Featured image for this comprehensive guide about what is better nvr or dvr
Image source: igzy.com
In today’s world, securing your home isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. With a myriad of options available, choosing the right video surveillance system can feel like navigating a maze. Two primary contenders often emerge in this decision-making process: DVR and NVR systems. You’ve likely heard these acronyms thrown around, but what do they truly mean, and more importantly, what is better, NVR or DVR, for your specific home security needs?
The choice between an NVR system and a DVR system isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. Each technology offers distinct advantages and disadvantages tailored to different requirements, budgets, and technical savviness. This comprehensive guide will demystify both options, helping you understand their core differences, benefits, and ultimately, empowering you to make an informed decision for robust home security.
📋 Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics: DVR vs. NVR Technology
Before we dive into the “better” debate, let’s establish a foundational understanding of what each system entails. While both serve the purpose of recording video surveillance, they operate on fundamentally different principles.
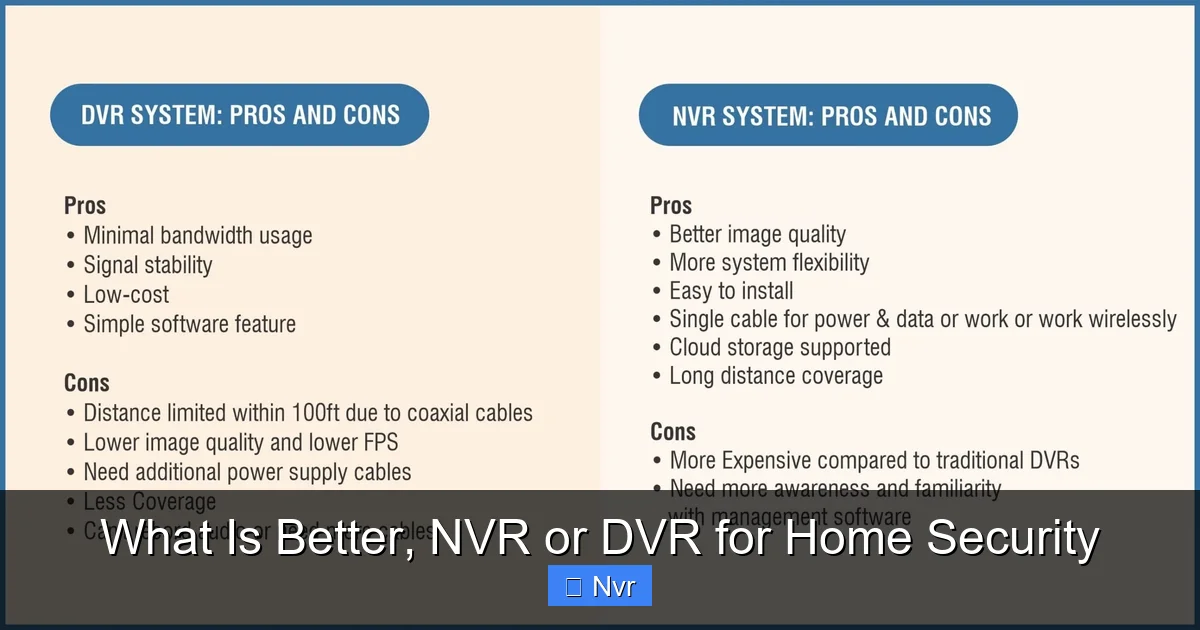
What is a DVR System?
A DVR, or Digital Video Recorder, is the more traditional approach to video surveillance. It works by connecting directly to analog security cameras via coaxial cables. Here’s how it generally functions:
| Feature/Aspect | NVR (Network Video Recorder) | DVR (Digital Video Recorder) |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | IP Cameras (Ethernet/Wi-Fi) | Analog Cameras (Coaxial BNC) |
| Video Resolution | Higher; typically 1080p up to 4K, 8K+ | Lower; typically 720p, 1080p (max 5MP for HD-TVI/CVI/AHD) |
| Cabling & Power | Single Ethernet cable for video, power (PoE) & data | Separate coaxial video cable and power cable per camera |
| Flexibility & Placement | Cameras connect via network, offering greater placement flexibility | Cameras connect directly to DVR, limited by coaxial cable length |
| Initial Cost (Approx.) | Generally higher due to advanced camera technology | Generally lower for cameras and recorder |
- Analog Cameras: DVR systems rely on analog cameras, which capture raw, uncompressed video signals.
- Coaxial Cables: These cables transmit the video signal from each camera to the DVR unit. Power for the cameras often requires separate wiring.
- On-Site Processing: The DVR unit itself is responsible for processing, compressing, and storing the video footage. It converts the analog signal into a digital format for storage on a hard drive.
DVR technology has been a staple in home and business security for decades, known for its reliability and relatively straightforward setup for basic applications.
What is an NVR System?
An NVR, or Network Video Recorder, represents a newer, more advanced approach to video surveillance, primarily designed for IP (Internet Protocol) cameras. Key characteristics include:
- IP Cameras: NVR systems use IP cameras, which are essentially small computers with their own operating systems. These cameras process video footage directly at the camera.
- Ethernet Cables (PoE): IP cameras connect to the NVR via standard Ethernet cables. Many NVRs support Power over Ethernet (PoE), meaning a single cable provides both power and data transmission, simplifying installation.
- Network-Based: The NVR typically doesn’t process raw video; instead, it receives already processed and compressed digital streams from the IP cameras over a network. Its primary role is recording and managing these streams.
NVR systems leverage network technology to offer greater flexibility and advanced features, making them a popular choice for modern security setups.
Key Differences: NVR vs. DVR at a Glance
To truly understand what is better, NVR or DVR, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental distinctions that impact performance, installation, and capabilities:

Learn more about what is better nvr or dvr – What Is Better, NVR or DVR for Home Security
Image source: securitycamcenter.com
- Camera Type: DVR uses analog cameras; NVR uses IP cameras.
- Video Processing Location: With a DVR system, the recorder processes the raw video. With an NVR system, the camera processes the video before sending it to the recorder.
- Cabling: DVRs use coaxial cables; NVRs primarily use Ethernet cables (often PoE).
- Flexibility: NVRs generally offer much greater flexibility in camera placement and connectivity options (including wireless IP cameras).
- Resolution & Quality: IP cameras (NVR) typically offer significantly higher resolutions and better image quality than analog cameras (DVR).
The Advantages of an NVR System
If you’re leaning towards a more future-proof and feature-rich security setup, an NVR system often stands out. Here’s why:

Learn more about what is better nvr or dvr – What Is Better, NVR or DVR for Home Security
Image source: innobytech.com
- Superior Image Quality: IP cameras support much higher resolutions, from 4MP to 4K and even 8K, delivering incredibly clear and detailed footage. This is crucial for identifying faces or license plates, a key benefit when deciding NVR or DVR.
- Simpler Installation (PoE): Thanks to Power over Ethernet (PoE), a single Ethernet cable can power the camera and transmit data to the NVR. This dramatically simplifies wiring, reducing installation time and costs.
- Greater Flexibility and Coverage: IP cameras can be placed virtually anywhere a network connection is available, even wirelessly. This allows for broader coverage and easier expansion of your home security camera systems.
- Advanced Features & Analytics: NVR systems, powered by smart IP cameras, often come with advanced features like AI-powered facial recognition, object detection, perimeter intrusion detection, two-way audio, and remote pan/tilt/zoom capabilities.
- Enhanced Security: IP camera footage can be encrypted before transmission, offering a more secure video stream compared to analog DVR systems.
- Scalability: It’s generally easier to add or remove cameras from an NVR system, as it leverages existing network infrastructure.
The Advantages of a DVR System
While NVRs boast cutting-edge features, DVR systems still hold significant appeal for certain users, particularly those on a budget or with existing infrastructure:
- Lower Cost: Generally, DVR systems are more affordable than NVRs, especially when considering the initial hardware purchase of the recorder and analog cameras. This can be a major factor if budget is a primary concern in your NVR or DVR decision.
- Simpler Technology: For users who prefer a straightforward, less complex system without the need for advanced network configuration, a DVR system can be easier to set up and manage.
- Compatibility with Legacy Systems: If you already have analog cameras installed and only need to upgrade your recording unit, a DVR might be the most cost-effective solution, allowing you to reuse existing cabling.
- Robustness: Since DVRs are hardwired with coaxial cables, they are often less susceptible to network interference or Wi-Fi signal issues that can sometimes affect IP camera performance.
NVR vs. DVR: A Quick Comparison Table
To help you quickly visualize the distinctions, here’s a side-by-side comparison of key features when considering NVR or DVR:
| Feature | NVR System | DVR System |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | IP Cameras (Digital) | Analog Cameras |
| Video Processing | Processed at the camera | Processed at the recorder |
| Cabling | Ethernet (often PoE) | Coaxial |
| Video Quality | High (4MP, 4K, 8K) | Standard (720p, 1080p) |
| Cost (Initial) | Higher | Lower |
| Installation Ease | Simpler (PoE single cable) | More complex (power/data separate) |
| Advanced Features | Yes (AI, analytics, 2-way audio) | Limited / Basic |
| Flexibility/Scalability | High | Limited |
Which Security System Is Right For You?
The question of what is better, NVR or DVR, ultimately boils down to your specific needs and priorities. Consider the following factors:
- Your Budget: If cost is your absolute top priority and you need a basic, functional system, a DVR system is often the more economical choice. If you have a larger budget and see security as a long-term investment, an NVR system offers more value.
- Desired Image Quality: Do you need crystal-clear footage for detailed identification? If so, the higher resolutions of an NVR system with IP cameras are indispensable. For general monitoring where fine details aren’t critical, a DVR might suffice.
- Installation Preferences: Are you comfortable with network setup, or do you prefer a simpler, traditional wiring method? NVR systems with PoE cameras offer simpler wiring, making DIY installation more feasible for some. DVRs require more separate wiring, which can be more labor-intensive if starting from scratch.
- Future-Proofing and Features: If you want advanced analytics, smart home integration, and a system that can easily expand and adapt to future technologies, an NVR is the clear winner.
- Existing Infrastructure: Do you have existing coaxial cables or analog cameras you wish to retain? A DVR would be a more straightforward upgrade path. If you’re starting fresh, an NVR offers more modern capabilities.
Conclusion
Deciding what is better, NVR or DVR, isn’t about one being inherently superior in all aspects, but rather which system aligns best with your individual requirements. A DVR system offers an affordable, reliable, and straightforward solution for basic surveillance needs, especially when budget is tight or existing analog infrastructure is present. On the other hand, an NVR system provides advanced features, superior image quality, and greater flexibility, making it ideal for those seeking a high-performance, scalable, and future-proof home security solution.
Take the time to assess your priorities – budget, image clarity, installation complexity, and desired features – and you’ll be well-equipped to choose the surveillance system that offers you the most peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main difference between NVR and DVR systems for home security?
DVR (Digital Video Recorder) systems use analog cameras and process video at the recorder, while NVR (Network Video Recorder) systems utilize IP cameras that process video at the camera itself before sending it to the recorder. This fundamental distinction impacts video quality, installation, and flexibility within your home security setup.
Which offers better video quality, an NVR or DVR system?
NVR systems generally offer significantly better video quality, often supporting resolutions up to 4K and beyond. This is because they use IP cameras that capture and process higher-resolution digital signals, whereas DVR systems are limited by the analog signal standard, typically maxing out at 1080p.
Is NVR or DVR easier to install for home security?
NVR systems using PoE (Power over Ethernet) cameras are often considered easier to install as a single Ethernet cable provides both power and data. DVR systems, however, require two cables per camera – one for video and one for power – which can complicate wiring in some scenarios.
Which is more affordable, an NVR or DVR security system?
Typically, DVR systems tend to be more affordable upfront due to the lower cost of analog cameras and recorders. NVR systems, with their advanced IP cameras and digital capabilities, represent a higher initial investment but often provide better long-term value and scalability for your home security.
How do NVR and DVR systems handle camera connectivity and placement?
NVR systems offer greater flexibility as IP cameras connect via Ethernet and can be placed anywhere on a network, even wirelessly. DVR systems require coaxial cables to run directly from each analog camera to the DVR, limiting placement based on cable length and complexity.
For future expansion, is NVR or DVR a better home security choice?
NVR systems are generally more future-proof and scalable. Their IP-based nature allows for easy integration of new cameras, higher resolutions, and advanced features as technology evolves, whereas DVR systems are more constrained by older analog standards and limited upgrade paths.