Implementing syndromic surveillance is vital to detect potential outbreaks, facilitating timely public health interventions to prevent widespread illnesses. Hence, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) developed the Syndromic Surveillance Implementation Guide for healthcare facilities, providing recommendations for designing and implementing an effective syndromic surveillance system. This guide assists healthcare providers and facilities in efficiently identifying and reporting disease outbreaks by monitoring diseases’ patterns and associated symptoms.
With this guide, healthcare providers can improve their disease surveillance systems, enhancing public health outcomes by acting promptly to mitigate the spread of infections. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the Syndromic Surveillance Implementation Guide’s impact on creating resilient public health surveillance systems.
What is Syndromic Surveillance?
Syndromic surveillance is a method of monitoring health conditions within a population in real-time by collecting and analyzing data from various sources, including hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. This approach uses a set of predefined symptoms or indicators, called syndromes, to identify potential outbreaks of infectious diseases or other public health threats. The goal is to detect and respond to health issues quickly before they become widespread.
The implementation of syndromic surveillance requires careful planning and collaboration between public health officials, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders. A comprehensive syndromic surveillance implementation guide should cover various topics, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation, as well as the legal, ethical, and operational considerations that come with implementing this method. Overall, the use of syndromic surveillance can help public health officials stay one step ahead of emerging health threats and protect the well-being of the population.
Understand the basics of Syndromic Surveillance
Syndromic surveillance is the process of detecting and monitoring patterns of symptoms or diseases in a population to identify potential outbreaks or public health emergencies. This type of surveillance is based on real-time data collected from various sources, including hospitals, clinics, emergency departments, and other health care facilities. The goal of syndromic surveillance is to detect early warning signs of disease outbreaks before they become widespread.
This information can then be used to mobilize resources and take action to prevent the spread of disease. The process is similar to a smoke detector in a house, which alerts homeowners to a potential fire before it spreads. By monitoring patterns of symptoms in real-time, public health officials can respond quickly and effectively to potential health threats, ultimately keeping the population safe and healthy.

Why Implement Syndromic Surveillance?
Thinking of implementing syndromic surveillance in your organization, but unsure of the benefits? A syndromic surveillance implementation guide can help you understand why it’s worth the investment. Syndromic surveillance is a public health tool that monitors symptoms and other health indicators to detect disease outbreaks early on. It can help identify patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed, allowing authorities to respond quickly and efficiently.
With the increase in global travel and urbanization, the risk of disease outbreaks is higher than ever before. Syndromic surveillance can help prevent the spread of infectious diseases and save lives. By implementing a syndromic surveillance system, you can help protect your community and promote public health.
So why wait? Start exploring the benefits of syndromic surveillance today and get ready to make a positive impact on your community.
Exploring the benefits of Syndromic Surveillance implementation
Syndromic Surveillance Syndromic surveillance is becoming increasingly important in public health surveillance. It involves monitoring and tracking the symptoms or syndromes of multiple diseases to detect and respond to emerging outbreaks or bioterrorist attacks. Implementing syndromic surveillance can provide several benefits, such as detecting diseases earlier and minimizing the spread of infection, reducing healthcare costs, and improving public health response.
By analyzing data in real-time, public health officials can identify patterns and trends that may indicate an outbreak or an increase in an existing disease. With this information, they can promptly respond by taking appropriate control measures such as initiating clinic-based outbreak investigations, updating diagnostic and treatment pathways and recommending prevention measure for upcoming community events or travel. As a result, the implementation of syndromic surveillance systems has the potential to improve public health outcomes and reduce morbidity and mortality from communicable diseases.
Getting Started with Syndromic Surveillance
If you’re looking to get started with syndromic surveillance, it’s essential to follow a clear implementation guide to ensure success. Syndromic surveillance has become increasingly popular in recent years as a way to monitor public health and detect disease outbreaks early. To get started, you’ll need to establish a surveillance system, define your population, select data sources, and determine the syndromes you’ll be monitoring.
Once you have your infrastructure in place, you can begin collecting and analyzing data to identify trends and patterns in disease prevalence. It’s important to keep in mind that the effectiveness of your syndromic surveillance will depend on the quality and completeness of your data sources. With careful planning and implementation, you can use syndromic surveillance to help protect public health and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Guiding steps to initiate Syndromic Surveillance implementation
If your healthcare facility is considering implementing syndromic surveillance, there are some key steps you can take to get started. First, determine which syndromes you want to monitor and define them clearly. This will help you identify the specific symptoms to watch for and establish protocols for reporting and responding to cases.
Next, assess your data sources and determine the best way to capture, analyze, and report the necessary information. It may be helpful to work with an experienced vendor or consultant to identify the most appropriate tools and workflows. Once you have your system in place, make sure to provide adequate training to staff members and establish protocols for ongoing monitoring, reporting, and response.
With these steps in place, you’ll be well on your way to implementing effective syndromic surveillance and keeping your community safe.
Defining surveillance objectives
When starting a syndromic surveillance program, it’s crucial to define your surveillance objectives. This involves figuring out what diseases or health concerns you want to monitor, as well as the desired outcomes and goals for your surveillance system. Defining your surveillance objectives will help you focus your efforts and resources efficiently.
You’ll be able to identify the most relevant data sources and develop effective algorithms to detect any potential outbreaks or trends. It’s also important to consider the data collection methods, such as real-time data streaming or retrospective data analysis. By setting clear surveillance objectives, you’ll be able to implement a successful syndromic surveillance system that serves your specific needs.
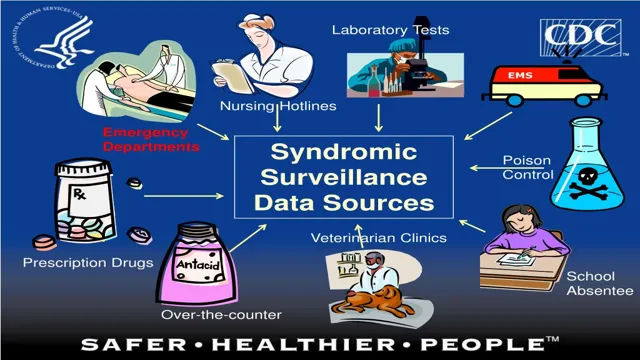
Identifying data sources
Syndromic surveillance is a powerful tool for identifying disease outbreaks and monitoring public health trends. To get started with syndromic surveillance, it’s essential to identify data sources that can provide the necessary information. One excellent source of data is emergency room visits.
Healthcare facilities can monitor the chief complaints of patients to detect unusual patterns that may indicate the start of an outbreak. Other data sources include school absenteeism rates, over-the-counter medication sales, and internet search trends for specific symptoms. By analyzing these various forms of data, public health officials can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the community’s health status and take appropriate measures to prevent the spread of disease.
However, it’s important to note that syndromic surveillance is just one part of a comprehensive public health response. It’s crucial to have trained personnel who can interpret the data correctly and identify potential outbreaks before they become a more significant public health concern.
Selecting syndromes to monitor
Syndromic surveillance involves monitoring certain syndromes to detect disease outbreaks and other public health threats in real-time. But how do we know which syndromes to monitor? Selecting syndromes to monitor requires consideration of various factors, including the frequency of occurrence, severity, and potential for rapid spread. For example, respiratory syndromes such as influenza-like illness and pneumonia are often closely monitored due to their high frequency and potential for widespread transmission.
Similarly, gastrointestinal syndromes like vomiting and diarrhea can indicate foodborne illness outbreaks and are also closely monitored. Other syndromes, such as fever of unknown origin or rash illnesses, may be less common but still important to monitor. In general, selecting syndromes to monitor involves a balancing act between frequency, severity, and potential public health impact.
By monitoring the right syndromes, public health officials can quickly detect outbreaks and respond effectively to protect the community.
Collaborating with stakeholders
Getting started with syndromic surveillance can be both exciting and daunting. One essential step is collaborating with stakeholders, such as public health officials and medical professionals, to ensure that surveillance systems capture valuable data. Syndromic surveillance refers to the monitoring of patterns in health-related data to detect and respond to outbreaks swiftly.
To achieve this, various types of data sources are used, including electronic health records and social media analytics. By engaging different stakeholders, a comprehensive syndromic surveillance system can be developed, which takes into account the unique attributes of a specific population. This includes the demographics, infectious disease prevalence, and behavioral patterns of the population.
The development of syndromic surveillance is critical in responding to emerging infectious diseases, bioterrorism, and other public health threats. Working together, public health officials and medical professionals can create a centralized system that detects and mitigates public health threats rapidly.
Tools and Technologies for Syndromic Surveillance
If you’re considering implementing syndromic surveillance, it’s important to be familiar with the various tools and technologies available. One such technology is Health Information Exchange (HIE), which facilitates the sharing of patient data across different healthcare facilities and jurisdictions. With HIE, it’s possible to aggregate and analyze data on a larger scale, which can help identify outbreaks and trends that might not be apparent at the local level.
In addition, there are specialized syndromic surveillance software solutions that can help automate the process of data collection, analysis, and reporting. Other technologies to consider include real-time data feeds from emergency departments and urgent care centers, as well as social media monitoring tools that can help detect early warning signs of potential outbreaks. When selecting tools and technologies, it’s important to consider your organization’s specific needs and capabilities, as well as any legal and ethical considerations that may apply.
With the right tools and technologies in place, implementation of a syndromic surveillance program can help improve patient outcomes and minimize the impact of both infectious and non-infectious diseases.
Exploring available tools and technologies for effective implementation
Syndromic Surveillance Syndromic surveillance is a critical tool in detecting health threats and identifying potential outbreaks of diseases. However, implementing effective syndromic surveillance requires the right tools and technologies. One critical tool is a surveillance system that captures and integrates various data sources, including emergency department visits, laboratory results, and pharmacy data.
Additionally, data visualization tools can help identify unusual patterns and analyze trends quickly. These tools must be user-friendly, intuitive, and customizable to fit specific needs. Lastly, machine learning and artificial intelligence can help automate some aspects of surveillance, such as detecting anomalies and predicting future trends.
Overall, investing in the right tools and technologies for syndromic surveillance can help identify and respond to health threats quickly, ultimately saving lives.
Data collection and management
Syndromic Surveillance Tools and Technologies for Syndromic Surveillance: Syndromic surveillance is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting health-related data in near real-time. This process is essential in detecting outbreaks or potential public health emergencies before they become widespread. The collection of data for syndromic surveillance can come from various sources such as emergency departments, primary care clinics, and even social media platforms.
One tool used for data management in syndromic surveillance is the Electronic Health Record (EHR). EHRs are an excellent source of information because they contain a patient’s medical history, laboratory data, clinical notes, and other information that can be used for surveillance. Another tool for syndromic surveillance is the use of data visualization software.
This software can be used to display data trends such as the number of patients presenting with flu-like symptoms over time. The use of these tools has significantly improved the effectiveness of syndromic surveillance and helped health officials respond quickly to potential public health threats.
Data analysis and visualization
Syndromic surveillance is a crucial public health tool that keeps track of emerging health threats in real-time. Data analysis and visualization tools are essential for making sense of the vast amounts of data collected through syndromic surveillance systems. One of the most popular data visualization tools used for syndromic surveillance is Tableau.
Tableau allows users to create interactive dashboards that enable them to drill down into the data and analyze it in different ways. Another useful tool for syndromic surveillance is SAS. SAS is a powerful statistical software package that is widely used in the healthcare industry.
It allows users to conduct data mining, predictive modeling, and statistical analysis, which are essential for identifying potential outbreaks. Other data analysis and visualization tools commonly used in syndromic surveillance include R, Python, and Excel. These tools provide a range of capabilities for analyzing and visualizing data, allowing public health officials to detect and respond to health threats in a timely manner.
Overall, having the right tools and technologies in place is critical for successful syndromic surveillance and ensuring public health.
Challenges and Solutions
Syndromic surveillance implementation guide can be a helpful tool for healthcare facilities to monitor and detect outbreaks of infectious diseases. However, implementing such a system can present some challenges. One major challenge is the availability of real-time data from different sources.
Gathering data from various sources, such as hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, and integrating them into a single system can be a difficult task. Additionally, ensuring the availability of timely and accurate data can be challenging, as data may be incomplete or delayed. There is also a need for adequate personnel and resources to manage and interpret the data.
However, there are solutions to these challenges. One solution is to establish collaborations and agreements between different sources to provide a steady supply of data. Another solution is to leverage technology and automate data collection and analysis using machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence.
Additionally, providing training and resources to personnel can help ensure successful implementation and management of the syndromic surveillance system. With careful planning and implementation, a syndromic surveillance system can be an effective tool in detecting and responding to infectious disease outbreaks.
Overcoming challenges in Syndromic Surveillance implementation
Implementing syndromic surveillance systems can be challenging, and overcoming these challenges requires careful consideration of various factors. One of the most common challenges is data quality. Syndromic surveillance relies on timely and accurate data from multiple sources, including healthcare providers, laboratories, and public health agencies.
Ensuring that the data is comprehensive, standardized, and reliable can be a complex process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Another challenge is the integration of different data sources to generate meaningful insights. This requires a robust IT infrastructure and skilled staff to manage and analyze large volumes of data.
Other challenges may include privacy concerns, resource constraints, and stakeholder buy-in. To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to leverage innovative technologies such as AI and machine learning in data analysis and invest in capacity building and training to ensure staff have the required skills. Engaging and communicating with stakeholders such as healthcare providers is also crucial to building trust and ensuring collaboration in the implementation of syndromic surveillance systems.
Ultimately, the success of syndromic surveillance relies on comprehensive planning, continuous evaluation, and collaboration across different sectors and stakeholders.
Implementing effective solutions
Implementing effective solutions can be a challenging task, especially in dynamic environments where circumstances may change rapidly. One of the main roadblocks that organizations and businesses face is carrying out solutions that cater to the needs of all stakeholders. It is imperative to take diverse opinions into account to arrive at workable solutions.
Another key challenge is identifying the root cause of the problem, which requires a systematic approach and thorough analysis. It is also essential to establish clear communication channels that allow all stakeholders to share their ideas and express their concerns. Effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings and fosters collaboration among teams.
Moreover, implementing solutions requires careful planning to ensure that all resources are allocated optimally. Planning ensures that solutions are realistic and that they address the underlying causes of the problem. Additionally, organizations must evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented solutions to determine if they deliver the expected outcomes.
It is essential to monitor the results, gather feedback, and make any necessary adjustments to the solutions. By addressing these challenges and implementing effective solutions, organizations can overcome obstacles and achieve their goals successfully.
Moving Forward with Syndromic Surveillance
Are you considering implementing syndromic surveillance in your healthcare facility? Look no further than the syndromic surveillance implementation guide. This guide is designed to provide step-by-step instructions on how to set up syndromic surveillance in your facility, from collecting data to analyzing and interpreting it. With syndromic surveillance, you can detect disease outbreaks and other public health concerns much earlier than with traditional surveillance methods.
The guide is easy to follow and can help you take the first steps towards enhancing your facility’s ability to protect public health. Don’t let outbreaks catch you off guard – consider implementing syndromic surveillance today using the syndromic surveillance implementation guide.
Sustaining and improving Syndromic Surveillance implementation
Syndromic Surveillance Syndromic surveillance has become an integral part of public health responses. Moving forward, it is essential to sustain and improve its implementation. One way to achieve this is by integrating syndromic surveillance into electronic health records (EHR) systems.
This will enable data collection to be automated, increasing efficiency, accuracy, and timeliness. The integration will also allow for better data sharing between healthcare facilities and public health departments, aiding in early detection and response to potential outbreaks. To sustain syndromic surveillance, it is also important to continually train and educate healthcare workers on how to use the system correctly and the importance of reporting unusual patterns of illnesses.
Furthermore, advances in data analysis techniques and artificial intelligence can improve the system’s capabilities in detecting disease patterns in real-time. These techniques can also assist in predicting and identifying possible outbreaks, allowing for early intervention and containment. In conclusion, sustaining and improving the implementation of syndromic surveillance requires integrating it into EHR systems, continually training healthcare workers, and utilizing advances in data analysis techniques and artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing syndromic surveillance is like having a superhero on your team. It allows you to identify and respond to potential health threats before they become full-blown disasters. With the right tools and strategies in place, you can stay one step ahead of the curve and protect your community from any unusual spikes in illness.
So don your cape and mask, and let syndromic surveillance be your trusty sidekick in the fight against disease outbreaks!”
FAQs
What is syndromic surveillance?
Syndromic surveillance is a public health practice that uses non-specific indicators, such as symptoms or healthcare utilization records, to detect potential disease outbreaks or unusual health events.
How can syndromic surveillance be implemented in practice?
Syndromic surveillance can be implemented through the collection and analysis of health-related data from various sources, such as hospitals, clinics, emergency departments, and public health agencies. It can involve the use of specialized software or algorithms to identify patterns and anomalies that may signal an outbreak or other potential health threat.
What are some of the advantages of syndromic surveillance?
Syndromic surveillance can help public health officials detect outbreaks more quickly, which can enable faster and more effective response efforts. It can also help identify new and emerging diseases, detect bioterrorism or other deliberate attacks on public health, and monitor trends and patterns in disease incidence and prevalence.
What are some of the challenges involved in implementing effective syndromic surveillance systems?
Some of the challenges associated with implementing effective syndromic surveillance systems include data quality issues, the need for robust and reliable data sources, the complexity of the algorithms and analytics used to analyze the data, and the need for effective communication and collaboration among different stakeholders (e.g. healthcare providers, public health officials, and emergency responders).