
Featured image for this comprehensive guide about what is nvr and how it works
Image source: securitycamcenter.com
In an increasingly security-conscious world, choosing the right surveillance system is paramount. You’ve likely heard terms like DVR and NVR thrown around, but what do they really mean for your home or business security? While DVRs (Digital Video Recorders) have been a long-standing solution, modern security demands have ushered in the era of NVR CCTV systems. But what exactly is NVR, and how does it revolutionize the way we monitor our spaces?
If you’re looking to upgrade your security, understand the latest technology, or simply differentiate between the options, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will demystify Network Video Recorders, explain their inner workings, highlight their advantages, and clarify how they stand apart from their DVR predecessors.
📋 Table of Contents
What Exactly is NVR CCTV?
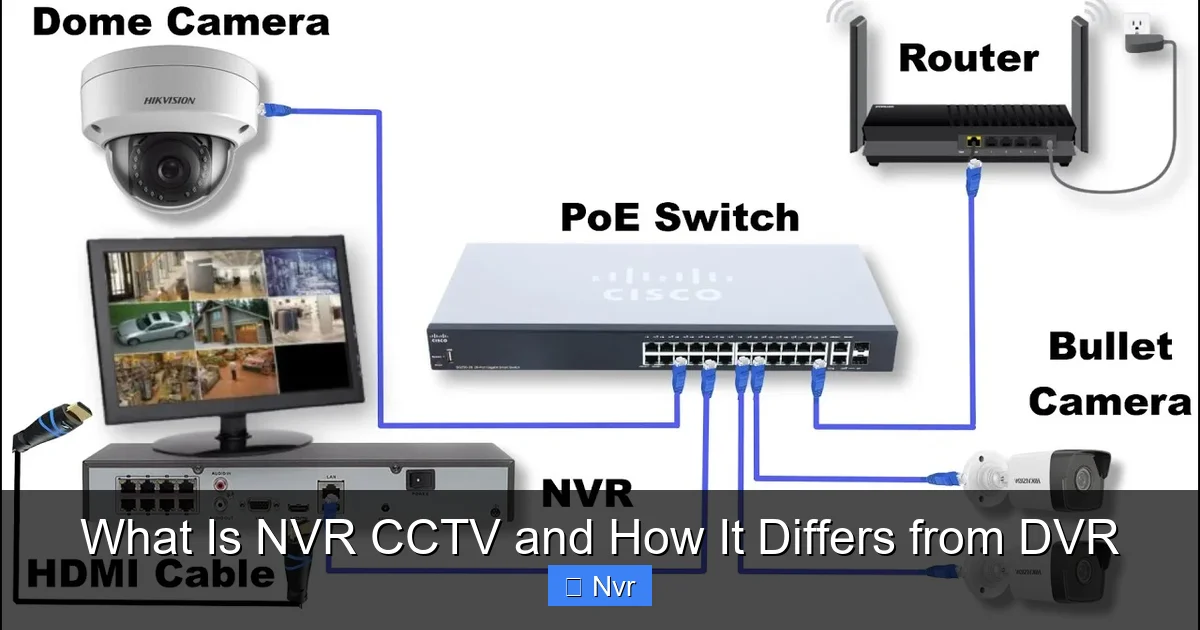
At its core, NVR stands for Network Video Recorder. As the name suggests, it’s a dedicated device used to record and store video footage from IP cameras (Internet Protocol cameras) over a network. Unlike traditional analog systems, an NVR system is entirely digital, designed to work seamlessly with advanced network-based cameras.
Think of the NVR as the central hub for your entire IP camera surveillance system. It receives digital video streams directly from each camera via an Ethernet connection, manages these streams, and stores them on a hard drive for later viewing. This digital-first approach is what gives NVR CCTV its significant edge in performance, flexibility, and features.
| NVR Aspect | How it Works / Description | Key Benefit / Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| **Core NVR Function** | Digitally records, stores, and manages video streams received directly from IP (Internet Protocol) cameras over a network. | Processes video *at the camera* before streaming to NVR, ensuring higher video quality (e.g., 4K, 8MP). |
| **IP Cameras** | Each camera is a “smart” network device with its own IP address, encoder, and often built-in analytics. Connects directly to the network. | Superior image resolution, advanced features (motion detection, facial recognition), flexible placement. |
| **Network Connectivity** | Cameras transmit video data packets via standard Ethernet cables (often with PoE – Power over Ethernet) or Wi-Fi to the NVR or a network switch. | Simplified cabling (PoE provides power and data), easy scalability, remote access over the internet. |
| **Video Storage** | NVR stores compressed digital video streams on internal hard disk drives (HDDs), typically supporting multiple drives for extended capacity. | Storage capacities range from 1TB to 16TB+, allowing weeks to months of continuous or event-based recording. |
| **Remote Access & Management** | NVR connects to the internet, enabling users to view live feeds, playback recordings, and manage settings via dedicated mobile apps or web browsers. | Monitor your property from anywhere, receive instant alerts, and manage multiple NVRs/cameras centrally. |
How Does a Network Video Recorder (NVR) System Work?
Understanding the “how” behind an NVR system reveals its inherent strengths. The operational process is fundamentally different from older DVR systems:

Learn more about what is nvr and how it works – What Is NVR CCTV and How It Differs from DVR
Image source: blog.swann.com
- Camera Processing First: The critical distinction lies in where the video processing occurs. With an NVR system, each IP camera is essentially a mini-computer. It captures the raw video footage, compresses it into a digital format (like H.264 or H.265), and then encodes it. This “processing at the source” ensures higher quality and more intelligent features directly at the camera level.
- Network Transmission: Once processed, the digital video stream is transmitted from the IP camera to the NVR over a standard Ethernet network cable (Cat5e, Cat6, etc.). This can be a dedicated network or part of your existing local area network (LAN).
- PoE Simplicity: Many modern NVRs come with built-in Power over Ethernet (PoE) ports. This means a single Ethernet cable can provide both power and data connectivity to the IP camera, significantly simplifying installation and reducing wiring complexity.
- NVR Recording & Management: The NVR receives these pre-processed digital video streams, decodes them if necessary for display, and writes them to its internal hard drives for storage. It also provides the interface for viewing live feeds, playing back recorded footage, configuring camera settings, and managing the overall system.
The Unmistakable Advantages of NVR Systems
The digital nature of NVR systems brings a host of benefits that make them the preferred choice for modern security applications:
Learn more about what is nvr and how it works – What Is NVR CCTV and How It Differs from DVR
Image source: i.ytimg.com
- Superior Image Quality: NVRs work with high-resolution IP cameras, supporting resolutions far beyond traditional analog systems – commonly 1080p, 4K, and even 8K. This translates to incredibly clear, detailed footage, crucial for identification purposes.
- Greater Flexibility and Scalability: Because cameras connect over a network, they don’t need to be physically close to the NVR. This allows for wider camera placement, even across multiple buildings or remote locations accessible via the internet. Adding new cameras is often as simple as connecting them to the network.
- Advanced Features and Analytics: IP cameras often come packed with intelligent features like motion detection zones, facial recognition, object detection, line crossing, and more. Since the processing happens at the camera, these features are often more robust and accurate, with the NVR simply recording the results or alerts.
- Simplified Installation with PoE: As mentioned, PoE functionality greatly streamlines wiring. A single cable handles both power and data, reducing the need for separate power outlets for each camera and making setup quicker and cleaner.
- Enhanced Remote Access: With network connectivity at its core, NVR systems offer robust remote viewing capabilities. You can typically access your live feeds and recorded footage from anywhere in the world using a smartphone app or web browser.
NVR vs. DVR: Understanding the Fundamental Differences
While both NVRs and DVRs serve the purpose of recording surveillance footage, their underlying technology and capabilities are vastly different. Understanding these distinctions is key to making an informed decision:
| Feature | NVR (Network Video Recorder) | DVR (Digital Video Recorder) |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | IP Cameras (digital) | Analog Cameras (coaxial, BNC) |
| Connection Type | Ethernet cable (Cat5e/Cat6) | Coaxial cable (BNC connectors) |
| Video Processing | Processed and encoded by the IP camera itself. | Processed and encoded by the DVR unit. |
| Image Quality | Superior (1080p, 4K, 8K+ supported) | Limited (typically 720p, 1080p for HD-TVI/CVI/AHD) |
| Flexibility/Scalability | Highly flexible; cameras can be anywhere on the network, easy to add. | Limited by coaxial cable length and direct connection to DVR. |
| Power Supply | Often via PoE (Power over Ethernet) from NVR/switch. | Requires separate power adapter for each camera. |
| Cable Runs | Longer distances possible without signal degradation. | Signal degrades over long coaxial cable runs. |
| Intelligence | Advanced analytics at the camera level. | Basic analytics, often processed by the DVR. |
Is NVR the Right Choice for Your Security Needs?
Choosing between an NVR and a DVR system largely depends on your specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and budget. Here are some actionable tips to help you decide:
- For New Installations: If you’re starting from scratch, an NVR system is almost always the recommended choice. The benefits in terms of image quality, flexibility, and advanced features far outweigh the initial cost difference for most users.
- For Upgrading Existing Analog Systems: If you have an existing analog system with serviceable coaxial cabling, a hybrid DVR (which can support both analog and some IP cameras) might be a temporary solution. However, to truly leverage modern surveillance, a full transition to an NVR system with new IP cameras is advisable.
- Consider Your Budget: While NVR systems and IP cameras can have a higher upfront cost than their analog counterparts, the long-term benefits in terms of performance, reduced maintenance, and advanced capabilities often justify the investment.
- Prioritize Image Quality: If clear identification, facial recognition, or detailed monitoring is crucial for your security, then an NVR system with high-resolution IP cameras is non-negotiable.
- Future-Proofing: NVR technology is constantly evolving, offering more intelligent features and integration possibilities. Investing in an NVR system ensures your security infrastructure is ready for future advancements.
The Future of Surveillance: Why NVR is Leading the Way
The landscape of security surveillance is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in digital technology and network capabilities. NVR CCTV systems are at the forefront of this evolution, offering robust, scalable, and intelligent solutions that traditional DVRs simply cannot match.
From crystal-clear 4K footage to advanced video analytics that can alert you to specific events, NVRs empower users with unprecedented control and insight into their security environments. As connectivity becomes more ubiquitous and intelligent features become standard, the Network Video Recorder will continue to be the backbone of effective and future-ready security systems. Embrace the digital age of surveillance and discover the power of NVR for comprehensive protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is NVR CCTV?
NVR stands for Network Video Recorder, and it’s a key component in a modern IP (Internet Protocol) based CCTV surveillance system. Unlike DVRs, an NVR records and manages video footage from digital IP cameras directly over a network connection.
How does an NVR CCTV system actually work?
In an NVR system, IP cameras encode and process video footage themselves, then transmit the digital video stream over a network (like Ethernet or Wi-Fi) to the NVR. The NVR’s primary role is to record, store, and allow viewing of this already processed digital footage, essentially acting as a central hub for your IP cameras.
What’s the main difference between NVR and DVR CCTV systems?
The core difference lies in the type of cameras they support and where the video processing occurs. DVRs (Digital Video Recorders) work with analog cameras, processing and digitizing the video signal at the DVR unit itself, whereas NVRs exclusively use IP cameras that process video digitally at the camera before sending it over the network.
What are the key advantages of choosing an NVR system over a DVR?
NVR systems generally offer superior image quality and higher resolutions, often supporting up to 4K and beyond, due to their use of IP cameras. They also provide greater flexibility in camera placement, easier scalability, and more advanced features like video analytics directly from the cameras.
What types of cameras are compatible with an NVR?
NVRs are designed to work with IP (Internet Protocol) cameras. These can be connected via Ethernet cables, often utilizing Power over Ethernet (PoE) for simplified installation, or through Wi-Fi for wireless connectivity, depending on the camera and NVR model.
How is video footage stored and accessed with an NVR?
Video footage is typically stored on internal hard drives within the NVR unit, offering large capacities for continuous recording. You can access and view the footage locally via a monitor connected to the NVR, or remotely through a dedicated mobile app or web browser, allowing you to monitor your property from anywhere with an internet connection.