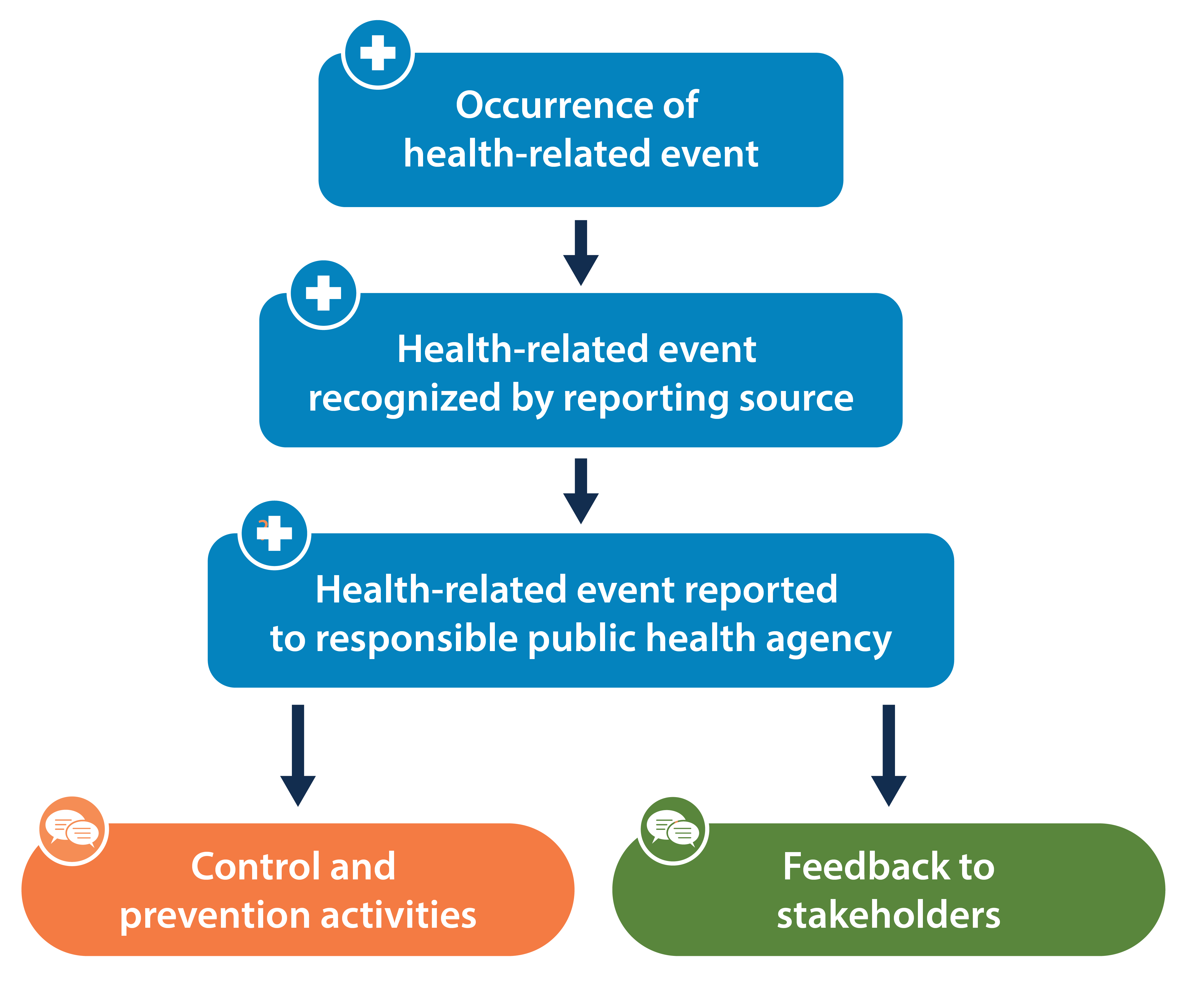
Public health surveillance is important. It helps us understand health problems. It also helps us take action. This article explains the steps involved in public health surveillance.
What is Public Health Surveillance?
Public health surveillance is the ongoing collection of health data. It looks for patterns of disease. It helps us understand how diseases spread. This information helps protect communities. It also helps save lives.
Why is Public Health Surveillance Important?
Surveillance helps track diseases. It shows where outbreaks happen. It helps find health trends over time. This information is crucial for public health decisions.
Public health officials use this data. They create policies to protect people. They also develop programs to improve health.
Steps of Public Health Surveillance
There are several key steps in public health surveillance. Each step is important to ensure effective health monitoring.
1. Define The Health Problem
The first step is to define the health problem. This means identifying what disease or health issue to track. It could be a new virus or an increase in cases of a known disease.
Clearly defining the problem helps focus efforts. It helps health officials know what to look for.
2. Collect Data
The next step is to collect data. Data can come from many sources. These include hospitals, labs, and surveys.
Data can be numbers, reports, or observations. This information is crucial for understanding health trends.
3. Analyze The Data
Once data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. This means looking for patterns or changes. Analysts use different tools to find these trends.
They might look for increases in cases. They also check if certain groups are more affected.
4. Interpret The Findings
After analyzing the data, the next step is interpretation. This means understanding what the data shows. Health officials need to know the meaning behind the numbers.
For example, if cases are rising, it may indicate an outbreak. Understanding these findings guides the next steps.
5. Take Action
Once the findings are interpreted, action must be taken. This could mean alerting the public. It might also mean setting up health programs.
Actions depend on the health problem identified. The goal is to protect the community and reduce health risks.
6. Monitor The Response
After taking action, it is important to monitor the response. This means checking if the actions are working. Public health officials need to see if cases are decreasing.
If the actions are not effective, changes may be needed. Adjustments can help improve outcomes.
7. Evaluate The Surveillance System
The final step is to evaluate the surveillance system. This means looking at how well the system works. Officials check if the data collected is useful.
They also look at the effectiveness of actions taken. This evaluation helps improve future surveillance efforts.
Examples of Public Health Surveillance
There are many examples of public health surveillance in action. Here are a few:
- Flu Surveillance: Tracking flu cases each season.
- COVID-19 Tracking: Monitoring cases and vaccination rates.
- Foodborne Illness Reporting: Identifying outbreaks from contaminated food.
Challenges in Public Health Surveillance
Public health surveillance faces several challenges. Understanding these helps improve efforts.
1. Data Collection Issues
Collecting accurate data can be difficult. Some people may not report illnesses. Others may not seek medical help. This leads to gaps in data.
2. Resource Limitations
Public health agencies often have limited resources. This can affect their ability to monitor health effectively. Staff shortages can also slow down response times.
3. Rapidly Changing Health Landscape
New diseases can emerge quickly. This makes it hard to keep up. Surveillance systems need to adapt to these changes.
4. Public Trust
Public trust is crucial for effective surveillance. If people do not trust health officials, they may not report data. Building trust is essential for good surveillance.
The Future of Public Health Surveillance
The future of public health surveillance looks promising. Technology plays a key role. Digital tools can help collect and analyze data faster.
Increased collaboration between countries is also important. Sharing data globally can help track diseases better.
Finally, educating the public is crucial. When people understand the importance of surveillance, they are more likely to participate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Steps In Public Health Surveillance?
Public health surveillance involves data collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health information.
Why Is Public Health Surveillance Important?
It helps identify health trends, outbreaks, and areas needing intervention to improve community health.
How Does Data Collection Occur In Surveillance?
Data is gathered from hospitals, labs, surveys, and other health sources to monitor health conditions.
What Types Of Data Are Used In Public Health Surveillance?
Quantitative and qualitative data, including statistics on diseases, demographics, and health behaviors, are used.
Conclusion
Public health surveillance is vital for protecting health. Understanding the steps involved helps improve the process. From defining health problems to evaluating systems, each step matters.
By working together, we can create healthier communities. Awareness and action are key to success in public health.