Featured image for this comprehensive guide about what is a wireless nvr camera system
Image source: i.pinimg.com
In today’s fast-paced world, security is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Whether you’re safeguarding your home, office, or retail space, a reliable surveillance system offers invaluable peace of mind. While traditional wired setups have been the norm, technological advancements have brought forth more flexible and convenient solutions. One such innovation rapidly gaining popularity is the wireless NVR camera system.
But what exactly is a wireless NVR camera system, and how does it stack up against its wired counterparts? If you’re feeling overwhelmed by the alphabet soup of security tech – DVR, NVR, IP cameras – you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will demystify wireless NVR technology, helping you understand its benefits, functionalities, and what to look for when choosing one for your needs.
📋 Table of Contents
What is a Wireless NVR Camera System?
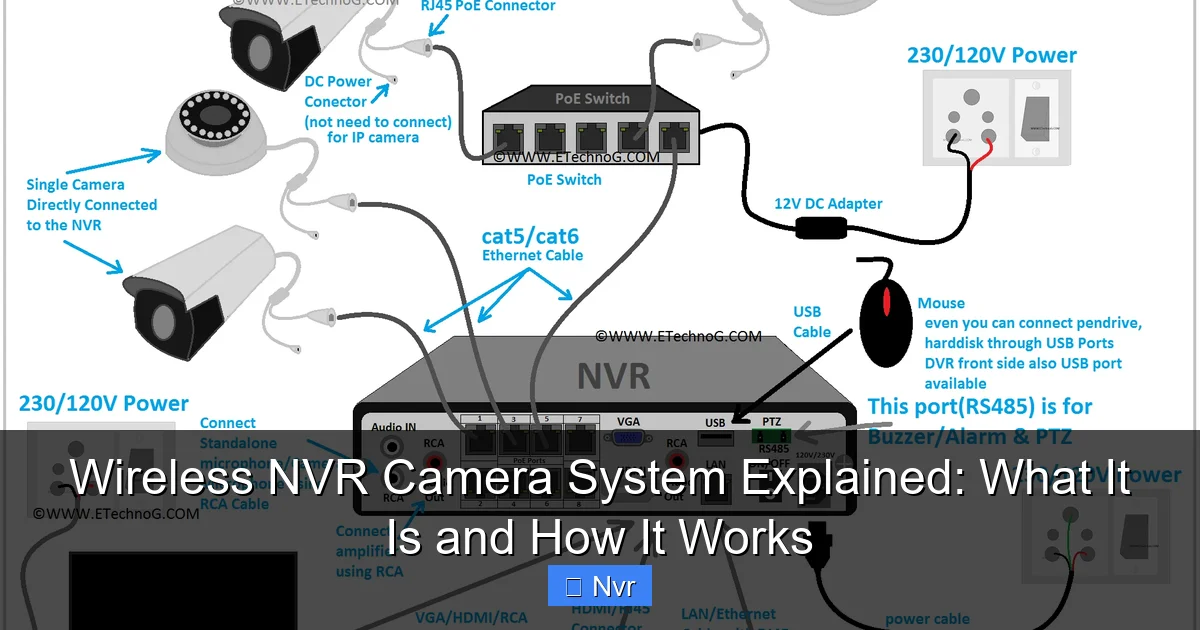
A wireless NVR camera system is a modern security solution that uses IP (Internet Protocol) cameras to capture video footage and transmit it wirelessly to a central recording device called an NVR (Network Video Recorder). Unlike traditional DVR systems that process analog signals, NVRs work with digital signals, offering superior image quality and advanced features.
The “wireless” aspect primarily refers to the connection between the IP cameras and the NVR. This means the cameras don’t need a physical data cable running back to the recorder, significantly simplifying installation. Power, however, is still often supplied via a power adapter plugged into a wall outlet, although some advanced models may feature battery power or solar charging.
| Characteristic | Wireless NVR System | Traditional Wired NVR System | User Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Cameras connect via Wi-Fi (2.4/5GHz) to NVR. | Cameras connect via Ethernet cables (often PoE) to NVR. | Wireless offers greater placement flexibility; wired offers higher stability. |
| Installation | Easier DIY setup, minimal cabling required (power only for cameras). | Requires running Ethernet cables, potentially complex and costly. | Significant savings on labor and time for wireless installation. |
| Camera Placement | Highly flexible, limited by Wi-Fi range and power outlet proximity. | Limited by physical cable runs and drilling requirements. | Wireless allows easier adaptation to various indoor/outdoor locations. |
| Data Reliability | Can be susceptible to Wi-Fi interference, potential for lower bandwidth. | Highly stable connection, high bandwidth suitable for 4K+ streams. | Wired offers more consistent performance, critical for high-stakes monitoring. |
Key Components of a Wireless NVR System:
- Wireless IP Cameras: These are the “eyes” of your system, capturing high-definition video. They communicate with the NVR over Wi-Fi.
- Network Video Recorder (NVR): The brain of the operation. It receives, records, stores, and manages video footage from all connected cameras. NVRs typically include a built-in hard drive for storage.
- Power Adapters: For each camera and the NVR (unless battery-powered).
- Monitor (Optional): For live viewing and playback, though many systems allow remote viewing via smartphones or computers.
How Does a Wireless NVR System Work?
The operational principle behind a wireless NVR camera system is surprisingly straightforward, leveraging network technology for seamless communication.

Learn more about what is a wireless nvr camera system – Wireless NVR Camera System Explained: What It Is and How It Works
Image source: home-cdn.reolink.us
- Capture: Each wireless IP camera captures high-definition video and audio (if equipped). These cameras are essentially mini-computers with their own operating systems.
- Encoding & Transmission: The cameras then encode the raw video data into a digital format. Instead of sending it through a coaxial cable, they transmit this digital data wirelessly (typically via Wi-Fi) to the NVR.
- Reception & Recording: The NVR, often equipped with its own Wi-Fi module, receives these digital streams. It then processes the data, compresses it, and stores it onto its internal hard drive. Most NVRs can record continuously, on a schedule, or only when motion is detected.
- Access & Playback: Users can access the live feed or recorded footage directly from the NVR (connected to a monitor) or remotely via a dedicated mobile app or web browser. This remote access is a game-changer for monitoring your property from anywhere in the world.
Many wireless NVR systems create their own dedicated wireless network between the cameras and the NVR, preventing them from hogging your home Wi-Fi bandwidth and improving connection stability. This also means fewer potential interference issues.
Key Benefits of Choosing a Wireless NVR System
Opting for a wireless NVR security system offers a host of advantages that make it an attractive choice for both residential and commercial users.

Learn more about what is a wireless nvr camera system – Wireless NVR Camera System Explained: What It Is and How It Works
Image source: m.media-amazon.com
- Simplified Installation: This is arguably the biggest selling point. Without the need to run extensive wiring for video transmission, installation is far less labor-intensive and quicker. A 2023 survey indicated that ease of installation was a top priority for 65% of first-time security camera buyers.
- Increased Flexibility & Scalability: Wireless cameras can be placed in locations where running cables would be difficult, impractical, or unsightly. Need to move a camera? It’s often as simple as unplugging it and repositioning. You can also easily add more cameras to your NVR system as your needs grow.
- High-Quality Footage: NVRs work with IP cameras, which inherently offer higher resolutions (1080p, 2K, 4K) compared to traditional analog cameras, providing clearer images and better digital zoom capabilities.
- Remote Access & Notifications: Modern wireless NVR systems come with robust mobile apps, allowing you to view live feeds, play back recordings, and receive instant motion detection alerts on your smartphone, no matter where you are.
- Advanced Features: IP cameras and NVRs often support advanced functionalities like two-way audio, AI-powered human/vehicle detection, facial recognition, and integration with smart home ecosystems.
What to Look for When Buying a Wireless NVR System
Choosing the right wireless NVR camera system requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure it meets your specific security requirements and budget.
Camera Specifications:
- Resolution: Aim for at least 1080p (Full HD). For larger areas or more detail, consider 2K or 4K.
- Field of View (FOV): A wider FOV means fewer cameras are needed to cover an area.
- Night Vision: Look for infrared (IR) night vision with a sufficient range. Color night vision (often requiring ambient light) is a bonus.
- Weatherproofing: If placing outdoors, ensure cameras have an IP65, IP66, or IP67 rating.
- Audio: Two-way audio allows you to listen and speak through the camera.
NVR Features:
- Number of Channels: How many cameras can the NVR support? Ensure it meets current and future needs.
- Hard Drive Storage: A larger hard drive (e.g., 1TB, 2TB) means more recorded footage. Consider systems with expandable storage.
- Wireless Range & Signal Strength: Check reviews for real-world performance, especially if you have a large property.
- Connectivity: Look for Ethernet ports for wired cameras (if desired), HDMI/VGA for monitors, and USB for backup.
Software & Usability:
- Mobile App: Is it intuitive, reliable, and feature-rich?
- Motion Detection: Are there customizable zones and sensitivity settings? Does it offer AI detection (human, vehicle)?
- Cloud Storage: Some systems offer optional cloud storage for off-site backup, often with a subscription.
- Ease of Setup: Look for “plug-and-play” or “auto-pairing” features.
Wireless NVR vs. Wired NVR: A Quick Comparison
While this article focuses on wireless, it’s helpful to understand the trade-offs between wireless and wired NVR systems.
| Feature | Wireless NVR System | Wired NVR System |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Ease | Very easy; minimal cabling for data | More complex; requires running Ethernet cables |
| Flexibility | High; easy to move cameras | Lower; fixed camera positions |
| Reliability (Data) | Susceptible to Wi-Fi interference, range limits | Very high; dedicated wired connection |
| Power Source | Typically needs power outlet per camera | Often Power over Ethernet (PoE) from NVR |
| Cost (Initial) | Often slightly higher per camera | Potentially lower per camera, but higher installation cost |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Wireless signal interception (if not encrypted) | Physical cable cutting (less common) |
For most home users seeking convenience and flexibility, a wireless NVR system is an excellent choice. For environments demanding absolute maximum reliability or where power outlets are sparse, a wired PoE NVR might be preferred.
Setting Up Your Wireless NVR System: A Simple Guide
One of the biggest advantages of a wireless NVR camera system is its relative ease of installation. While specific steps may vary by brand, here’s a general overview to get you started:
- Unbox and Connect NVR: First, unbox your NVR and connect it to power. If you plan to use a monitor directly, connect it via HDMI or VGA. Connect the NVR to your internet router via an Ethernet cable if remote viewing is desired (highly recommended).
- Power On Cameras: Place your cameras in their desired locations and connect each to its power adapter. Most cameras will automatically power on.
- Pair Cameras with NVR: Many systems are “plug-and-play,” meaning the cameras automatically pair with the NVR. If not, there’s usually a simple pairing process, often involving scanning a QR code or pressing a button on the NVR/camera.
- Install Hard Drive (If Separate): If your NVR came without a pre-installed hard drive, you’ll need to install it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Configure Settings: Access the NVR’s interface (via monitor or app) to adjust settings like recording schedule, motion detection zones, email alerts, and password security.
- Download Mobile App: Install the dedicated mobile app on your smartphone or tablet. Follow the in-app instructions to add your NVR, allowing you to view live feeds and recordings remotely.
- Test & Adjust: Walk around your property, triggering motion detection and checking camera angles to ensure optimal coverage. Make any necessary adjustments.
It’s estimated that a DIY installation of a 4-camera wireless NVR camera system can take as little as 1-2 hours for someone with basic technical skills, significantly less than a wired alternative.
Conclusion
The wireless NVR camera system represents a significant leap forward in DIY and professional security solutions. Offering the perfect blend of high-definition surveillance, easy installation, and remote accessibility, it empowers you to protect what matters most with unparalleled convenience.
By understanding what a wireless NVR system is, how it works, and what features to prioritize, you can make an informed decision and invest in a security setup that provides robust protection and ultimate peace of mind. Embrace the future of surveillance and take control of your security, wirelessly.
🎥 Related Video: Reolink NVR vs WIFI NVR vs Home Hub – Which ONE?
📺 LifeHackster
Watch this update video – https://youtu.be/PM28FOLA7dA Today, we are going to compare Reolink’s 3 storage options for the …
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Wireless NVR Camera System?
A Wireless NVR (Network Video Recorder) Camera System is a security setup where IP cameras connect wirelessly to a central NVR unit for recording and management. Unlike traditional wired systems, it reduces the need for extensive data cabling between the cameras and the recorder, simplifying installation.
How does a Wireless NVR Camera System operate?
These systems work by having individual IP cameras transmit video footage wirelessly to the NVR unit, typically over Wi-Fi or a dedicated proprietary wireless signal. The NVR then stores this footage on an internal hard drive, allows for live viewing, and provides options for remote access via mobile apps or web browsers.
What are the primary advantages of choosing a Wireless NVR Camera System?
The main advantages include easier installation due to reduced cabling, greater flexibility in camera placement, and the ability to expand your system more simply. It’s an ideal choice for renters or those who want to avoid drilling and extensive wiring.
Do the cameras in a Wireless NVR Camera System require power cables?
Yes, while the cameras transmit video data wirelessly, they still typically require a power source, usually via a power adapter plugged into an electrical outlet. Some models might use battery power or Power over Ethernet (PoE) if connecting to a wired NVR, but the “wireless” aspect primarily refers to data transmission, not power.
Is an internet connection necessary for a Wireless NVR Camera System to function?
No, a wireless NVR camera system can operate and record locally without an internet connection, as the cameras communicate directly with the NVR. However, an internet connection is required for remote viewing, receiving alerts, and accessing cloud-based features.
What kind of video storage options are available with a Wireless NVR Camera System?
Most wireless NVR camera systems primarily store video footage locally on a pre-installed or user-installed hard drive within the NVR unit itself. Some advanced systems or specific camera models may also offer secondary storage options like cloud storage subscriptions or local microSD card slots on individual cameras.