
Featured image for this comprehensive guide about are doorbells dc or ac
Image source: images.nexusapp.co
Ding-dong! It’s one of the most common sounds in any home, but have you ever stopped to wonder how that simple chime actually works? Specifically, what kind of electricity powers it? The question of are doorbells DC or AC is more nuanced than you might think, and understanding the difference can be crucial whether you’re troubleshooting an old system, installing a new smart doorbell, or simply satisfying your curiosity.
Many homeowners assume all electronics run on AC (Alternating Current) from their wall outlets or DC (Direct Current) from batteries. While both are true for various household gadgets, doorbells occupy a unique space. The answer isn’t a simple “yes” or “no” but rather, “it depends” on the type and age of your doorbell system. Let’s demystify the power behind your front door’s greeting.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the power requirements for traditional wired doorbells, modern wireless units, and cutting-edge smart doorbells. You’ll gain a clear understanding of what makes your doorbell chime, learn how to identify your system’s doorbell power supply, and even pick up some actionable tips for maintenance and upgrades.
📋 Table of Contents
- The Short Answer: It Depends on Your Doorbell Type
- Traditional Wired Doorbells: Usually Low-Voltage AC
- Wireless Doorbells: Exclusively DC Power
- Smart Doorbells: A Mix of AC and DC
- Why Low Voltage? Safety and Efficiency
- Key Differences: AC vs. DC Doorbell Systems at a Glance
- Conclusion: Knowing Your Doorbell’s Power Is Key
The Short Answer: It Depends on Your Doorbell Type
So, are doorbells DC or AC? The truth is, doorbells can be powered by either, depending on their design and installation. This often boils down to three main categories:
- Traditional Wired Doorbells: These almost universally rely on low-voltage AC power, supplied by a dedicated transformer.
- Wireless Doorbells: These are typically battery-powered, meaning they run on DC power.
- Smart Doorbells: These are the most versatile, often capable of using existing low-voltage AC wiring (which they convert to DC internally), or being entirely battery-powered (DC), or using a dedicated DC power adapter.
The key takeaway here is that while your home’s main electrical system uses high-voltage AC, most doorbells operate at a much safer, lower voltage, often converting or stepping down that power.
| Doorbell Category | Primary Power Source | Typical Voltage Range | Key Characteristics / Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Wired Doorbell | AC (Transformer-powered) | 8-24V AC | Most common type in older homes, uses existing electrical wiring, mechanical chime. |
| Wireless Doorbell | DC (Battery-powered) | 3-12V DC | Easy installation, portable, transmitter and receiver units, requires battery replacement. |
| Smart Video Doorbell | AC (Wired via transformer) OR DC (Rechargeable battery) | 16-24V AC (wired), 3.6-7.2V DC (battery) | Offers video/audio feed, Wi-Fi connectivity, app control, motion detection, can be wired or wireless. |
Traditional Wired Doorbells: Usually Low-Voltage AC
For decades, the standard wired doorbell system has operated using low-voltage Alternating Current (AC). This AC power is not directly from your wall outlet but is instead stepped down from your home’s 120V or 240V AC supply by a small, dedicated component called a transformer. This AC transformer doorbell is typically located near your main electrical panel, in a basement, attic, or sometimes even attached to a junction box near the doorbell chime unit itself.
Learn more about are doorbells dc or ac – Are Doorbells DC or AC Powered? The Clear Answer
Image source: doityourself.com
A typical wired doorbell voltage can range from 8V AC to 24V AC, with 16V AC being one of the most common outputs. The reason for using low-voltage AC is primarily safety and simplicity. You don’t need high voltage to make a chime sound, and low voltage reduces the risk of electrical shock during installation or maintenance. The AC current is also simple to step down using a transformer, making it a very robust and long-lasting system.
How a Wired Doorbell System Works
A traditional wired doorbell system comprises three main components:
- Transformer: Converts high-voltage AC from your home’s electrical system into low voltage doorbell AC. This is the heart of the power supply.
- Doorbell Button: When pressed, it completes a circuit, allowing the low-voltage AC to flow to the chime.
- Chime Unit: Receives the low-voltage AC signal, causing a solenoid to strike metal bars, producing the familiar “ding-dong” sound.
This setup means that if your wired doorbell is not working, the first places to check are often the transformer, the button, or the chime unit itself.
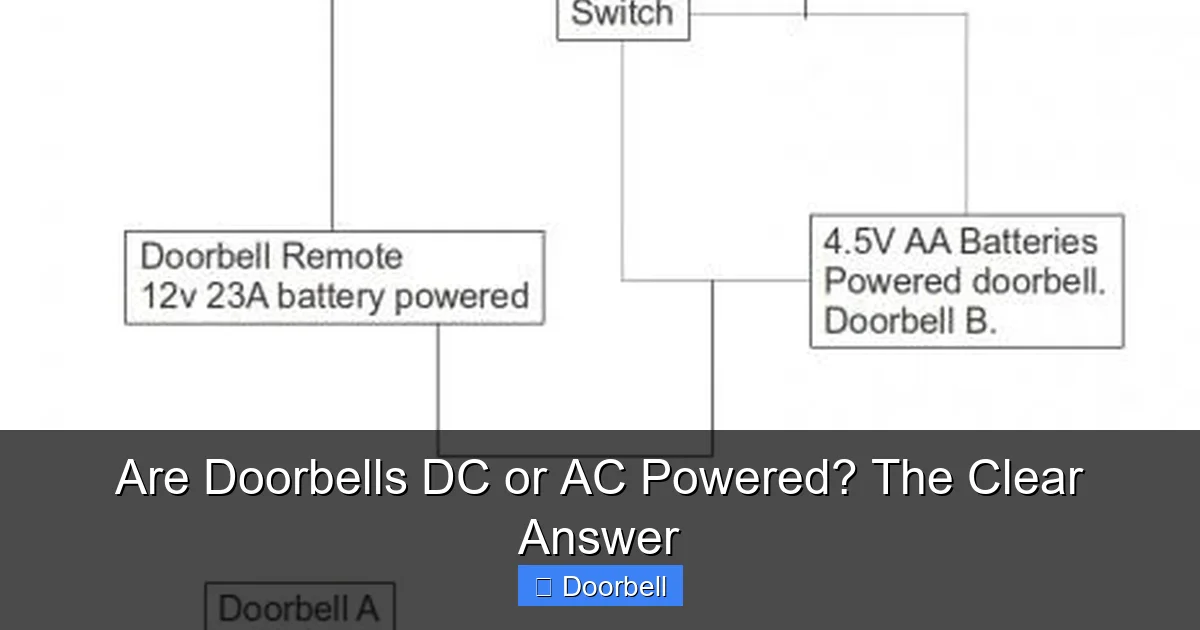
Wireless Doorbells: Exclusively DC Power
In stark contrast to their wired predecessors, modern wireless doorbells operate entirely on Direct Current (DC) power. Why? Because they are almost always battery-powered. Batteries, by their very nature, produce and store DC electricity. This makes wireless doorbells incredibly easy to install, as they don’t require any existing doorbell wiring or a transformer.

Learn more about are doorbells dc or ac – Are Doorbells DC or AC Powered? The Clear Answer
Image source: img2.tradewheel.com
A wireless system typically consists of two main parts: a transmitter (the doorbell button) and a receiver (the chime unit). Both usually require their own wireless doorbell battery supply. The button, when pressed, sends a radio frequency signal to the chime, which then plays a pre-programmed sound.
Battery Types and Lifespan
The type of batteries used in wireless doorbells varies widely:
- Button Transmitter: Often uses smaller batteries like CR2032 coin cells, A23 12V batteries, or sometimes AA/AAA.
- Chime Receiver: Typically uses larger batteries such as AA, AAA, C, or D cells, which provide longer operational life for the chime unit.
Battery lifespan can range from a few months to several years, depending on usage frequency, battery quality, and environmental factors.
Smart Doorbells: A Mix of AC and DC
Smart doorbells, like those from Ring, Nest, Arlo, and Eufy, represent the cutting edge of doorbell technology, and their power requirements reflect this versatility. When asking are doorbells DC or AC in the smart home era, the answer is often “both, or either!”
Many smart doorbells are designed to replace existing wired doorbells. In this scenario, they tap into the home’s existing low-voltage AC wiring (8V-24V AC). However, the internal electronics of a smart doorbell, including its Wi-Fi chip, camera, and sensors, typically require DC power. Therefore, these devices have an internal rectifier that converts the incoming AC power to the DC power needed for their operation.
Alternatively, many smart doorbells are available in entirely battery-powered versions. These operate purely on DC power, much like traditional wireless doorbells, and are ideal for homes without existing doorbell wiring. Some smart doorbells also offer the option of being powered by a dedicated DC power adapter doorbell that plugs into a standard wall outlet, providing a continuous charge without reliance on existing wiring.
How Smart Doorbells Handle Power Conversion
When a smart doorbell is connected to existing AC wiring, it’s equipped with a small circuit board that includes a component called a rectifier. This rectifier efficiently converts the incoming Alternating Current into Direct Current. This DC power then charges an internal battery (if present) and powers all the doorbell’s advanced features, ensuring continuous operation and readiness for recording video or sending notifications. This is a common method for smart doorbell power.
Why Low Voltage? Safety and Efficiency
The consistent use of low voltage (whether AC or DC) across almost all doorbell types is a deliberate engineering choice. High voltage (like the 120V or 240V found in wall outlets) is necessary for high-power appliances, but it also carries significant risks of electrical shock and fire if mishandled. Doorbells, needing very little power to operate a simple chime or trigger a sensor, simply don’t require such high voltage.
Operating at 8V-24V AC or a similar low DC voltage offers several advantages:
- Safety: Significantly reduces the risk of electrocution during installation, maintenance, or if wiring becomes exposed.
- Simplicity: Wiring is less complex and doesn’t require the same heavy-gauge wires or intricate insulation as high-voltage circuits.
- Efficiency: It’s more than enough power to perform the doorbell’s function without unnecessary energy consumption or heat generation.
Understanding the low-voltage aspect is key to both safety and effective troubleshooting. If you’re working with a wired doorbell, always ensure the power to the transformer is off before handling any wires.
Key Differences: AC vs. DC Doorbell Systems at a Glance
To summarize the power dynamics, here’s a quick comparison of how different doorbell types draw and utilize power:
| Doorbell Type | Primary Power Source | Voltage Type | Typical Voltage Range | Installation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Wired | Household AC via Transformer | Low-Voltage AC | 8V – 24V AC | Moderate (transformer, wiring) |
| Wireless (Battery) | Batteries (AA, AAA, C, D, etc.) | DC | 1.5V – 12V DC | Low (no wiring needed) |
| Smart (Wired) | Existing Low-Voltage AC via Transformer | AC (converted to DC internally) | 8V – 24V AC | Moderate (wiring, Wi-Fi setup) |
| Smart (Battery) | Rechargeable Battery Pack | DC | 3.7V – 7.2V DC | Low (no wiring needed, Wi-Fi setup) |
| Smart (Plug-in) | Household AC via DC Adapter | DC | Typically 5V – 12V DC | Low (plugs into outlet, Wi-Fi setup) |
This table clearly illustrates why the question “are doorbells DC or AC” doesn’t have a single universal answer, but rather depends on the specific technology used in your home.
Conclusion: Knowing Your Doorbell’s Power Is Key
Whether your doorbell greets visitors with a classic “ding-dong” or sends a live video feed to your smartphone, understanding its power source is fundamental. From the robust, low-voltage AC systems of traditional wired doorbells to the flexible DC power of battery-operated wireless and smart devices, each type has its own advantages and power requirements.
Next time you hear that familiar chime, you’ll know exactly what kind of electrical current is making it happen. This knowledge empowers you to troubleshoot effectively, choose the right replacement or upgrade, and ensure your front door’s welcoming signal is always ready. So, go forth with confidence, knowing the clear answer to are doorbells DC or AC – it’s all about the type!
🎥 Related Video: calling Bell connection
📺 Konwar Technical Assam
calling Bell connection #streat #fitting #wiring #connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are doorbells typically DC or AC powered?
Most traditional, wired doorbells operate on low-voltage AC (alternating current) power, supplied by a dedicated transformer. However, modern smart doorbells and wireless models often use batteries (DC, or direct current) or convert the incoming AC power to DC internally for their sophisticated electronics.
For wired doorbells, is AC or DC more common?
For wired doorbells, AC (alternating current) is almost universally more common. They draw low-voltage AC power from a doorbell transformer, which safely reduces standard household AC voltage to a usable 8-24 volts for the chime and button.
Do wireless and smart doorbells use DC or AC power?
Wireless doorbells primarily use DC power, typically sourced from batteries. Smart doorbells can often be wired into existing low-voltage AC doorbell systems, but they internally convert that AC power to DC to operate their sensitive electronics, cameras, and Wi-Fi components.
How can I determine if my existing doorbell is DC or AC powered?
To determine if your existing doorbell is DC or AC powered, first check if it’s wireless or battery-operated, which would make it DC. For wired systems, locate your doorbell transformer (often near your electrical panel or furnace); if present, your system uses AC power. If there’s no visible transformer and it’s wired, it’s almost certainly AC.
Why do traditional wired doorbells typically use AC power?
Traditional wired doorbells primarily use low-voltage AC power because it’s efficient and easy to step down the high household voltage using a simple, durable transformer. This method provides a continuous, reliable power supply without the need for battery replacements, making them very low maintenance over many years.
Can a single doorbell system be both AC and DC?
A single doorbell system can effectively utilize both AC and DC power within its operation. For instance, a smart doorbell might connect to your home’s existing AC doorbell wiring for a continuous power supply, but it then internally converts that AC power into DC to power its sensitive electronic components, camera, and Wi-Fi module.