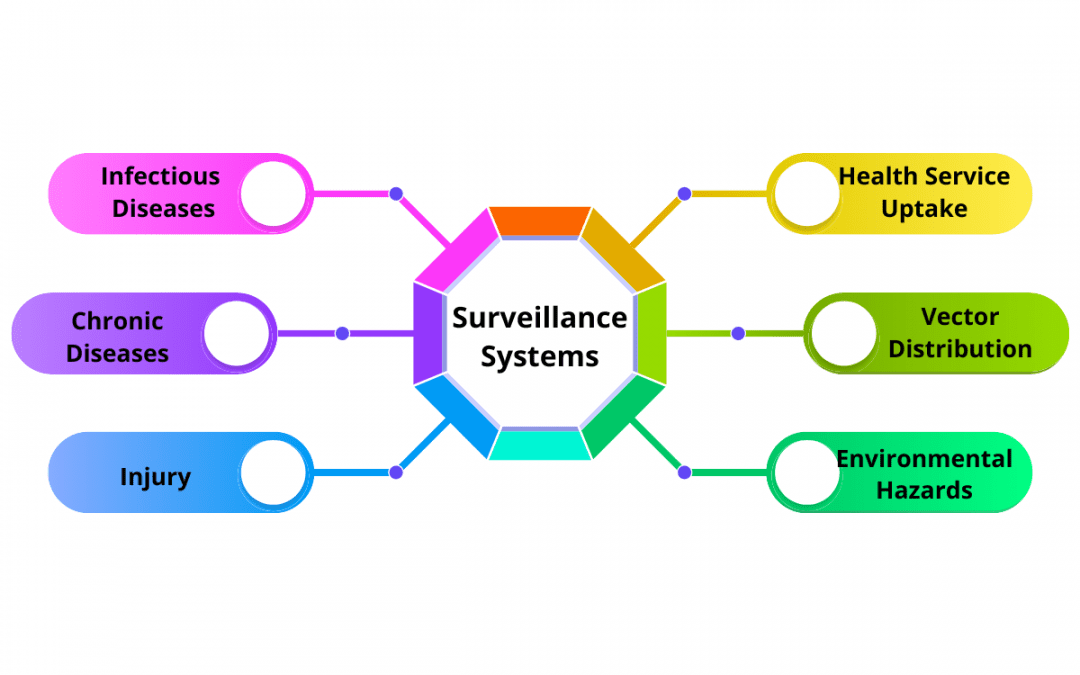
Example 1: Monitoring Influenza
One common example is tracking influenza. Each year, many people get the flu. Health departments collect data from doctors and hospitals. They look for flu symptoms and lab tests. This data helps them understand how the flu spreads.
They also use a system called “flu watch.” This system tracks flu cases across the country. By knowing when and where flu cases rise, health officials can prepare. They can increase vaccine availability. They can also inform the public about flu prevention.
Example 2: Tracking COVID-19
COVID-19 is a recent example of public health surveillance. When the virus first appeared, health officials acted quickly. They began collecting data on cases and deaths.
They used testing sites and hospitals to gather information. They also used contact tracing. This helps find people who were near someone with COVID-19. This data helped slow the virus’s spread.
Health departments shared this information. They provided updates to the public. This helped everyone understand the situation.
Example 3: Childhood Vaccination Rates
Surveillance also tracks vaccination rates in children. Vaccines protect children from serious diseases. Health departments collect data on how many kids get vaccinated.
They look at different areas. Some areas have lower rates. This information helps target education and resources. It encourages parents to vaccinate their children. Higher vaccination rates lead to healthier communities.
Example 4: Foodborne Illness Outbreaks
Foodborne illnesses are another area of public health surveillance. When people get sick from food, health officials investigate. They collect data on symptoms and foods eaten.
They use reports from hospitals and labs. This helps them find the source of the outbreak. Once they identify the source, they can take action. They may recall products or warn the public.
Example 5: Chronic Disease Monitoring
Surveillance is also used for chronic diseases. Diseases like diabetes and heart disease are common. Health officials track these conditions over time.
They collect data from hospitals, clinics, and surveys. This helps them see how many people are affected. They can also find risk factors, such as obesity.
With this information, they create health programs. These programs aim to reduce chronic diseases. They educate the public on healthy living.
Example 6: Mental Health Monitoring
Mental health is another important area. Public health surveillance looks at mental health trends. Health officials collect data on conditions like depression and anxiety.
They gather information from surveys and health records. This helps them understand how many people are affected. It also shows how mental health changes over time.
With this data, officials can create support programs. They can also raise awareness about mental health issues.
Example 7: Environmental Health Surveillance
Environmental health is crucial for public health. Surveillance looks at how the environment affects health. For example, air quality is monitored regularly.
Health officials track pollution levels in the air. They gather data from monitoring stations. This information shows how pollution affects health.
In cities with high pollution, health problems may rise. Officials can create policies to improve air quality. This helps protect the public’s health.
How is Data Collected in Public Health Surveillance?
Data collection is a key part of surveillance. There are many ways to collect health data:
- Hospital Reports: Hospitals send reports on diseases.
- Surveys: Surveys ask people about their health.
- Laboratory Data: Labs provide results from tests.
- Vital Records: Birth and death records are analyzed.
These methods help health officials gather accurate data. The data is then analyzed for trends.

Challenges in Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance has challenges. Here are some common issues:
- Data Privacy: Protecting personal information is important.
- Data Quality: Ensuring accurate data can be tough.
- Funding: Surveillance programs need funding to operate.
- Coordination: Different agencies must work together.
Despite these challenges, surveillance is vital. It helps us keep communities healthy.
The Future of Public Health Surveillance
The future looks bright for public health surveillance. New technology is changing how we collect data.
For example, mobile apps can track health information. People can report symptoms quickly. This helps officials respond faster.
Artificial intelligence can analyze data more effectively. It can find patterns that humans may miss. This will improve our understanding of health trends.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Public Health Surveillance Examples?
Public health surveillance examples include tracking diseases, monitoring health trends, and assessing health risks in populations.
Why Is Public Health Surveillance Important?
It helps identify outbreaks, monitor health trends, and guide public health actions to improve community health.
How Does Disease Surveillance Work?
Disease surveillance collects data on illness cases, analyzes trends, and informs health officials about necessary interventions.
What Are The Types Of Public Health Surveillance?
Common types include passive, active, sentinel, and syndromic surveillance, each serving different monitoring purposes.
Conclusion
Public health surveillance is essential. It helps us monitor diseases and health trends. By looking at examples like influenza and COVID-19, we see its importance.
Surveillance helps detect outbreaks early. It informs the public and shapes health policies. Despite challenges, the future of public health surveillance is promising. With new technology, we can improve health for everyone.
By understanding public health surveillance, we can all contribute to a healthier world.