
Featured image for this comprehensive guide about what is 485 nvr
Image source: i.ytimg.com
In the evolving world of surveillance technology, choosing the right components for your security system is paramount. You’ve likely heard of NVRs (Network Video Recorders), which are the brain behind many modern IP camera setups. But as you delve deeper, you might stumble upon a more specific term: “485 NVR.” What exactly does the “485” signify, and why is it a crucial consideration for advanced CCTV enthusiasts and professional installers? If you’re looking to gain more precise control over certain types of cameras, particularly Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) models, understanding the 485 NVR is key.
This comprehensive guide will demystify the 485 NVR, explaining its role, benefits, and how it seamlessly integrates into your surveillance infrastructure. We’ll break down the technical jargon, provide actionable insights, and help you determine if an 485 NVR is the right choice for your security needs. Let’s dive in and unlock the full potential of your CCTV system.
📋 Table of Contents
- Understanding the Core: What is an NVR?
- Demystifying the “485”: The Power of RS-485 in Surveillance
- How Does an 485 NVR Enable PTZ Camera Control?
- Key Benefits of Integrating a 485 NVR into Your Security System
- Choosing the Right 485 NVR: Essential Factors to Consider
- Maximizing Your 485 NVR: Setup Tips and Best Practices
Understanding the Core: What is an NVR?
Before we pinpoint the “485” aspect, let’s briefly revisit the fundamental role of an NVR. A Network Video Recorder is a specialized computer system designed to record video footage from IP (Internet Protocol) cameras. Unlike older DVRs (Digital Video Recorders) that process analog signals, NVRs work exclusively with digital video streams over a network. This allows for:
- Higher Resolution: NVRs support megapixel cameras, delivering crystal-clear images and videos.
- Flexible Placement: IP cameras can be anywhere on your network, not just physically connected to the recorder.
- Advanced Features: Many NVRs offer intelligent analytics, remote access, and seamless integration with other smart home or security systems.
In essence, an NVR is the central hub where all your IP camera footage is stored, managed, and can be accessed for live viewing or playback. It’s the cornerstone of any robust modern IP surveillance system.
| Feature | NVR with RS-485 (485 NVR) | Standard IP NVR (No Dedicated RS-485) |
|---|---|---|
| **PTZ Camera Control** | Direct serial control for Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) cameras via dedicated RS-485 wires (e.g., Pelco-D/P protocols). | PTZ control signals sent over the network (e.g., ONVIF, proprietary IP protocols). |
| **Peripheral Integration** | Can connect and control non-IP devices like alarm sensors, access control readers, or external keypads directly via RS-485 port. | Primarily integrates IP-based peripherals or requires separate gateways/relays for non-IP devices. |
| **Wiring for PTZ Cameras** | Requires separate RS-485 twisted pair wires in addition to the network cable for PTZ control. | PTZ control is embedded in the Ethernet data stream, typically simplifying wiring to a single network cable. |
| **Legacy System Compatibility** | Excellent for integrating older analog PTZ cameras or other legacy RS-485 controlled devices into an IP surveillance system. | Designed for modern IP-based systems; may require converters for RS-485 legacy equipment. |
Demystifying the “485”: The Power of RS-485 in Surveillance
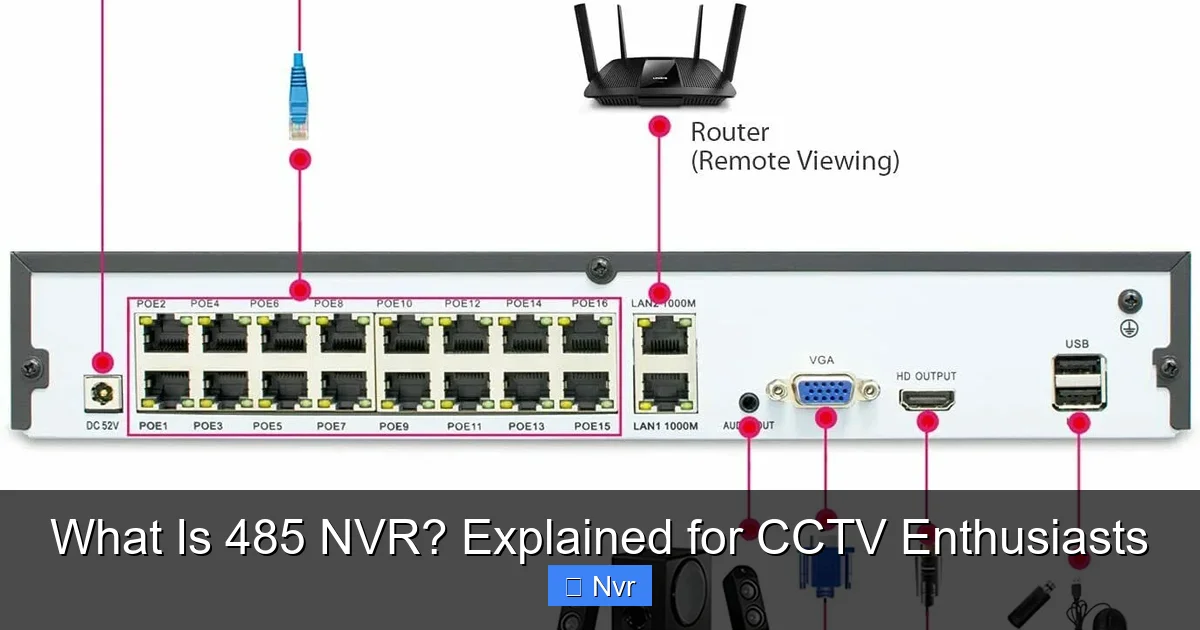
The “485” in 485 NVR refers to the RS-485 standard, a specific type of serial communication protocol. While many NVRs handle video and basic camera settings over the network, RS-485 plays a vital role in enabling direct, precise control over certain camera functions, primarily for PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras. It’s a robust, differential signaling system designed for industrial applications and long-distance data transmission.

Learn more about what is 485 nvr – What Is 485 NVR? Explained for CCTV Enthusiasts
Image source: waqwaq.sa
Key Characteristics of RS-485:
- Differential Signaling: Uses two wires for data transmission, which makes it highly resistant to electrical noise and interference.
- Long Distance: Can reliably transmit data over distances up to 4,000 feet (1,200 meters), making it ideal for large properties or complex installations.
- Multi-drop Capability: Multiple devices can share the same communication bus, allowing one NVR to control several PTZ cameras using a single RS-485 cable run.
- Cost-Effective: Uses simple twisted-pair cabling, which is generally inexpensive and easy to install.
In the context of surveillance, an RS-485 port on an NVR is specifically there to send control commands to compatible cameras, traditionally PTZ cameras, that also have an RS-485 interface. This dedicated control channel ensures that commands are delivered swiftly and reliably, even in environments with high electrical noise.
How Does an 485 NVR Enable PTZ Camera Control?
The primary function of an 485 NVR in a surveillance setup is to provide granular control over PTZ cameras. While many IP PTZ cameras can receive control commands (like pan, tilt, zoom, and preset calls) directly over the network, having a dedicated RS-485 connection offers several advantages, especially in professional or older hybrid setups.
Learn more about what is 485 nvr – What Is 485 NVR? Explained for CCTV Enthusiasts
Image source: cucctv.co.uk
Here’s how it works:
- Connection: The RS-485 port on your NVR is wired directly to the RS-485 input terminals on your PTZ camera. This typically involves a simple two-wire connection (A and B, or + and -).
- Protocol: The NVR communicates using a specific protocol like Pelco-D or Pelco-P, which are standard for PTZ control.
- Commands: When you use the NVR’s interface (via a monitor, web browser, or mobile app) to pan, tilt, or zoom your camera, the NVR translates these actions into RS-485 commands.
- Execution: The PTZ camera receives these commands via the RS-485 cable and executes the requested movement or zoom adjustment instantly and precisely.
This method provides a robust, low-latency control mechanism that is separate from the main video data stream, ensuring responsive camera manipulation even when network bandwidth is heavily utilized for video streaming. This dedicated channel makes an 485 NVR a powerful tool for monitoring large areas where manual camera control is frequently required.
Key Benefits of Integrating a 485 NVR into Your Security System
Opting for an 485 NVR brings several compelling advantages, particularly for users with specific control and reliability needs:
- Precise and Responsive PTZ Control: The dedicated RS-485 channel offers superior responsiveness and precision for controlling PTZ camera movements, minimizing lag compared to purely IP-based control, especially over busy networks.
- Enhanced Reliability: RS-485‘s differential signaling makes it highly resistant to electrical interference, ensuring consistent command delivery even in challenging industrial or outdoor environments.
- Long-Distance Capability: As mentioned, RS-485 can transmit control signals over significantly longer distances than typical Ethernet cables (without repeaters), providing greater flexibility in camera placement.
- Backward Compatibility: Many existing PTZ cameras, especially older but still functional models, rely on RS-485 for control. An 485 NVR allows you to integrate these cameras into a modern IP system without needing to replace them all.
- Simplified Wiring (for multiple PTZ cameras): With multi-drop capability, one RS-485 bus can control several cameras, potentially simplifying wiring compared to running individual Ethernet cables for control *if* your NVR and cameras support this configuration for control (though video would still be IP).
For large-scale deployments or situations demanding the utmost reliability in camera manipulation, the benefits of an 485 NVR are clear.
Choosing the Right 485 NVR: Essential Factors to Consider
When selecting an 485 NVR for your surveillance system, keep these critical factors in mind to ensure compatibility and optimal performance:
- RS-485 Port Availability: Confirm the NVR explicitly states it has an RS-485 port and supports relevant protocols (e.g., Pelco-D, Pelco-P).
- Camera Compatibility: Ensure your chosen PTZ cameras (or other devices you wish to control) are compatible with the NVR’s RS-485 protocols. Always check camera specifications.
- Number of Channels: How many IP cameras do you need to record? NVRs come with varying channel counts (e.g., 4, 8, 16, 32 channels).
- Storage Capacity: Consider your recording needs. Look for NVRs that support sufficient hard drive bays and capacities to store your footage without constant overwriting.
- Resolution Support: Make sure the NVR supports the resolution of your IP cameras (e.g., 1080p, 4K).
- Network Bandwidth: High-resolution cameras demand significant network bandwidth. Ensure the NVR has sufficient processing power and network capabilities.
- Additional Features: Look for features like PoE (Power over Ethernet) ports if you want to power IP cameras directly from the NVR, intelligent video analytics, and robust remote access capabilities.
By carefully evaluating these points, you can choose an 485 NVR that perfectly matches your system’s requirements and offers seamless control over your surveillance operations.
Maximizing Your 485 NVR: Setup Tips and Best Practices
Once you’ve selected your 485 NVR, proper setup is crucial for optimal performance. Here are some quick tips:
- Wiring the RS-485: Connect the A (+) and B (-) terminals of your NVR’s RS-485 port to the corresponding terminals on your PTZ camera. Ensure correct polarity to avoid communication issues.
- Address Configuration: If you’re connecting multiple PTZ cameras via a single RS-485 bus, each camera must have a unique address. Configure these addresses (usually via DIP switches on the camera or its OSD menu) and then set the corresponding addresses in your NVR’s PTZ control settings.
- Protocol Matching: In the NVR’s settings, select the correct PTZ control protocol (e.g., Pelco-D, Pelco-P) that matches your camera. Baud rate settings also need to match.
- Network Connectivity: Ensure all your IP cameras are properly connected to your network and discoverable by the NVR. Static IP addresses for cameras can simplify management.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for and install firmware updates for both your NVR and cameras to ensure compatibility, security, and access to the latest features.
- Testing: After initial setup, thoroughly test all PTZ functions (pan, tilt, zoom, presets) to confirm that the 485 NVR is communicating effectively with your cameras.
Following these best practices will help you unlock the full potential of your 485 NVR, providing you with reliable and precise control over your surveillance system.
Understanding what is 485 NVR and its specific role in modern surveillance provides a significant advantage for anyone serious about optimizing their security setup. The integration of RS-485 technology allows for incredibly reliable and responsive control of PTZ cameras, addressing the need for precision and long-distance communication that pure IP control sometimes struggles with.
Whether you’re managing a sprawling commercial property or a large residential estate, an 485 NVR offers a robust solution for hands-on control and enhanced operational efficiency. By carefully considering the benefits and setup requirements, you can leverage this powerful technology to achieve a more comprehensive and responsive surveillance system. Invest wisely, set up correctly, and gain unparalleled command over your security cameras with a capable 485 NVR.
🎥 Related Video: What is a PTZ Port? Exploring Connection Options
📺 Honey Optics
In this video, we delve into the world of PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras and their various connection options. PTZ cameras offer a …
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a 485 NVR?
A 485 NVR refers to a Network Video Recorder that is equipped with an RS-485 serial communication port. This port enables the NVR to send and receive data using the RS-485 standard, which is widely used in industrial and security systems for robust, long-distance communication.
Why would a CCTV enthusiast choose an NVR with RS-485 capabilities?
CCTV enthusiasts often choose a 485 NVR primarily for controlling Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) cameras that utilize RS-485 for movement and zoom functions. It’s also beneficial for integrating the NVR with other security devices, such as alarm systems or access control panels, to create a more unified security solution.
How does the RS-485 port on an NVR function for camera control?
The RS-485 port on an NVR typically sends control commands, like Pelco-D or Pelco-P protocols, directly to PTZ cameras. When a user manipulates the camera through the NVR’s interface, the NVR converts these actions into serial commands that are transmitted over the RS-485 connection to physically adjust the camera’s view.
Can I connect different types of devices to the 485 port of my NVR?
Yes, while PTZ camera control is the most common application, the 485 port on your NVR can potentially connect to other serial devices. This might include alarm system input/output modules, access control systems, or even environmental sensors, allowing for advanced automation and integrated event management within your security setup.
Is the 485 feature common on most modern NVRs?
The prevalence of the RS-485 feature varies among modern NVRs; while crucial for legacy PTZ cameras and specific integrations, it’s less universal on basic or entry-level models today. Many newer IP PTZ cameras now rely on direct IP-based control (ONVIF PTZ) over the network, reducing the need for a separate RS-485 connection. However, it remains a standard feature on higher-end professional NVRs designed for complex systems.
What are the key advantages of using the RS-485 connection on a 485 NVR?
A significant advantage of using the RS-485 connection on a 485 NVR is its capability for reliable, long-distance communication, which is crucial for controlling PTZ cameras over expansive sites without signal degradation. It also supports multi-drop configurations, allowing multiple devices to share the same two-wire bus, simplifying cabling and offering robust control for various serial equipment.