Featured image for how to run a poe camera to rs-485 connections
Image source: home-cdn.reolink.us
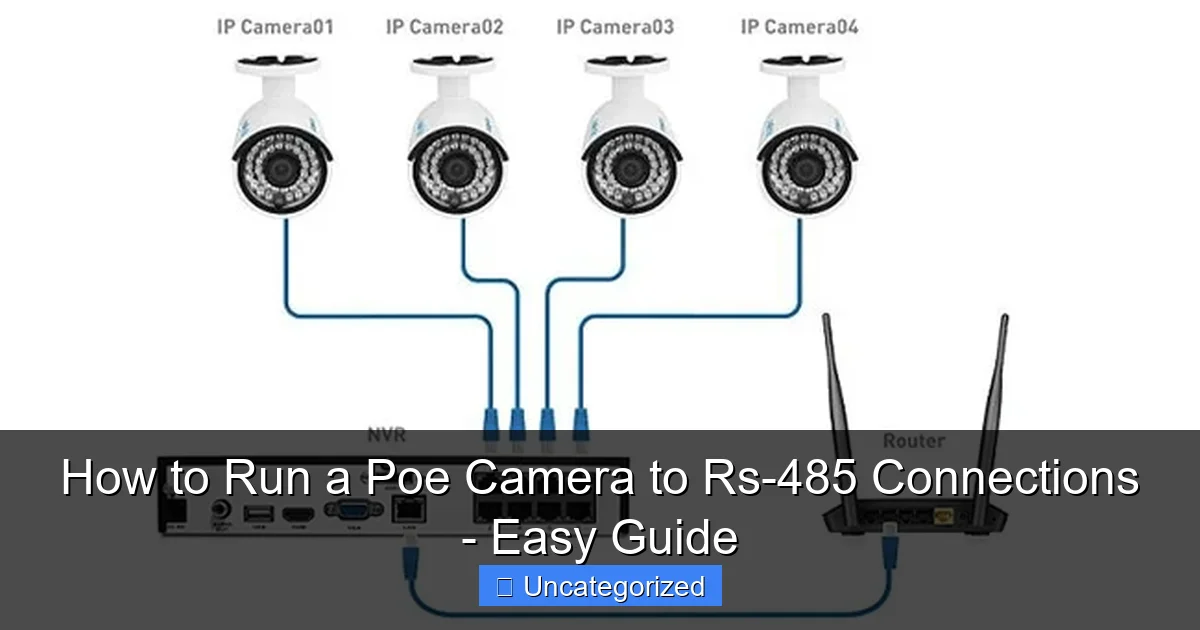
Power and connect your PoE camera to an RS-485 network seamlessly using a PoE splitter and RS-485 converter for reliable, long-distance communication. This easy setup allows you to transmit both power and data over a single Ethernet cable while enabling integration with legacy serial devices. Ideal for industrial and surveillance systems, this method ensures stable performance and simplified cabling.
Key Takeaways
- Use a PoE switch: Power and connect your camera via a single Ethernet cable.
- Check RS-485 compatibility: Ensure camera and devices support RS-485 protocol.
- Terminate with 120Ω resistor: Prevent signal reflection on long RS-485 runs.
- Follow wiring standards: Use twisted-pair cables and maintain correct polarity.
- Test connections early: Verify communication before finalizing installation.
- Ground properly: Avoid ground loops by connecting shields at one end.
- Use converters if needed: Bridge PoE and RS-485 with reliable adapters.
📑 Table of Contents
- Understanding PoE Cameras and RS-485 Technology
- Why Integrate PoE Cameras with RS-485?
- Required Hardware and Tools for PoE to RS-485 Setup
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Run PoE Camera to RS-485 Connections
- Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
- Performance Optimization and Best Practices
- Conclusion
Understanding PoE Cameras and RS-485 Technology
Modern surveillance systems are increasingly leveraging advanced technologies to improve efficiency, scalability, and reliability. Among these innovations, Power over Ethernet (PoE) cameras and RS-485 communication have emerged as powerful tools for both commercial and residential security setups. While PoE cameras simplify installation by delivering both power and data through a single Ethernet cable, RS-485 offers a robust, long-distance, noise-resistant communication protocol ideal for connecting peripheral devices like pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) controllers, sensors, and access control systems. Understanding how to run a PoE camera to RS-485 connections is essential for building a seamless, integrated security infrastructure.
This guide explores the technical and practical aspects of integrating PoE cameras with RS-485 devices. Whether you’re setting up a large-scale surveillance network for a warehouse, a multi-building campus, or a smart home with automated access points, knowing how to bridge these two technologies ensures reliable data transmission, remote control capabilities, and future-proof scalability. From hardware requirements to wiring techniques and troubleshooting, this comprehensive walkthrough will equip you with the knowledge to execute the integration with confidence.
What Is Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows both electrical power and data to be transmitted over standard Category 5e, 6, or 6a Ethernet cables. This eliminates the need for separate power sources at each camera location, reducing clutter and lowering installation costs. PoE is governed by IEEE standards such as 802.3af (15.4W), 802.3at (30W), and 802.3bt (up to 90W), enabling support for a wide range of devices, from basic fixed cameras to high-powered PTZ units with heaters and blowers.
What Is RS-485 Communication?
RS-485 (also known as TIA/EIA-485) is a serial communication standard that supports differential signaling, allowing for long-distance data transmission (up to 1,200 meters or 4,000 feet) with high noise immunity. It’s commonly used in industrial automation, building management systems, and surveillance networks where multiple devices (like cameras, sensors, and motorized mounts) need to communicate over a shared bus. Unlike USB or standard Ethernet, RS-485 can support up to 32 devices on a single bus line, making it ideal for daisy-chained configurations.
Why Integrate PoE Cameras with RS-485?
Integrating PoE cameras with RS-485 peripherals unlocks a range of benefits that enhance the functionality and reliability of your surveillance system. While PoE handles power and video data, RS-485 enables bidirectional control of devices that PoE alone cannot address. This combination allows you to remotely manage PTZ cameras, control lighting, trigger alarms, and monitor environmental sensors—all from a centralized location.

Visual guide about how to run a poe camera to rs-485 connections
Image source: securitycamcenter.com
Enhanced Remote Control and Automation
One of the primary advantages of connecting a PoE camera to an RS-485 network is the ability to remotely control PTZ functions. For example, a PTZ dome camera powered via PoE can receive video data through the Ethernet cable, but its pan, tilt, and zoom motors require a separate control signal. By integrating RS-485, you can send control commands from a central NVR (Network Video Recorder) or a dedicated PTZ controller. This is especially useful in large facilities where manual adjustment is impractical.
Consider a scenario in a warehouse: a PoE PTZ camera mounted on the ceiling needs to follow a moving forklift. Instead of sending someone to adjust the camera, the security operator uses a joystick connected to the RS-485 bus to direct the camera’s movement in real time. The video stream travels over PoE, while the control signal uses RS-485—creating a seamless, responsive system.
Long-Distance Communication Without Signal Degradation
RS-485 excels in environments with long cable runs. While standard Ethernet is limited to 100 meters (328 feet) without signal boosters, RS-485 can operate reliably at 1,200 meters (4,000 feet) at lower data rates (e.g., 100 kbps). This makes it ideal for connecting PoE cameras located far from the control room, such as perimeter cameras on a large campus or cameras mounted on tall poles.
For instance, a school campus may have PoE cameras installed at the far end of a sports field. Instead of installing an additional network switch (which adds cost and complexity), you can run an RS-485 line from the central server room to the camera’s RS-485 interface, allowing control signals to travel the full distance without degradation.
Scalability and Device Integration
RS-485 supports a multi-drop topology, meaning multiple devices can be connected to the same bus. This is perfect for integrating not just PTZ cameras but also door locks, motion sensors, temperature monitors, and relay switches into a unified system. For example, when a PoE camera detects motion, it can trigger an RS-485-connected relay to turn on lights or lock a gate—all without requiring additional network infrastructure.
Moreover, many PoE cameras (especially professional-grade models) come with built-in RS-485 ports or support external RS-485 adapters. This allows them to act as hubs for other RS-485 devices, reducing the need for additional controllers and simplifying system design.
Required Hardware and Tools for PoE to RS-485 Setup
Before running a PoE camera to an RS-485 connection, it’s essential to gather the correct hardware and tools. A successful integration depends on compatibility, quality cabling, and proper configuration. Below is a breakdown of the components you’ll need.
1. PoE Camera with RS-485 Support
Not all PoE cameras support RS-485 communication. You need a model that either has a built-in RS-485 terminal block or supports an external RS-485 adapter (often via a USB-to-RS-485 converter or a proprietary module). Look for cameras labeled as “PTZ with RS-485 control” or check the product specifications for terms like “RS-485 interface,” “485 port,” or “PTZ control via RS-485.”
Example models: Hikvision DS-2DE4225IW-DE, Dahua SD49225T-HN, Axis Q6155-E. These cameras typically include a 2- or 3-pin terminal block for A, B, and ground connections.
2. RS-485 Cabling
Use shielded twisted pair (STP) cable for RS-485 connections. The most common type is CAT5e or CAT6 STP, which provides excellent noise rejection and flexibility. For industrial environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI), consider using dedicated RS-485 cable (e.g., Belden 3106A) with a foil and braid shield.
- Pinout: Use one twisted pair for A and B signals (e.g., orange/white and orange), and the shield for ground.
- Termination: Always terminate the RS-485 bus at both ends with a 120-ohm resistor to prevent signal reflections.
3. Power and Data Infrastructure
You’ll need:
- PoE switch or PoE injector to power the camera (ensure it meets the camera’s power requirements, e.g., 802.3at for PTZ cameras).
- Standard Ethernet cable (CAT5e/6) to carry video and control data from the camera to the NVR or network.
- Network Video Recorder (NVR) with RS-485 control capabilities or a separate RS-485 controller (e.g., a joystick or software-based control system).
4. RS-485 Converters and Adapters (if needed)
If your camera lacks a native RS-485 port, you can use:
- USB-to-RS-485 converter (plugged into the camera’s USB port, if supported).
- Ethernet-to-RS-485 gateway (for converting network-based control signals to RS-485).
- Proprietary RS-485 modules (e.g., Hikvision’s DS-1005KI or Dahua’s RS-485 adapter).
5. Tools
You’ll also need:
- Wire strippers and crimpers
- Multimeter (to test continuity and voltage)
- Screwdrivers (for terminal blocks)
- Cable ties and conduit (for cable management)
- Labeling kit (to identify cables and devices)
Pro Tip: Always verify voltage and polarity before connecting RS-485 lines. Incorrect wiring can damage devices or create communication failures.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Run PoE Camera to RS-485 Connections
Now that you have the necessary hardware, let’s walk through the process of connecting a PoE camera to an RS-485 network. This section provides a clear, actionable sequence to ensure a reliable and safe installation.
Step 1: Plan Your Network Layout
Before any physical work begins, create a detailed plan:
- Map out camera locations, the NVR/server room, and RS-485 device positions.
- Determine cable routes (avoid running near power lines to reduce EMI).
- Calculate cable lengths and ensure RS-485 runs do not exceed 1,200 meters.
- Assign unique RS-485 addresses (node IDs) to each device to avoid conflicts.
Step 2: Install PoE Infrastructure
- Mount the PoE camera at its designated location.
- Run a CAT6 cable from the PoE switch/injector to the camera.
- Connect the cable to the camera’s Ethernet port and power it on.
- Verify the camera appears on the network and streams video via the NVR.
Step 3: Prepare the RS-485 Connection
- Strip the ends of the RS-485 cable (shielded twisted pair).
- Identify the A (positive) and B (negative) wires—typically color-coded (e.g., A = white/orange, B = orange).
- Connect the A wire to the A terminal on the camera’s RS-485 block.
- Connect the B wire to the B terminal.
- Connect the cable shield to the GND (ground) terminal to ensure EMI protection.
Note: Maintain consistent polarity across the entire bus. If A and B are reversed at any point, communication will fail.
Step 4: Run the RS-485 Bus to Other Devices
- Continue the RS-485 cable from the camera to the next device (e.g., PTZ controller, sensor).
- Connect A to A, B to B, and GND to GND at each device.
- Use a daisy-chain (linear) topology—avoid star or T-taps, which can cause signal reflections.
- Install a 120-ohm termination resistor at the first and last device on the bus.
Example: If you have three PTZ cameras and one central controller, daisy-chain them in order: Controller → Camera 1 → Camera 2 → Camera 3. Terminate at the controller and Camera 3.
Step 5: Configure the NVR or Control Software
- Access your NVR or control software (e.g., Hikvision iVMS-4200, Dahua SmartPSS).
- Navigate to the camera’s PTZ settings.
- Enable RS-485 control and set the correct parameters:
- Baud rate: 9600, 19200, or 38400 (match across all devices)
- Data bits: 8
- Stop bits: 1
- Parity: None
- Protocol: Pelco-D, Pelco-P, or manufacturer-specific (e.g., Hikvision)
- Address (Node ID): Unique ID for each device
- Save settings and restart the camera if required.
Step 6: Test the Connection
- Use the NVR’s PTZ controls to pan, tilt, or zoom the camera.
- Verify smooth, responsive movement.
- Check for error messages in the NVR logs.
- Use a multimeter to test voltage between A and B (should be 0.2–5V when idle).
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with careful planning, issues can arise during or after installation. Here are the most common problems and how to resolve them.
1. No Communication or Intermittent Signal
- Cause: Loose connections, reversed A/B wires, or missing termination resistors.
- Fix: Recheck all terminal block connections. Use a multimeter to verify continuity. Install or replace termination resistors (120 ohms) at both ends of the bus.
2. Camera Responds Slowly or Erratically
- Cause: High cable capacitance (long runs), EMI interference, or incorrect baud rate.
- Fix: Reduce baud rate (e.g., from 38400 to 9600) for long cables. Route RS-485 cables away from power lines. Use shielded cable and ground the shield at one end only to avoid ground loops.
3. Address Conflicts
- Cause: Two devices assigned the same RS-485 address.
- Fix: Assign unique addresses to each device. Use the NVR’s “search” or “discover” function to identify conflicts.
4. Voltage Drop Over Long Distances
- Cause: Thin gauge wire or excessive cable length.
- Fix: Use thicker gauge wire (e.g., 18 AWG) for long runs. Consider installing a RS-485 repeater every 1,200 meters to boost the signal.
5. Ground Loops
- Cause: Multiple ground paths between devices, creating noise.
- Fix: Connect the shield to ground at only one end (usually the NVR side). Use isolated RS-485 converters if ground potential differences are significant.
Pro Tip: Label all cables and devices clearly. This speeds up troubleshooting and makes future upgrades easier.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
To ensure your PoE-to-RS-485 system operates at peak efficiency, follow these best practices.
Use High-Quality Cabling and Connectors
Invest in shielded, stranded copper cable for flexibility and noise resistance. Avoid cheap, unshielded cables, especially in industrial or outdoor environments. Use waterproof connectors (e.g., IP67-rated) for outdoor installations.
Minimize EMI Exposure
- Run RS-485 cables at least 12 inches away from AC power lines.
- Use metal conduit for added protection.
- Ground the shield at one end only to prevent ground loops.
Optimize Network Topology
Stick to a linear daisy-chain for RS-485. Avoid star configurations. If branching is necessary, use an RS-485 hub or repeater to maintain signal integrity.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
- Schedule periodic inspections of cable integrity and connections.
- Monitor NVR logs for communication errors.
- Update camera and NVR firmware to fix known bugs.
Data Table: Recommended RS-485 Cable Types
| Cable Type | Max Distance | Noise Resistance | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAT5e STP | 1,200 m (4,000 ft) | High | Indoor, office environments |
| CAT6 STP | 1,200 m (4,000 ft) | Very High | Industrial, high-EMI areas |
| Belden 3106A | 1,200 m (4,000 ft) | Excellent | Outdoor, harsh environments |
| 18 AWG Twisted Pair | 1,200 m (4,000 ft) | High | Long runs with low capacitance |
By following these guidelines, you can build a robust, scalable, and future-ready surveillance system that leverages the strengths of both PoE and RS-485 technologies.
Conclusion
Running a PoE camera to RS-485 connections is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic enhancement that brings control, flexibility, and reliability to your security infrastructure. By combining the power and data efficiency of PoE with the long-distance, noise-resistant communication of RS-485, you create a system capable of handling complex automation tasks, remote management, and multi-device integration.
From planning and hardware selection to wiring, configuration, and troubleshooting, this guide has covered every critical step. Whether you’re a security integrator, IT professional, or a tech-savvy homeowner, the knowledge you’ve gained empowers you to build a smarter, more responsive surveillance network. Remember, success lies in attention to detail: proper cabling, consistent polarity, correct termination, and clear addressing. With these principles in mind, your PoE-to-RS-485 setup will deliver years of reliable performance.
As surveillance technology continues to evolve, the ability to integrate diverse communication protocols will remain a key differentiator. Mastering PoE and RS-485 integration today prepares you for tomorrow’s challenges—whether it’s adding AI analytics, IoT sensors, or cloud-based management. So go ahead: connect, configure, and control with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to connect a PoE camera to an RS-485 system?
To connect a PoE camera to an RS-485 system, use an RS-485 to Ethernet converter or a PoE-powered converter module. Ensure the converter supports your camera’s voltage and protocol requirements for seamless integration.
Can I run a PoE camera to RS-485 connections without a converter?
No, a direct connection isn’t possible because PoE cameras use Ethernet (IP-based) signals, while RS-485 relies on serial communication. An RS-485 to Ethernet converter is essential for bridging these two technologies.
How do I power an RS-485 device when using a PoE camera?
Many RS-485 to Ethernet converters draw power from the PoE camera’s line, eliminating the need for separate power. If your converter doesn’t support PoE, use a PoE splitter to provide power to both devices.
What cable should I use for PoE camera to RS-485 connections?
Use shielded twisted-pair cable (e.g., Cat5e/Cat6) for RS-485 data lines to reduce interference. For PoE, ensure the Ethernet cable meets the required standard (e.g., Cat5e or higher) to support both power and data.
How do I troubleshoot communication issues between a PoE camera and RS-485?
Check baud rates, parity, and protocol settings on both devices—mismatches are common issues. Also, verify cable integrity, grounding, and termination resistors (120Ω) at both ends of the RS-485 line.
Are there PoE cameras with built-in RS-485 support?
Yes, some advanced PoE cameras include native RS-485 ports, allowing direct connection without converters. Look for models labeled as “PoE camera with RS-485” to simplify setup and reduce hardware dependencies.