Public health surveillance programs help keep people safe. They collect important health information. This information helps communities stay healthy. It also helps fight diseases. Let’s explore what public health surveillance programs are and why they matter.
What is Public Health Surveillance?
Public health surveillance is the ongoing collection of health data. It looks at diseases, injuries, and health behaviors. The goal is to find problems early. This helps health officials respond quickly. For example, if many people get sick, quick action is needed.

Why Are Surveillance Programs Important?
Surveillance programs are important for many reasons:
- Identify Health Trends: They show how diseases spread.
- Monitor Outbreaks: They help track disease outbreaks.
- Guide Public Health Policies: They inform health policies.
- Improve Health Services: They help improve health services.
- Educate the Public: They keep the public informed.
Types of Public Health Surveillance Programs
There are different types of public health surveillance programs. Each type has a special focus. Here are some common types:
1. Active Surveillance
Active surveillance means health workers actively look for cases. They contact hospitals and doctors. They ask about new cases of diseases. This helps gather more accurate data.
2. Passive Surveillance
Passive surveillance relies on reports from healthcare providers. Doctors and hospitals report diseases to health agencies. This is easier but may miss some cases.
3. Sentinel Surveillance
Sentinel surveillance uses selected sites for data collection. These sites provide information on specific health issues. This helps monitor trends over time.
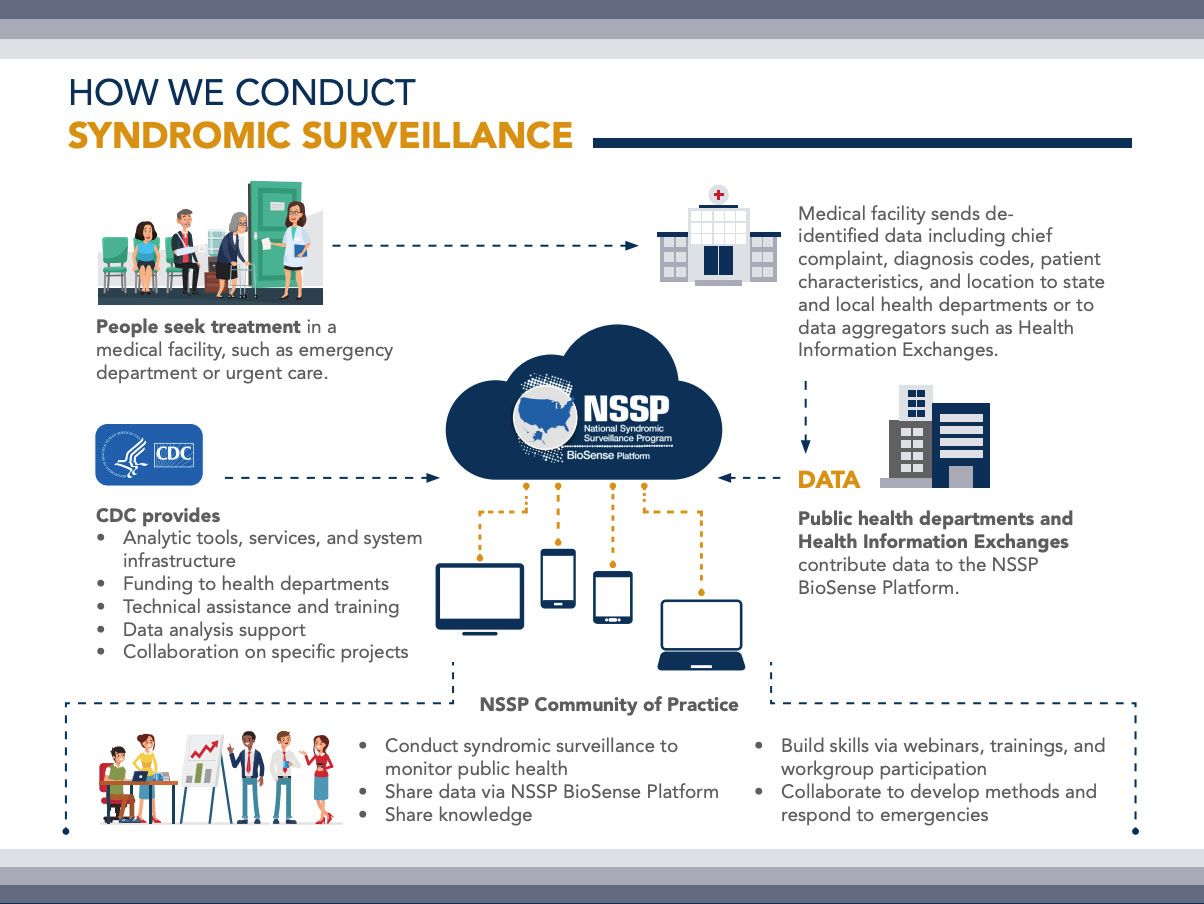
4. Syndromic Surveillance
Syndromic surveillance looks at symptoms rather than confirmed diagnoses. This helps detect outbreaks early. For example, if many people report flu-like symptoms, action can be taken quickly.
5. Laboratory Surveillance
Laboratory surveillance focuses on laboratory data. It tracks test results for diseases. This helps identify outbreaks through lab findings.
How Surveillance Programs Work
Surveillance programs work in several steps:
1. Data Collection
The first step is collecting data. Health agencies gather information from hospitals, clinics, and labs. They look for patterns in the data.
2. Data Analysis
Next, experts analyze the data. They look for trends and changes in health. This helps identify outbreaks or health issues.
3. Reporting
After analyzing, health agencies report their findings. They share information with government and public health officials. This helps them make informed decisions.
4. Response
Finally, officials take action based on the data. They may launch vaccination campaigns or health education programs. The goal is to protect public health.
Challenges in Public Health Surveillance
Surveillance programs face several challenges:
1. Data Quality
Data quality can vary. Some reports may be missing or incorrect. This makes it hard to get an accurate picture of health trends.
2. Funding
Many programs depend on funding. Limited funds can reduce the effectiveness of programs. This can lead to fewer resources for monitoring health.
3. Privacy Concerns
Privacy is important in health data. People may not want their health information shared. Programs must balance data collection and privacy.
4. Communication
Communication is key. Public health officials must share information quickly. If they do not, the public may not be aware of health risks.
Examples of Successful Surveillance Programs
Several successful surveillance programs exist worldwide:
1. The Flu Surveillance Program
This program tracks flu cases in many countries. It helps predict flu seasons and vaccine needs.
2. The Cdc’s National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System
This system collects data on diseases. It helps the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) monitor health trends.
3. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative
This initiative uses surveillance to track polio cases. It has led to a significant decrease in polio worldwide.
The Role of Technology in Surveillance
Technology plays a big part in public health surveillance:
1. Data Collection Tools
Smartphones and apps help collect health data. They make it easier to report symptoms and cases.
2. Data Analysis Software
Software can analyze large amounts of data quickly. This helps experts find trends faster.
3. Geographic Information Systems (gis)
GIS helps map health data. It shows where diseases are spreading. This helps target responses in affected areas.
How You Can Help
Everyone can contribute to public health surveillance:
1. Report Illnesses
If you get sick, report it to your doctor. This helps keep track of diseases.
2. Stay Informed
Keep up with health updates in your community. Awareness can help you stay safe.
3. Participate In Surveys
Participate in health surveys when asked. Your input matters and can help improve health programs.
4. Follow Health Guidelines
Follow public health guidelines. This helps prevent the spread of diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Public Health Surveillance Programs?
Public health surveillance programs collect and analyze health data. They help track diseases and monitor health trends.
Why Are Surveillance Programs Important In Public Health?
Surveillance programs are important because they help prevent disease outbreaks. They inform health policies and improve community health.
How Do Public Health Surveillance Programs Work?
These programs gather data from hospitals, clinics, and labs. They analyze this data to identify health issues.
What Types Of Diseases Do These Programs Monitor?
Programs monitor infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and environmental health risks. They cover a wide range of health issues.
Conclusion
Public health surveillance programs are essential. They help identify health issues early. They protect communities from diseases. By understanding these programs, we can all contribute to better health.
Healthy communities depend on active participation. Everyone plays a role in keeping each other safe. By working together, we can build a healthier future.
