Epidemiologic surveillance is a big term. But it means something simple. It is about watching diseases. This helps keep people healthy. In this article, we will talk about why this is important.
What is Epidemiologic Surveillance?
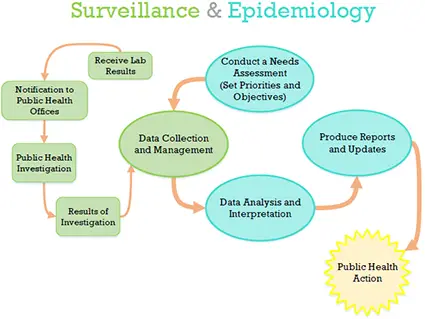
Epidemiologic surveillance means collecting and studying health data. This data shows how diseases spread. It also helps find out who gets sick. Public health workers use this information. They use it to stop diseases before they spread.
Why is Surveillance Important?
Surveillance has many benefits. Let’s look at a few key reasons.
1. Early Detection Of Diseases
One main reason is early detection. When health workers monitor diseases, they see new cases quickly. This helps catch outbreaks early. Early detection can save lives. It helps doctors treat people faster.
2. Understanding Disease Patterns
Surveillance helps understand how diseases work. It shows patterns over time. For example, it can show if a disease is spreading. It can also show if it is getting worse. This information helps health workers plan better.
3. Informing Public Health Policies
Surveillance data helps make health policies. Governments use this information. They can create plans to control diseases. For example, if a flu outbreak happens, they may start a vaccination campaign. This helps protect people.
4. Resource Allocation
Surveillance helps decide where to send resources. If a disease is spreading fast in one area, more help is needed. This can include medicines, vaccines, or health workers. Proper allocation saves lives and helps control diseases.
5. Monitoring The Effectiveness Of Interventions
Health workers also need to know what works. Surveillance helps monitor health programs. For example, if a new vaccine is given, surveillance shows how well it works. This feedback helps improve health services.
Types of Epidemiologic Surveillance
There are different types of surveillance. Each type has its own purpose. Here are a few types:
1. Passive Surveillance
Passive surveillance is when health workers wait for reports. Hospitals and clinics send data when they see cases. This method is cost-effective. But it can miss some cases.
2. Active Surveillance
Active surveillance is more hands-on. Health workers contact hospitals. They look for cases directly. This method is more accurate. But it takes more time and money.
3. Sentinel Surveillance
Sentinel surveillance uses selected sites. These sites report cases. This method helps track trends. It is effective for important diseases.
4. Syndromic Surveillance
Syndromic surveillance looks at symptoms. It does not wait for a diagnosis. This method helps find outbreaks quickly. For example, if many people have similar symptoms, action can be taken.

Challenges in Epidemiologic Surveillance
Surveillance is not always easy. There are challenges to overcome. Here are some common challenges:
1. Data Quality
Data quality is very important. Sometimes, data is missing or incorrect. This can lead to wrong conclusions. It is crucial to ensure accurate data collection.
2. Funding Issues
Surveillance needs money. Sometimes, funds are limited. This affects how well surveillance works. More funding can help improve systems.
3. Technology Barriers
Technology can help collect data. But not all places have good technology. This can create gaps in surveillance.
4. Public Cooperation
Public cooperation is essential. People must report illnesses. If they do not report, data may be incomplete. Education is important to encourage reporting.
Examples of Successful Epidemiologic Surveillance
Many countries have seen success with surveillance. Here are a few examples:
1. Influenza Monitoring
Many countries track influenza cases. They collect data during flu season. This helps predict outbreaks. Vaccination campaigns are planned based on this data.
2. Covid-19 Response
The COVID-19 pandemic showed the need for surveillance. Countries monitored case numbers. They tracked the spread of the virus. This helped implement health measures quickly.
3. Measles Control
Measles is a preventable disease. Countries with strong surveillance reduced cases. They monitored vaccination rates. This helped keep communities safe.
How to Improve Epidemiologic Surveillance
Improving surveillance is important for public health. Here are some ways to do it:
1. Invest In Technology
Investing in better technology helps collect data. This includes software and tools. Better technology leads to better data quality.
2. Train Health Workers
Training health workers is essential. They must understand how to collect and report data. Regular training keeps skills up-to-date.
3. Increase Public Awareness
Public awareness campaigns are important. They help people understand the importance of reporting illnesses. This can lead to better data collection.
4. Foster Collaborations
Collaboration is key in public health. Different organizations can share data. This leads to a better understanding of disease trends.

Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is Epidemiologic Surveillance Crucial For Public Health?
Epidemiologic surveillance helps track diseases and outbreaks. It guides public health actions to prevent illness.
What Role Does Data Play In Epidemiologic Surveillance?
Data is vital. It helps identify health trends, monitor outbreaks, and inform public health decisions.
How Does Surveillance Improve Disease Prevention?
Surveillance detects diseases early. This helps stop the spread and protects community health.
Why Is Timely Reporting Important In Surveillance?
Timely reporting allows quick action. It prevents further spread and saves lives.
Conclusion
Epidemiologic surveillance is important for public health. It helps detect diseases early. It informs policies that protect communities. Despite challenges, it is vital for health systems.
By improving surveillance, we can save lives. Together, we can create a healthier future for everyone.